Abstract
Cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia (CN-AML) is the largest and most heterogeneous cytogenetic AML subgroup. For the practicing clinician it is difficult to know how to use the prognostic information of the growing number of clinical and molecular markers. Our purpose was to develop a widely applicable prognostic model by combining well-established pre-treatment patient and molecular characteristics.
Two prognostic indices for CN-AML, one with regard to overall survival (PINAOS) and the other regarding relapse-free survival (PINARFS) were derived based on a cohort of 669 CN-AML patients treated within the AML Cooperative Group 99 (AMLCG99) study.
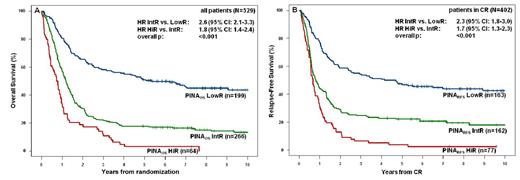
Based on age (median: 60 years [range: 17-85 years]), performance status, white blood count, and presence or absence of NPM1 mutation, biallelic CEBPA mutation, and FLT3-ITD, patients were classified into three risk groups according to PINAOS and PINARFS: 29% of all and 32% of responding patients had low risk (5-year OS 72%; 5-year RFS 55%), 56% and 39% intermediate risk (5-year OS 28%; 5-year RFS 27%), and 15% and 29% high risk disease (5-year OS 3%; 5-year RFS 8%) (Figure 1). PINAOS and PINARFS further subdivided the European LeukemiaNet (ELN) favorable-genetic group as well as the ELN intermediate-I-genetic group. Both, PINAOS and PINARFS were confirmed in a large, independent, and comparable CN-AML cohort of 529 patients from the Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB/Alliance) trials (Figure 2).
Outcome of CN-AML patients according to the new prognostic indices in the AMLCG cohort. (A) OS according to PINAOS in 641 patients evaluable for PINAOS (B) RFS according to PINARFS in 432 patients with CR evaluable for PINARFS. HR=Hazard Ratio, CI=Confidence Interval, LowR=low risk, IntR=intermediate risk, HiR=high risk.
Outcome of CN-AML patients according to the new prognostic indices in the AMLCG cohort. (A) OS according to PINAOS in 641 patients evaluable for PINAOS (B) RFS according to PINARFS in 432 patients with CR evaluable for PINARFS. HR=Hazard Ratio, CI=Confidence Interval, LowR=low risk, IntR=intermediate risk, HiR=high risk.
Validation of the new prognostic indices in an independent data set of CALGB CN-AML cases. (A) OS according to PINAOS (B) RFS according to PINARFS. HR=Hazard Ratio, CI=Confidence Interval, LowR=low risk, IntR=intermediate risk, HiR=high risk.
Validation of the new prognostic indices in an independent data set of CALGB CN-AML cases. (A) OS according to PINAOS (B) RFS according to PINARFS. HR=Hazard Ratio, CI=Confidence Interval, LowR=low risk, IntR=intermediate risk, HiR=high risk.
We have developed and validated the first prognostic indices specifically designed for CN-AML patients of all ages combining well-established molecular and clinical variables easily applicable in routine clinical care. The integration of both clinical and molecular markers could provide a basis for individualized patient care by risk-adapted therapy of CN-AML.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.


This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal