Abstract
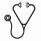
Introduction: TKIs have changed the natural history of CML with a markedly reduced risk of transformation to CML-BP. However, some patients (pts) become resistant to therapy and progress and a few pts present with CML-BP at diagnosis. In this study, we have identified the clinical characteristics, prognostic factors and outcome of pts with CML-BP from a single center cohort of pts treated with a TKI at some point during the course of their disease.
Methods: We analyzed all CML pts diagnosed with CML-BP (defined as ≥30% blasts or extramedullary disease) from 07/1997 to 07/2015. Among a total of 498 pts included with CML-BP, 302 presented to MDACC already in BP (of whom 72 had BP at the time of initial diagnosis, in many instances prior to referral to MDACC); 84 presented in accelerated phase (AP) and later progressed, and 112 presented in chronic phase (CP) and progressed to BP. All pts were enrolled in clinical trials with different TKI/non-TKI based therapies. Clinical characteristics were collected at the time of initial presentation to MDACC in BP. Failure free survival (FFS) and overall survival (OS) were defined from the time of initial presentation to MDACC to treatment failure/death, respectively.
Results: Median age for all 498 pts was 52 years (range, 2 to 84); 63% were male and 64% were Caucasian. Median time from initial diagnosis to BP was 36 months (0.4 to 298 months) for all pts excluding the 72 pts who were already in BP at diagnosis; median time from AP to BP (n=160) was 14 months (0.3-161). Immunophenotype was myeloid in 67%, lymphoid in 29%, mixed lineage in 3%, biphenotypic in 1% and megakaryocytic in 0.2%. Sixty-one percent of pts had additional chromosomal abnormalities besides the Ph chromosome, including double Philadelphia (17%), iso17q (7%), trisomy 8 (16%), chromosome 3 aberration (11%), del7q (8%), and trisomy 19 or 21 (4% each). Six percent of pts had a variant Ph. BCR-ABL mutation screening was performed in 174 pts at the time of BP, with mutations identified in 68 (39%), most commonly T315I (n=24) and E255K (n=13). Extramedullary (EMD) BP was detected in 26% pts, the most common being CNS involvement in 39% pts with EMD. Eighty-four percent had received one or more TKI by the time of transformation. The median OS was 12 months (10 months for myeloid and 17 months for lymphoid) and median FFS was 5 months. In univariate analysis, factors significantly associated with inferior OS were older age, high bone marrow blast %, female gender, lower hemoglobin, higher LDH, presence of trisomy 19 or chromosome 3 aberrations, prior TKI treatments, myeloid phenotype and prior AP (Figure-1 A-C). Recursive partitioning analysis revealed that age ≥56 years and LDH ≥888 were associated with increased risk of death. In multivariate analysis (MVA), adjusting for the above variables, age ≥ 56 yrs (HR=1.73, p<0.001), prior TKI (HR=1.53, p=0.02), LDH ≥888 (HR 1.56, p=0.002) and myeloid phenotype (HR=1.67, p<0.001) were significantly associated with inferior OS. We then analysed FFS in pts with information available on their initial therapy for BP (n=319). As for OS, myeloid phenotype and prior TKI therapy were predictive of inferior FFS by MVA. In a subset analysis, with only pts with EMD, presence of CNS involvement (vs other EMD) and advanced age were associated with inferior OS while high LDH and prior TKI therapy predicted for inferior FFS.
Conclusions: Despite progress in therapy for CML, those who transform to CML-BP have a dismal outcome, particularly if previously treated with TKI. Patients with age ≥ 56, LDH ≥ 888 and those pts with myeloid phenotype had the worst outcomes. Better treatment options are needed for this small but poor prognosis subset of patients.
Jabbour:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy. Konopleva:Calithera: Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding. Wierda:Acerta: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding. Daver:Ariad: Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Otsuka: Consultancy, Honoraria; Kiromic: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Honoraria, Research Funding. O'Brien:Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pharmacyclics, LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Cortes:ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract