Abstract
Background:
Patients with a history of bariatric surgery are often excluded from clinical trials evaluating oral therapies. This is due to concerns that these surgeries alter bioavailability and drug metabolism. Oral tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are the mainstay treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). However, the impact of bariatric surgeries on CML treatment outcomes is largely unknown.
Methods:
In a retrospective analysis, we screened patients with CML treated at our institution and identified those who had any type of bariatric surgery including gastric bypass, gastric sleeve surgery or gastric banding. Subsequently, we compared their responses and outcomes to a control cohort of patients without history of bariatric surgery, using propensity score matching for Sokal Risk and body mass index (BMI) at a 2:1 ratio. In addition to cytogenetic and molecular responses, we assessed times to achieving responses and BCR-ABL1 halving times to investigate differences in response dynamics (Branford, Blood 2014). Event-free survival (EFS) was measured from treatment start to loss of response, progression or death, whereas failure-free survival (FFS) additionally accounted for therapy discontinuation for any other reason such as intolerance. Overall survival (OS) was measured from treatment start date to death, or censored at last follow-up. Univariate and multivariate analyses (MVA) were used to assess the association between characteristics and overall survival.
Results:
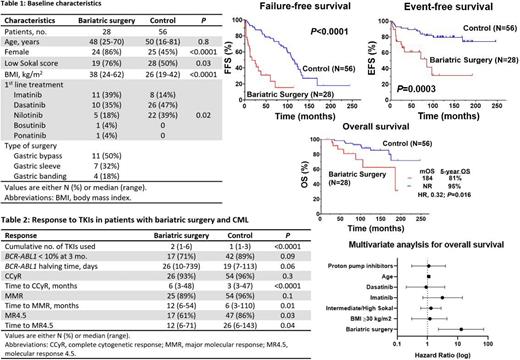
We identified 28 patients with CML and bariatric surgery, of whom 22 (79%) had their surgery before CML. Their baseline characteristics are summarized below (Figure 1). Despite propensity score matching, patients with bariatric surgery compared to control had a higher BMI at time of CML diagnosis (median: 38 vs 26 Kg/m 2, P<0.0001) and lower Sokal Risk (76% vs 50%, P=0.03). More patients in the bariatric surgery group were treated with imatinib (39% vs 14 %, P=0.02).
Patients with history of bariatric surgery received a higher number of TKIs throughout their CML treatment because of resistance or intolerance compared to control (median of 2, range 1-6 vs median of 1, range 1-3, P<0.0001). They tended to have slower response dynamics evidenced by a lower proportion of patients with BCR-ABL1 <10% at 3 months (71% vs 89%, P=0.09), and a longer halving time (26 vs 19 days, P=0.06). Despite having a similar complete cytogenetic response rate (CCyR) (93% vs 96%, P=0.2), their median time to achieve CCyR was significantly longer (6 months vs 3 months; P<0.0001). In addition, they had longer median time to achieve a major molecular remission (MMR) (12 months vs 6 months, P=0.013) and a lower rate of MR4.5 (61% vs 86%, P=0.02) (Figure 1).
Patients with bariatric surgery and CML had inferior EFS compared to control (5-year EFS rate: 61% vs 87% respectively, P=0.0003) and inferior FFS (5-year FFS rate: 15% vs 77% respectively, P<0.0001). Bariatric surgery was associated with worse OS with a 5-year rate of 81% compared to 95% in the control group (P=0.01) (Figure 1). There was no difference in OS comparing patients who had bariatric surgery and received imatinib as first-line treatment vs those that received other TKIs (P=0.5). To account for the impact of co-variates such as BMI, type of TKI and Sokal Risk on survival, we conducted univariate and multivariate analyses. We found that bariatric surgery was an independent predictor of the risk of death with a hazard ratio (HR) of 13 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.3-71.4, P=0.004). The only other independent predictor of OS in the MVA was age where older patients had an increased risk of death with a HR of 1.1 (95% CI, 1.0-1.2, P<0.0001). However, BMI, Sokal Risk and type of TKI used as frontline therapy were not independent predictors of OS in the MVA.
Conclusion:
Bariatric surgery is associated with slower responses to TKIs in patients with CML, and a lower chance of deep remission. It is also associated with higher rates of treatment failure and worse overall survival. There is an unmet need to design treatment strategies for these patients. Although not readily available in the clinical setting, studies measuring drug level in these patients are needed to assess which TKI has a better bioavailability, which in turn could translate to improved outcomes.
Kantarjian: Aptitude Health: Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding; Astellas Health: Honoraria; Jazz: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Immunogen: Research Funding; KAHR Medical Ltd: Honoraria; Ascentage: Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; NOVA Research: Honoraria; Daiichi-Sankyo: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria; Ipsen Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Precision Biosciences: Honoraria; Taiho Pharmaceutical Canada: Honoraria. Jabbour: Amgen, AbbVie, Spectrum, BMS, Takeda, Pfizer, Adaptive, Genentech: Research Funding. Short: Takeda Oncology: Consultancy, Research Funding; NGMBio: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Astellas: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Pemmaraju: Roche Diagnostics: Consultancy; Dan's House of Hope: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sager Strong Foundation: Other; ASCO Leukemia Advisory Panel: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Other: Research Support, Research Funding; Plexxicon: Other, Research Funding; HemOnc Times/Oncology Times: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Samus: Other, Research Funding; Celgene Corporation: Consultancy; Stemline Therapeutics, Inc.: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Research Funding; Clearview Healthcare Partners: Consultancy; Protagonist Therapeutics, Inc.: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Abbvie Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other, Research Funding; ASH Communications Committee: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Affymetrix: Consultancy, Research Funding; Cellectis S.A. ADR: Other, Research Funding; CareDx, Inc.: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo, Inc.: Other, Research Funding; Blueprint Medicines: Consultancy; LFB Biotechnologies: Consultancy; Aptitude Health: Consultancy; Springer Science + Business Media: Other; DAVA Oncology: Consultancy; MustangBio: Consultancy, Other; Bristol-Myers Squibb Co.: Consultancy; ImmunoGen, Inc: Consultancy; Pacylex Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Ravandi: Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Xencor: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Astex: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Taiho: Honoraria, Research Funding; Syros Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Prelude: Research Funding; Agios: Honoraria, Research Funding; Jazz: Honoraria, Research Funding. Sasaki: Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi-Sankyo: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding. Issa: Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Syndax Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Kura Oncology: Consultancy, Research Funding.