Abstract
To understand the role of cytoskeleton and membrane signaling molecules in erythroblast enucleation, we developed a novel analysis protocol of multiparameter high-speed cell imaging in flow. This protocol enabled us to observe F-actin and phosphorylated myosin regulatory light chain (pMRLC) assembled into a contractile actomyosin ring (CAR) between nascent reticulocyte and nucleus, in a population of enucleating erythroblasts. CAR formation and subsequent enucleation were not affected in murine erythroblasts with genetic deletion of Rac1 and Rac2 GTPases because of compensation by Rac3. Pharmacologic inhibition or genetic deletion of all Rac GTPases altered the distribution of F-actin and pMRLC and inhibited enucleation. Erythroblasts treated with NSC23766, cytochalasin-D, colchicine, ML7, or filipin that inhibited Rac activity, actin or tubulin polymerization, MRLC phosphorylation, or lipid raft assembly, respectively, exhibited decreased enucleation efficiency, as quantified by flow cytometry. As assessed by high-speed flow-imaging analysis, colchicine inhibited erythroblast polarization, implicating microtubules during the preparatory stage of enucleation, whereas NSC23766 led to absence of lipid raft assembly in the reticulocyte-pyrenocyte border. In conclusion, enucleation is a multistep process that resembles cytokinesis, requiring establishment of cell polarity through microtubule function, followed by formation of a contractile actomyosin ring, and coalescence of lipid rafts between reticulocyte and pyrenocyte.
Introduction
Erythropoiesis in mammals concludes with the dynamic process of enucleation, by which the orthochromatic erythroblast generates a reticulocyte that will mature to become a red blood cell, and a pyrenocyte, a membrane-encased nucleus surrounded by a thin rim of cytoplasm.1-3 After enucleation, the reticulocytes are released into the bloodstream, whereas the pyrenocytes expose apoptotic signals on their surface, resulting in engulfment and degradation by the central macrophage of the erythroblastic island.3,4 The mechanism of enucleation has been a long-standing matter of investigation and remains controversial.
Early electron microscopy studies suggested that enucleation may be analogous to cytokinesis, pointing to the resemblance of the cytoplasmic constriction between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte to the cleavage furrow at the equatorial region of a mitotic cell.5 Koury et al demonstrated with electron and immunofluorescent microscopy, using mouse splenocytes infected with the anemia-inducing strain of Friend virus, that F-actin bundles concentrate at the furrow behind the extruding nucleus, and that cytochalasin-D, a potent inhibitor of actin polymerization, inhibits enucleation.6 In parallel, a quantitative study by Chasis et al showed that inhibition of microtubule polymerization by colchicine stalls enucleation in vivo and in vitro in rat bone marrow.7 A recent study by Keerthivasan et al using primary mouse and human erythroblasts supported the hypothesis that vesicle trafficking and subsequent vacuole coalescence provide additional membrane for the separating nucleus and reticulocyte.8,9 Actin polymerization was again seen to play a role by Ji et al who found that Rac GTPase deregulation by overexpression of either dominant negative or constitutively active mutants of Rac1 or Rac2 or by pharmacologic inhibition by the Rac-specific inhibitor NSC2376610,11 decreases enucleation of mouse fetal liver erythroblasts in culture. Moreover, down-regulation of mDia2, a downstream effector of Rho GTPases, by small interfering RNA (siRNA) blocks erythroblast enucleation.10
Rac GTPases are subfamily members of the Rho GTPases family and Ras superfamily. Rac1 and Rac2 GTPases have been shown to play distinct and overlapping roles in hematopoietic stem/progenitor and mature blood cells.12-14 Rac1, Rac2, and Rac3 are known to regulate, among other processes, actin structures and vesicular transport pathways.15 As noted earlier in this section, both actin and vesicle trafficking have been implicated in separate proposed models of the enucleation mechanism. On the other hand, cytokinesis has been shown to require microtubules, actin, and vesicle trafficking along with associated signaling proteins in a sequential rather than mutually exclusive manner.16,17 In the present study, we developed a novel analysis protocol of high-speed cell imaging in flow (using the ImagestreamX imaging-flow cytometer; Amnis) to identify a population of enucleating erythroblasts from mouse bone marrow or spleen and study the distribution of cytoskeletal components during enucleation. We used erythroblasts genetically deficient of all 3 mammalian Rac GTPases along with wild-type (WT) control erythroblasts, and WT erythroblasts treated with pharmacologic inhibitors of cytoskeletal or lipid raft assembly to determine the roles of these elements in the enucleation process. We demonstrate a distinct role of microtubules in the establishment of cell polarity before enucleation, with subsequent formation of a contractile actomyosin ring and coalescence of lipid rafts between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte, controlled by Rac GTPases. These data reveal a coordinated assembly in time and space of microtubules, F-actin, and lipid rafts conducting the enucleation process.
Methods
Mice
Mx1CreTg/+;Rac1flox/flox;Rac2−/− mice, bred in a 129Sv and C57BL/6J background, were generated as described previously (supplemental Methods, available on the Blood Web site; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).14,18 These mice were bred with Rac3−/− mice19 to create Mx1CreTg/+;Rac1flox/flox;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− mice. Cre-mediated recombination to induce hematopoietic specific deletion of Rac1 (resulting in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− mice, respectively) was carried out by polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (pI-pC; Amersham-Pharmacia Biotech) treatment using 4 to 6 intraperitoneal injections of pI-pC.14,20 All animal protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center.
In vitro erythropoiesis and enucleation
To study erythroid enucleation, we used 2 in vitro systems. The first was a modification of the long-term ex vivo erythroid differentiation culture protocol described by Giarratana et al,21 adapted for mouse cells. Low-density bone marrow cells were cultured in erythroblast growth medium (StemPro-34 with 2.6% StemPro-34 supplement; Invitrogen), 20% BIT 9500 (StemCell Technologies), 900 ng/mL ferrous sulfate, 90 ng/mL ferrous nitrate, 10−6M hydrocortisone, penicillin/streptomycin, l-glutamine), in 3 steps. In the first proliferative step (days 1-5), the medium was supplemented with 100 ng/mL SCF, 5 ng/mL IL-3, and 2 IU/mL human erythropoietin (Amgen). SCF and IL-3 retard differentiation of the erythroid progenitors while they promote proliferation,22 facilitating expansion of erythroid precursors by adding all 3 cytokines fresh every other day. In the second step (days 6-7), the cells were resuspended at a concentration of 5 × 105 cells/mL, in wells coated with fibronectin at 50 μg/mL, in fresh medium supplemented with only erythropoietin. The medium was changed on day 7 to fresh medium without cytokines, and the cells proceeded to enucleation (days 8-9). For Rac inhibition studies, 50 or 100μM of the Rac specific inhibitor NSC2376611 was added on day 7 and replaced with fresh NSC23766 at the same concentration with medium change on day 8.
The second system is the fast enucleation assay described by Yoshida et al,3 with slight modifications. Briefly, stress erythropoiesis was induced by phlebotomy of 500 μL whole blood with equal volume of normal saline replacement intraperitoneally in adult WT C57BL/6 mice. After 4 days, the mice were killed to obtain the spleen, which was gently homogenized. Splenocytes were separated from parenchyma by filtration through a 40-μm cell-strainer (BD Biosciences), suspended in IMDM plus 2% FBS, separated by Ficoll gradient using Histopaque 1.083 g/mL (Sigma-Aldrich), and treated with red blood cell-lysis buffer (Sigma-Aldrich). The isolated low-density splenocytes, highly enriched in erythroblasts after the phlebotomy, were suspended in erythroblast growth medium supplemented with erythropoietin (10 IU/mL) and cultured on plastic, overnight at 37°C. The next day, cells were lifted using PBS plus 10mM EDTA on ice, washed, and plated at a concentration of 106 cells/well in cytokine-free erythroblast growth medium, in a 24-well plate coated with MS5 cells and incubated to enucleation for 6 to 8 hours (time guided by microscopic observation of ∼ 30%-40% enucleation in the untreated WT sample) at 37°C, with and without the following pharmacologic inhibitors: cytochalasin-D, colchicine, filipin (Sigma-Aldrich), ML-7 (EMD4 Biosciences; Merck KGaA), taxol (Cayman Chemical), or NSC23766, at the concentrations indicated in the corresponding figures.
All experiments involving erythroblasts from Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− or Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− mice (see Figures 1A-B and 2,Figure 3–4) were performed with the long-term enucleation assay to avoid phlebotomy in these mice within the first week after pI-pC induction, a procedure that would increase their already high mortality rate. This assay allowed production of sufficient number of enucleating cells for protein pull-down assays to determine activity of Rac GTPases. The remainder of the figures present experiments that were performed with the fast enucleation assay, which allowed evaluation of inhibitors, such as colchicine and ML-7, which appear to cause cell toxicity with more than 12-hour incubations. Cytospins were prepared at 400 rpm for 3 minutes in a Cytospin-4 Cytocentrifuge (Thermo Shandon), stained with Wright stain (Harleco EMD), and photographed using an Olympus BX51 microscope equipped with an Optronics Macrofire Camera and a PictureFrame Application Version 2.3 software (Optronics).
Flow cytometric analysis
To study the enucleation process quantitatively, we evaluated the percentage of enucleated cells at the conclusion of each experiment by flow cytometry. The cells from each well were collected by washing with PBS plus 10mM EDTA on ice and stained with PE-Cy7-anti–Ter119 (BD Biosciences) in 100 μL of PBS plus 0.5% BSA (FACS buffer), for 20 minutes. After gentle washing to remove unbound antibody, the cells were resuspended in 10mM HEPES buffer, pH 7.4, containing 140mM NaCl and 5mM MgCl2 with 0.25μM SYTO16 (Invitrogen) or FACS buffer with Hoechst 33342 (Invitrogen) for nuclei detection. In both cases, cells were stained with 7-amino-actinomycin D for exclusion of dead cells from the investigation. FACS analysis was conducted on a FACSCanto Flow Cytometer or an LSR-II Flow Cytometer, with FacsDiva Version 6.1.3 software (BD Biosciences).
High-speed cell imaging analysis in flow using ImagestreamX
The distribution of cytoskeletal molecules within enucleating erythroblasts was studied by ImagestreamX (Amnis), which combines flow cytometry and microscopy (40×/numerical aperture 0.75 and 60×/numerical aperture 0.9 objective lens) capabilities. Erythroblasts were collected at the completion of fast enucleation assay using PBS plus 10mM EDTA on ice, were pelleted for 30 seconds at 2000g in a bench-top centrifuge, and fixed in PBS containing 4% formaldehyde for 20 minutes at room temperature. Formaldehyde was removed by centrifugation (30 seconds at 2000g) and aspiration of the supernatant, and the cell pellet was cooled on ice for 10 minutes, before permeabilization by consecutive suspensions in ice-cold (kept at −20°C) 50% acetone, then 100% acetone, and then again 50% acetone solution,24 followed by one wash with FACS buffer. Cells were resuspended in FACS buffer and incubated with PE-Cy7– or PE-anti–Ter119 antibody (BD Biosciences) and either AlexaFluor-488–anti–β-tubulin antibody (BD Biosciences), AlexaFluor-488–conjugated or rhodamine-phalloidin (Invitrogen), AlexaFluor-594–conjugated cholera toxin subunit B (CTB; Invitrogen), anti–pMRLC (Ser19) primary antibody (Cell Signaling Technology), followed by AlexaFluor-488–conjugated secondary antibody (Invitrogen), and anti–γ-tubulin primary antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) followed by AlexaFluor-555–conjugated secondary antibody (Invitrogen). After washing once with FACS buffer, the nuclear stain Draq5 (Cell Signaling Technology) was added at a concentration of 40μΜ in FACS buffer and the samples were processed by ImagestreamX. Approximately 10 000 events per experiment were collected and analyzed with the associated Image Data Exploration and Analysis software (IDEAS; Amnis). Bright Detail Intensity R3 was determined in the CTB-stained enucleating erythroblasts by computing the intensity of localized bright spots within the image that are 3 pixels in radius or less after the local background around the spots is removed (similarly to the “top-hat morphologic transformation” in microscopy image analysis using a 3-pixel radius structuring element and then computing the intensity of the resulting image).
Statistical analysis
Statistical significance for enucleation efficiency differences was evaluated using Student t test for unpaired data with equal variance (results presented as mean ± SEM). The ImagestreamX data of the individual values of centroid distances and bright detail intensities in the experiments shown in Figures 5 and 6 were exported for statistical evaluation. Both delta centroid distance and bright detail intensity measurements take non-negative values, and their probability distribution is asymmetric with a skew toward large values, indicating non-normality. Therefore, to assess the statistical significance of the difference in the medians of the test and control groups, we used the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (nonparametric test for 2 independent samples), which makes no assumptions about the underlying probability distributions and is thus appropriate for non-normal data. For each set of measurements, we report the mean and the median for each group and the 2-tailed P value according to the Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
Results
Quantitation of enucleation efficiency in vitro by flow cytometry and identification of enucleating erythroblasts by ImagestreamX
To study erythroid enucleation quantitatively, we used 2 in vitro systems detailed in “In vitro erythropoiesis and enucleation,” a long-term ex vivo erythroid differentiation culture protocol,21 adapted for mouse cells, and a fast enucleation assay as described by Yoshida et al,3 with slight modifications. We evaluated the percentage of enucleated cells at the conclusion of each experiment by flow cytometry. After gating on Ter119-positive cells, the SYTO16-low and negative population represents the enucleated erythrocytes (Figure 1A-B).
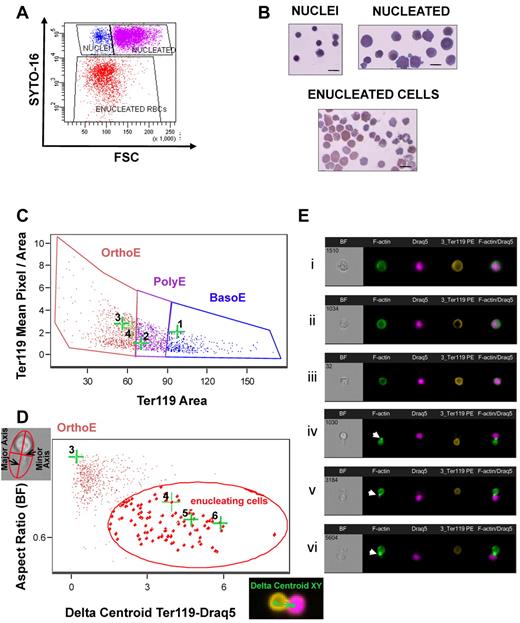
Focusing on a population of enucleating cells. (A) Flow cytometry was used to quantitate enucleation efficiency. Erythroid cells (Ter119+) at the final stage of the long-term in vitro enucleation cultures were gated based on their size (FSC) and DNA content (Syto-16). The populations FSChighSyto-16high (purple), FSClowSyto-16high (blue), and FSClowSyto-16low (red) were sorted and examined by cytospins (B) shown to correspond to nucleated erythroblasts, nuclei, and enucleated red blood cells, respectively. Bar represents 10 μm. (C) A novel analysis in ImagestreamX (Amnis) was used to identify enucleating erythroblasts (here produced in a fast in vitro enucleation assay) and visualize the distribution of cytoskeleton and signaling molecules during enucleation. Erythroblasts were first gated according to size (Ter119 Area) and intensity of staining for Ter119 (mean pixel/area) into basophilic (BasoE), polychromatophilic (PolyE), and orthochromatic (OrthoE) erythroblasts, as previously described.26 (D) Orthochromatic erythroblasts were then evaluated based on the following characteristics: “aspect ratio” of their shape (ratio of the minor axis/major axis) in bright-field image and “Delta centroid Ter119-Draq5,” calculated as the distance of the center of the Ter119-labeled erythroblast or reticulocyte from the center of the Draq5-labeled nucleus. The population of small cells with high Ter119 expression that also exhibited a low aspect ratio and high δ centroid Ter119-Draq5 (gated here by red elliptical) was enriched in enucleating cells. (E) Representative images of cells, stained with phalloidin–AlexaFluor-488, Ter119-PE, and Draq5, are shown along with their corresponding dot-points on the flow cytograms in panels C and D. F-actin was visible to form a CAR, shown by white arrowheads in subpanels Eiv, Ev, and Evi, in the cleavage furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte.
Focusing on a population of enucleating cells. (A) Flow cytometry was used to quantitate enucleation efficiency. Erythroid cells (Ter119+) at the final stage of the long-term in vitro enucleation cultures were gated based on their size (FSC) and DNA content (Syto-16). The populations FSChighSyto-16high (purple), FSClowSyto-16high (blue), and FSClowSyto-16low (red) were sorted and examined by cytospins (B) shown to correspond to nucleated erythroblasts, nuclei, and enucleated red blood cells, respectively. Bar represents 10 μm. (C) A novel analysis in ImagestreamX (Amnis) was used to identify enucleating erythroblasts (here produced in a fast in vitro enucleation assay) and visualize the distribution of cytoskeleton and signaling molecules during enucleation. Erythroblasts were first gated according to size (Ter119 Area) and intensity of staining for Ter119 (mean pixel/area) into basophilic (BasoE), polychromatophilic (PolyE), and orthochromatic (OrthoE) erythroblasts, as previously described.26 (D) Orthochromatic erythroblasts were then evaluated based on the following characteristics: “aspect ratio” of their shape (ratio of the minor axis/major axis) in bright-field image and “Delta centroid Ter119-Draq5,” calculated as the distance of the center of the Ter119-labeled erythroblast or reticulocyte from the center of the Draq5-labeled nucleus. The population of small cells with high Ter119 expression that also exhibited a low aspect ratio and high δ centroid Ter119-Draq5 (gated here by red elliptical) was enriched in enucleating cells. (E) Representative images of cells, stained with phalloidin–AlexaFluor-488, Ter119-PE, and Draq5, are shown along with their corresponding dot-points on the flow cytograms in panels C and D. F-actin was visible to form a CAR, shown by white arrowheads in subpanels Eiv, Ev, and Evi, in the cleavage furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte.
The low frequency of erythroblasts engaged in enucleation that can be studied microscopically is often a limiting factor in enucleation studies. Consequently, we sought to develop a method that would enable us to identify and study a significant number of enucleating erythroblasts under specific conditions. To this end, we expanded a method previously described by McGrath et al using the ImagestreamX imaging flow cytometer (Amnis) that allows separation of basophilic, polychromatophilic, and orthochromatic erythroblasts by gating the cells according to their size and intensity of Ter119 staining (Figure 1C).26 We used the aspect ratio and δ centroid XY, morphologic cell parameters measurable through the use of the associated software IDEAS (Amnis). The aspect ratio is the ratio of the minor cell axis divided by the major axis and describes how round or oblong the cell is. The δ centroid XY parameter measures the distance between the centers of 2 chosen (X and Y) stains, in this case, Ter119 and Draq5. The population with low aspect ratio and high δ centroid Ter119-Draq5 value is highly enriched in enucleating cells, in which the nucleus is moving away from the main body of an elongated cell (Figure 1D). This method facilitated the visualization of fixed enucleating cells (Figure 1Eiv-vi) and consequently the study of localization of cytoskeleton and signaling components during enucleation. In the representative experiment shown in Figure 1C through E, we gated 103 enucleating cells within the population encircled by the red line. Thirty-one of these 103 events were at a stage during enucleation and at an imaging section where F-actin was visible as a ring in the cleavage furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte, suggesting that visualization of a significant number of enucleating events is necessary to ascertain the distribution of structures during this highly dynamic process (supplemental Figure 1).
Rac GTPases (Rac1, Rac2, or Rac3) are interchangeably required for erythroblast enucleation
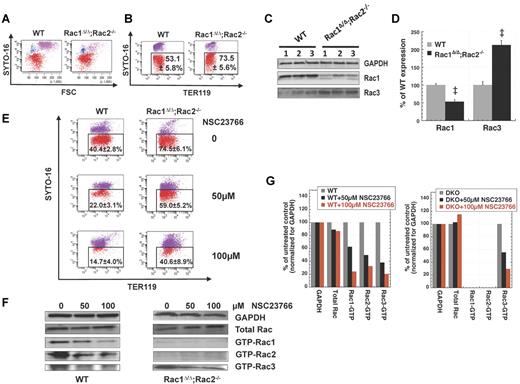
Deregulation of Rac GTPases with overexpression of either dominant negative or constitutively active mutants of Rac1 or Rac2 or by pharmacologic inhibition by the Rac-specific inhibitor NSC2376611 has been shown by Ji et al to decrease enucleation of mouse fetal liver erythroblasts in culture.10 However, we found that the in vitro enucleation efficiency of Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts, produced in Mx1CreTg/+;Rac1flox/flox;Rac2−/− adult mouse bone marrow after inducing deletion of the floxed Rac1 gene in vivo by pI-pC injections, was increased compared with the enucleation of WT erythroblasts in parallel long-term erythropoiesis cultures as quantitated by flow cytometry (Figure 2A-B). Because we and others have demonstrated compensatory cross-talk between members of the Rho GTPase family (Rho, Rac, and Cdc42),28-30 we evaluated the protein levels of these GTPases in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− versus WT erythrocytes by immunoblotting. Whereas RhoA and Cdc42 was unchanged (data not shown), Rac3 was significantly increased in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythrocytes (Figure 2C-D). Thus, it appears that Rac1 and Rac2 ablation is not sufficient to impair enucleation because of compensatory up-regulation of Rac3 expression and/or protein stabilization. To determine the physiologic relevance of increased Rac3 level in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts, we used the Rac-specific inhibitor NSC2376611 to simultaneously inhibit Rac1, Rac2, and Rac3. In agreement with the results of Ji et al in fetal liver cells,10 NSC23766 inhibited enucleation of adult bone marrow erythroblasts by more than 60% in WT and by more than 45% in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− samples, in a dose-dependent fashion (Figure 2E). The inhibition of enucleation by NSC23766 was accompanied by parallel inhibition of Rac1, Rac2, and Rac3 activities, as confirmed by pull-down assays and consequent immunoblotting (Figure 2F-G). The enucleation efficiency of Rac3−/− erythroblasts was evaluated by flow cytometry in fast enucleation assays in vitro and was found similar to that of WT erythroblasts (41.5% ± 2.5% vs. 43.7% ± 1.8%, n = 3, P = .14). These results indicate that the overall Rac GTPase activity plays a key role in regulating enucleation.
Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts do not demonstrate decreased enucleation. Total inhibition of Rac-GTPases is required to inhibit enucleation of erythroblasts in long-term in vitro erythropoiesis cultures. Representative flow cytograms per Syto-16 and FSC (A) and per Syto-16 and Ter119 expression (B) demonstrating that enucleation of Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts was more efficient than that of WT erythroblasts in parallel ex vivo erythropoiesis cultures. Percentages of SYTO16low/− cells (red) out of the Ter119+ cells are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 6. P < .05. (C) Up-regulation of Rac3 in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythrocytes (representative example of 3 biologic repeats). Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythrocytes show residual Rac1 expression from Rac1flox/flox hematopoiesis with competitive advantage.18,27 (D) Densitometry of Rac1 and Rac3 expression in the above blot, expressed as percentage of the corresponding protein in WT red blood cells. (E) Pharmacologic inhibition of all Rac GTPases by NSC23766 at a dose of 50 and 100μM inhibited enucleation in WT (n = 8, P < .01 between 0 and 50μM, 0 and 100μM, and 50 and 100μM) and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts (n = 5, P < .05 between 0 and 50μM, 0 and 100μM, not statistically significant between 50 and 100μM). (F) Rac1, Rac2, and Rac3 activity (GTP-bound isoforms) of WT and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroid cells at the enucleation stage of a long-term in vitro erythropoiesis culture after treatment with increasing concentrations of NSC23766 (representative blots of at least 3 different samples for each effector domain pull-down assay). Total Rac protein for each sample before performing pull-down is detected with polyclonal anti-Rac1, Rac2, Rac3 antibody. GAPDH from the same samples (before pull-down) is shown as loading control. (G) Densitometry of the above blot, demonstrating total Rac protein and Rac1, Rac2, and Rac3 activity normalized for GAPDH loading control for each sample and expressed as percentage of the corresponding protein expression or activity in the sample not treated with NSC23766. The faint bands in the GTP-Rac1 and Rac2 lanes of the Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− sample are not plotted because they represent either minimal residual activity (possible for Rac1) or a nonspecific antibody reaction (especially true for the Rac2 lane because the sample is Rac2-null).
Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts do not demonstrate decreased enucleation. Total inhibition of Rac-GTPases is required to inhibit enucleation of erythroblasts in long-term in vitro erythropoiesis cultures. Representative flow cytograms per Syto-16 and FSC (A) and per Syto-16 and Ter119 expression (B) demonstrating that enucleation of Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts was more efficient than that of WT erythroblasts in parallel ex vivo erythropoiesis cultures. Percentages of SYTO16low/− cells (red) out of the Ter119+ cells are shown as mean ± SEM; n = 6. P < .05. (C) Up-regulation of Rac3 in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythrocytes (representative example of 3 biologic repeats). Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythrocytes show residual Rac1 expression from Rac1flox/flox hematopoiesis with competitive advantage.18,27 (D) Densitometry of Rac1 and Rac3 expression in the above blot, expressed as percentage of the corresponding protein in WT red blood cells. (E) Pharmacologic inhibition of all Rac GTPases by NSC23766 at a dose of 50 and 100μM inhibited enucleation in WT (n = 8, P < .01 between 0 and 50μM, 0 and 100μM, and 50 and 100μM) and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts (n = 5, P < .05 between 0 and 50μM, 0 and 100μM, not statistically significant between 50 and 100μM). (F) Rac1, Rac2, and Rac3 activity (GTP-bound isoforms) of WT and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroid cells at the enucleation stage of a long-term in vitro erythropoiesis culture after treatment with increasing concentrations of NSC23766 (representative blots of at least 3 different samples for each effector domain pull-down assay). Total Rac protein for each sample before performing pull-down is detected with polyclonal anti-Rac1, Rac2, Rac3 antibody. GAPDH from the same samples (before pull-down) is shown as loading control. (G) Densitometry of the above blot, demonstrating total Rac protein and Rac1, Rac2, and Rac3 activity normalized for GAPDH loading control for each sample and expressed as percentage of the corresponding protein expression or activity in the sample not treated with NSC23766. The faint bands in the GTP-Rac1 and Rac2 lanes of the Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− sample are not plotted because they represent either minimal residual activity (possible for Rac1) or a nonspecific antibody reaction (especially true for the Rac2 lane because the sample is Rac2-null).
Rac GTPases organize the actomyosin ring during enucleation
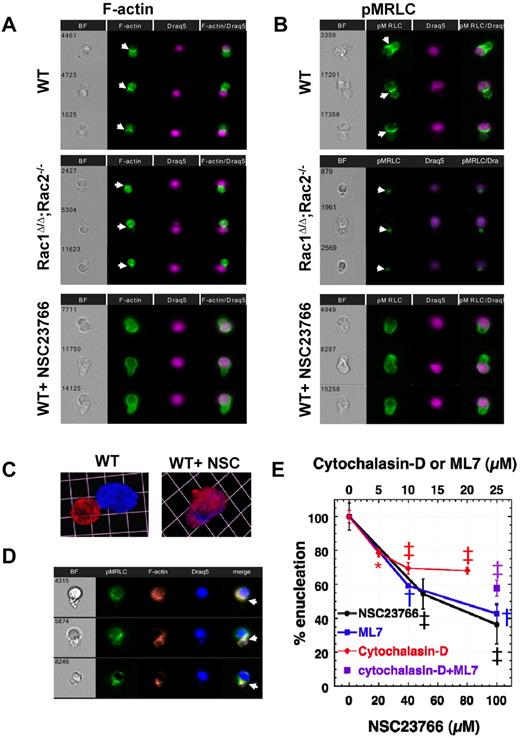
Rac GTPases are well-known regulators of actin in cells.15 We used the ImagestreamX imaging flow cytometer to study actin and myosin distribution in WT or Rac-deficient (after genetic or pharmacologic manipulation) enucleating erythroblasts produced in vitro in long-term enucleation assays. Actin filaments appeared to form a CAR between the nascent reticulocyte and the nucleus in WT erythroblasts, as described before,6 distributed in a similar pattern with actin in the cleavage furrow of a cell in cytokinesis (Figure 3A). In cytokinesis, furrow ingression is driven by assembly and contraction of actomyosin filaments.16,31 Therefore, we examined whether myosin is also localized at the same area during enucleation. Labeling for phosphorylated myosin regulatory light chain (pMRLC) demonstrated that pMRLC and, consequently, activated myosin is contributing to the formation of CAR between reticulocyte and nucleus in WT enucleating erythroblasts, providing the necessary collaborator for actin to contract (Figure 3B). Parallel imaging of enucleating Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts demonstrated more intense membrane staining for actin in the incipient reticulocytes, as expected from the phenotype of Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythrocytes,18 as well as decreased intensity of staining for pMRLC. However, both actin and pMRLC were still able to assemble in CAR formation between reticulocyte and nucleus. In contrast, when NSC23766 was used to inhibit all Rac GTPases, neither F-actin nor pMRLC concentrated at the cleavage furrow to assemble a functional contractile ring; instead, these proteins continued to surround the nucleus (Figure 3A-B). This mislocalization probably results in the inhibition of enucleation that we observed by flow cytometric studies (Figure 2). Confocal microscopy of WT enucleating erythroblasts incubated without and with NSC23766 confirmed the persistent distribution of F-actin around the nucleus, when all Rac-GTPases are inhibited (Figure 3C). Staining of WT erythroblasts with both AlexaFluor-488–conjugated-pMRLC antibody and rhodamine-phalloidin for multiparameter high-speed cell imaging in flow showed colocalization of actin and myosin at the cleavage furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte (Figure 3D).
Rac GTPases organize F-actin and myosin into an actomyosin ring between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte during enucleation. An actomyosin ring made up of F-actin (A) and pMRLC (B) is shown in enucleating WT and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts (indicated by white arrowheads). In contrast, an actomyosin ring is not formed in WT erythroblasts incubated with NSC23766 (100μM) that inhibits all Rac GTPases. In the erythroblasts observed to attempt enucleation under total Rac inhibition, actin and pMRLC continue to surround the nucleus. Three representative images are shown in each panel from at least 30 cells with similar morphology in each category studied. Images were obtained with a 40× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (C) Confocal microscopy image of WT erythroblasts incubated without and with NSC23766 confirms lagged distribution of F-actin around the nucleus when Rac-GTPases are inhibited. In the WT image (on the left), the contractile ring is not visible, probably because the cell is at the final stage of enucleation with the nucleus almost separating. F-actin was labeled with rhodamine-phalloidin (red) and nucleus with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Images were obtained with a 100× oil-immersed objective lens, numerical aperture 1.45, and processed using Volocity Version 4.1 software to produce a 3-dimensional reconstruction of the cells visualized; 1 unit represents 4.1 μm. (D) F-actin and myosin (labeled on pMRLC) colocalize at the cleavage furrow to form an actomyosin ring. Images were obtained with a 60× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (E) Effect of pharmacologic inhibitors of actin filament assembly (cytochalasin-D), MRLC phosphorylation (ML7), and Rac GTPase activity (NSC23766) on the enucleating efficiency of WT erythroblasts in fast enucleation assay as percentile of the control sample. The absolute enucleation efficiency of the control sample in this experiment was 40.4% ± 5.3%. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 3. *P < .02 (control vs each of the inhibitor-treated samples). ‡P < .005 (control vs each of the inhibitor-treated samples). †P < .0005 (control vs each of the inhibitor-treated samples). Sample treated with both cytochalasin-D (10μM) and ML7 (25μM) demonstrated inhibition of enucleation compared with control (P < .005) but not a statistically significant difference from cytochalasin-D or ML7-alone treated samples.
Rac GTPases organize F-actin and myosin into an actomyosin ring between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte during enucleation. An actomyosin ring made up of F-actin (A) and pMRLC (B) is shown in enucleating WT and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts (indicated by white arrowheads). In contrast, an actomyosin ring is not formed in WT erythroblasts incubated with NSC23766 (100μM) that inhibits all Rac GTPases. In the erythroblasts observed to attempt enucleation under total Rac inhibition, actin and pMRLC continue to surround the nucleus. Three representative images are shown in each panel from at least 30 cells with similar morphology in each category studied. Images were obtained with a 40× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (C) Confocal microscopy image of WT erythroblasts incubated without and with NSC23766 confirms lagged distribution of F-actin around the nucleus when Rac-GTPases are inhibited. In the WT image (on the left), the contractile ring is not visible, probably because the cell is at the final stage of enucleation with the nucleus almost separating. F-actin was labeled with rhodamine-phalloidin (red) and nucleus with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; blue). Images were obtained with a 100× oil-immersed objective lens, numerical aperture 1.45, and processed using Volocity Version 4.1 software to produce a 3-dimensional reconstruction of the cells visualized; 1 unit represents 4.1 μm. (D) F-actin and myosin (labeled on pMRLC) colocalize at the cleavage furrow to form an actomyosin ring. Images were obtained with a 60× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (E) Effect of pharmacologic inhibitors of actin filament assembly (cytochalasin-D), MRLC phosphorylation (ML7), and Rac GTPase activity (NSC23766) on the enucleating efficiency of WT erythroblasts in fast enucleation assay as percentile of the control sample. The absolute enucleation efficiency of the control sample in this experiment was 40.4% ± 5.3%. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 3. *P < .02 (control vs each of the inhibitor-treated samples). ‡P < .005 (control vs each of the inhibitor-treated samples). †P < .0005 (control vs each of the inhibitor-treated samples). Sample treated with both cytochalasin-D (10μM) and ML7 (25μM) demonstrated inhibition of enucleation compared with control (P < .005) but not a statistically significant difference from cytochalasin-D or ML7-alone treated samples.
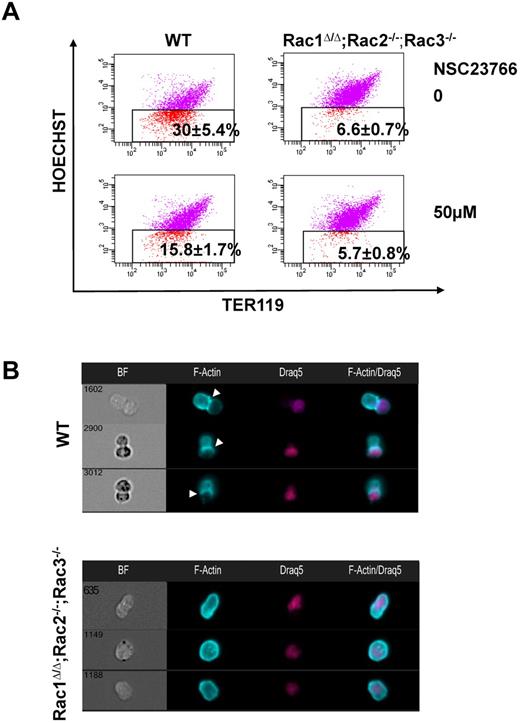
We investigated the significance of the contractile ring components in enucleation through flow cytometric analysis after incubation with pharmacologic inhibitors (Figure 3E). Inhibition of actin filament polymerization by cytochalasin-D at doses of 5, 10, and 20μM resulted in a statistically significant and dose-dependent decrease in enucleation efficiency, in agreement with data by Koury et al,6 leveling out by 20μM. Inhibition of MRLC phosphorylation through the use of the myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) inhibitor ML7 had a strong negative impact on the number of erythroblasts that achieved enucleation. Use of both cytochalasin-D and ML7 did not produce additive or synergistic results, indicating that both inhibitors target the common step of CAR formation. Inhibition of all Rac GTPases with NSC23766 led to decreased enucleation efficiency, interestingly to a greater degree than cytochalasin-D alone, suggesting the possibility that Rac GTPases affect enucleation not only via actin regulation. None of the inhibitor concentrations used in these studies led to cell apoptosis, as measured by 7-amino-actinomycin D staining, or to any morphologic alteration of the cells as evaluated in cytospin preparations, and their inhibition of enucleation was reversible on their removal from the medium (supplemental Figure 2A). We further confirmed the requirement of Rac GTPases for appropriate actin distribution during enucleation and ruled out off-target effects of NSC23766 by studying the enucleation efficiency of Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts in long-term erythropoiesis cultures in vitro (Figure 4A) and evaluating the actin distribution of these cells by ImagestreamX (Figure 4B). The abnormal F-actin distribution surrounding the nucleus in those cells was the same as in the NSC23766-treated cells. Hence, Rac GTPases regulate enucleation, at least in part, through the organization of a contractile actomyosin ring.
Genetic deletion of all Rac GTPases results in impaired distribution of F-actin in enucleating erythroblasts. (A) Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts exhibited statistically significant inhibition of enucleation in long-term in vitro erythropoiesis culture compared with WT erythroblasts (n = 3, P < .05 between WT and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts). Incubation of Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts with 50μM NSC23766 did not enhance inhibition of enucleation in a significant manner, indicating that the inhibitory effect of NSC23766 in enucleation is probably not caused by off-target effects. (B) F-actin in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts continues to surround the nucleus in the enucleating erythroblast and does not assemble into CAR formation to separate the nucleus from the reticulocyte, in a similar pattern with the erythroblasts incubated with NSC23766. Images were obtained with a 40× objective lens by Imagestreamx.
Genetic deletion of all Rac GTPases results in impaired distribution of F-actin in enucleating erythroblasts. (A) Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts exhibited statistically significant inhibition of enucleation in long-term in vitro erythropoiesis culture compared with WT erythroblasts (n = 3, P < .05 between WT and Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts). Incubation of Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts with 50μM NSC23766 did not enhance inhibition of enucleation in a significant manner, indicating that the inhibitory effect of NSC23766 in enucleation is probably not caused by off-target effects. (B) F-actin in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/−;Rac3−/− erythroblasts continues to surround the nucleus in the enucleating erythroblast and does not assemble into CAR formation to separate the nucleus from the reticulocyte, in a similar pattern with the erythroblasts incubated with NSC23766. Images were obtained with a 40× objective lens by Imagestreamx.
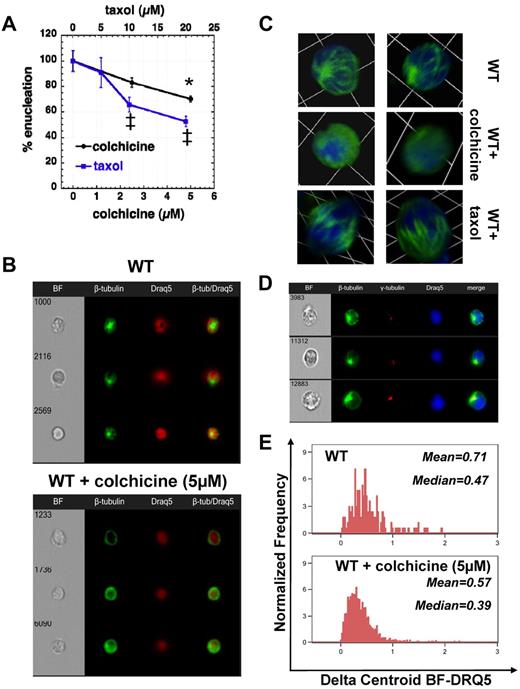
Microtubules mediate erythroblast polarization in preparation for enucleation
Inhibition of microtubule polymerization in rat bone marrow cells in vivo or in vitro by colchicine has been shown by Chasis et al to cause an increased number of erythroblasts arrested at the act of nuclear extrusion.7 We also observed inhibition of enucleation by colchicine and taxol in the fast enucleation assay in vitro (Figure 5A), but there was no difference in staining with AlexaFluor-488–anti–β-tubulin within the enucleating erythroblasts exposed to 5μM colchicine for 6 hours versus the control sample (data not shown). However, when we specifically analyzed the population of orthochromatic erythroblasts, we could see polarized microtubule formation visible in control WT erythroblasts, whereas β-tubulin was diffusely stained in WT orthochromatic erythroblasts incubated with colchicine (5μM) for 6 hours in vitro as seen by Imagestreamx (Figure 5B). This unipolar microtubule assembly embracing the nucleus was also visualized in WT erythroblasts by confocal microscopy (Figure 5C). Incubation with colchicine that inhibits microtubule polymerization caused a diffuse staining for β-tubulin, whereas incubation with taxol that inhibits microtubule depolymerization produced thickened microtubule bundles. Microtubules radiated from a γ-tubulin–rich area within the narrow area between nucleus and plasma membrane as seen by Imagestreamx, whereas the nucleus moved toward the opposite direction for establishment of erythroblast polarity (Figure 5D). Statistical evaluation of the ImagestreamX data, by measuring the parameter delta centroid BF-DRQ5 between the center of the cell body as seen in bright-field and the center of the nuclear staining achieved with Draq5, demonstrated that inhibition of tubulin polymerization by colchicine abolished cell polarization with the nucleus remaining at a central location in the cell (Figure 5E). Moreover, when adding colchicine in a fast enucleation assay after pretreatment with cytochalasin-D and/or ML7 to first inhibit the contractile ring, no additive inhibitory effect on enucleation was observed (supplemental Figure 2B). These results indicate the critical role of microtubules in enucleation at a stage preceding contractile actomyosin ring formation.
Inhibition of tubulin polymerization or depolymerization impedes enucleation by inhibition of erythroblast polarization. (A) Effect of an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization (colchicine) or an inhibitor of tubulin depolymerization (taxol) on the enucleating efficiency of WT erythroblasts in fast enucleation assay, normalized as percentile of the control sample (mean ± SEM; n = 3). *P < .05 for 5μM colchicine-treated sample versus control. ‡P < .005 for 10 and 20μM taxol-treated samples vs control. The absolute enucleation efficiency of the control sample in this experiment was 47.9% ± 4.6%. (B) Polarized microtubule formation is visible in control WT erythroblasts (stained with β-tubulin–AlexaFluor-488 and the nuclear stain Draq5), whereas β-tubulin is diffusely stained in the erythroblasts incubated with colchicine (5μM) for 6 hours in the fast in vitro enucleation assay. Images were obtained with a 40× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (C) Confocal microscopy images of WT erythroblasts incubated without and with colchicine or taxol. β-tubulin was labeled with AlexaFluor-488 (green) and nucleus with DAPI (blue). Z-stack images were obtained with a 63× oil-immersed objective lens, numerical aperture 1.45, and processed using Volocity Version 4.1 software to produce a 3-dimensional reconstruction of the cells visualized; 1 unit represents 6.8 μm. WT orthochromatic erythroblasts demonstrate a unipolar microtubule assembly embracing the nucleus that appears to be pushed through as the cell elongates. Inhibition of microtubule polymerization with colchicine caused a diffuse staining for β-tubulin, whereas inhibition of microtubule depolymerization with taxol produced thickened microtubule bundles (previously seen by Koury et al6 ) that appear to maintain a grip around the nucleus. (D) Microtubules radiate from a γ-tubulin–rich area in orthochromatic erythroblasts to induce cell polarization. β-tubulin was labeled with AlexaFluor-488 (green), γ-tubulin with AlexaFluor-555 (red), and nucleus with DAPI (blue), and images were obtained with a 60× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (E) Inhibition of tubulin polymerization by colchicine inhibited cell polarization, as demonstrated from the distribution of the parameter Delta Centroid BF-DRQ5, which measures the distance between the center of the cell body as seen in bright-field and the center of the nuclear staining achieved with Draq5; median and mean values of the Delta Centroid BF-DRQ5 of control and colchicine-treated WT orthochromatic erythroblasts are shown, and the difference of the 2 samples is statistically significant (P < .001).
Inhibition of tubulin polymerization or depolymerization impedes enucleation by inhibition of erythroblast polarization. (A) Effect of an inhibitor of tubulin polymerization (colchicine) or an inhibitor of tubulin depolymerization (taxol) on the enucleating efficiency of WT erythroblasts in fast enucleation assay, normalized as percentile of the control sample (mean ± SEM; n = 3). *P < .05 for 5μM colchicine-treated sample versus control. ‡P < .005 for 10 and 20μM taxol-treated samples vs control. The absolute enucleation efficiency of the control sample in this experiment was 47.9% ± 4.6%. (B) Polarized microtubule formation is visible in control WT erythroblasts (stained with β-tubulin–AlexaFluor-488 and the nuclear stain Draq5), whereas β-tubulin is diffusely stained in the erythroblasts incubated with colchicine (5μM) for 6 hours in the fast in vitro enucleation assay. Images were obtained with a 40× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (C) Confocal microscopy images of WT erythroblasts incubated without and with colchicine or taxol. β-tubulin was labeled with AlexaFluor-488 (green) and nucleus with DAPI (blue). Z-stack images were obtained with a 63× oil-immersed objective lens, numerical aperture 1.45, and processed using Volocity Version 4.1 software to produce a 3-dimensional reconstruction of the cells visualized; 1 unit represents 6.8 μm. WT orthochromatic erythroblasts demonstrate a unipolar microtubule assembly embracing the nucleus that appears to be pushed through as the cell elongates. Inhibition of microtubule polymerization with colchicine caused a diffuse staining for β-tubulin, whereas inhibition of microtubule depolymerization with taxol produced thickened microtubule bundles (previously seen by Koury et al6 ) that appear to maintain a grip around the nucleus. (D) Microtubules radiate from a γ-tubulin–rich area in orthochromatic erythroblasts to induce cell polarization. β-tubulin was labeled with AlexaFluor-488 (green), γ-tubulin with AlexaFluor-555 (red), and nucleus with DAPI (blue), and images were obtained with a 60× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (E) Inhibition of tubulin polymerization by colchicine inhibited cell polarization, as demonstrated from the distribution of the parameter Delta Centroid BF-DRQ5, which measures the distance between the center of the cell body as seen in bright-field and the center of the nuclear staining achieved with Draq5; median and mean values of the Delta Centroid BF-DRQ5 of control and colchicine-treated WT orthochromatic erythroblasts are shown, and the difference of the 2 samples is statistically significant (P < .001).
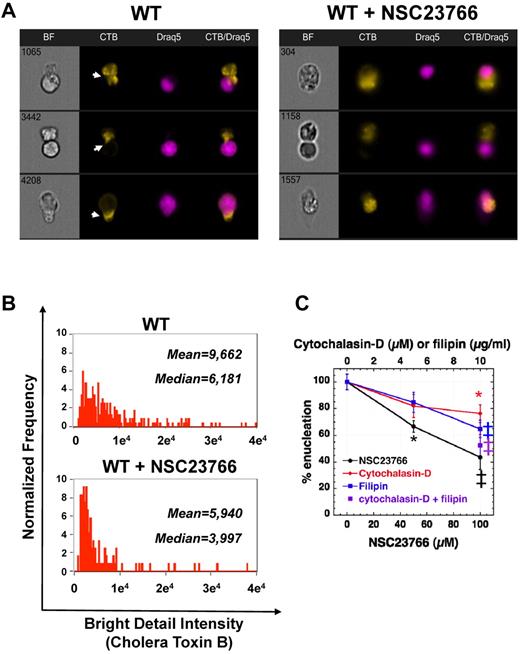
Rac GTPases are necessary for clustering of lipid rafts at the furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte
Cholesterol-rich liquid-ordered plasma membrane microdomains (lipid rafts) are well known as platforms of signaling molecules and are essential for completion of cytokinesis after the formation of the actomyosin ring in the cleavage furrow.16 Rac GTPases have been shown to associate with lipid rafts when they bind to membrane to initiate signaling.32,33 Because enucleation is regulated by Rac GTPases and uses an actomyosin ring in a cytokinesis-like mechanism, we investigated the potential role of lipid rafts during enucleation. Staining of erythroblasts incubated in the fast enucleation assay with fluorescent CTB, which binds to the lipid raft marker GM1-ganglioside, revealed that lipid rafts do merge in the furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte (Figure 6A). Inhibition of Rac GTPases with NSC23766, apart from inhibition of enucleation and altered distribution of actomyosin, led also to the absence of lipid rafts between reticulocyte and pyrenocyte, within the elongated cells attempting enucleation (Figure 6A). The clustering of lipid rafts, as seen by evaluating bright detail intensity, decreased in enucleating erythroblasts incubated with NSC23766 compared with the control erythroblasts (Figure 6B). Filipin, an inhibitor of lipid rafts through cholesterol depletion, has been shown to inhibit cytokinesis.16 Incubation of WT erythroblasts in vitro with filipin, in the fast enucleation assay, inhibited enucleation in a dose-dependent fashion. Moreover, combining cytochalasin-D and filipin had a synergistic effect, reaching a similar level of inhibition with the Rac-inhibitor NSC23766, implicating that Rac GTPases probably control both F-actin and lipid raft assembly during enucleation.
Lipid raft clustering is necessary for enucleation and is regulated by Rac GTPases. (A) Staining of control and NSC23766-treated enucleating erythroblasts with CTB-AlexaFluor-594, which labels the lipid raft marker ganglioside GM1, revealed that Rac inhibition inhibits lipid raft clustering in the cleavage furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte (indicated by white arrowheads). Three representative images are shown in each panel from at least 40 cells with similar morphology in each category. Images were obtained with a 60× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (B) The bright detail intensity of lipid raft staining decreased significantly in enucleating WT erythroblasts incubated with the Rac GTPases inhibitor NSC23766 (50μM). Medians and means for bright detail intensity of CTB staining in control WT and NSC23766-inhibited enucleating erythroblasts are shown, and the difference of the 2 samples is statistically significant with P < .001. (C) Effect of pharmacologic inhibitors of actin filament assembly (cytochalasin-D), lipid raft organization (filipin), and Rac GTPase activity (NSC23766) on the enucleating efficiency of WT erythroblasts in a fast enucleation assay as percentile of the control sample. The absolute enucleation efficiency of the control sample in this experiment was 51.5% ± 3.4%. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 6. *P < .05 (vs control). ‡P < .005 (vs control).
Lipid raft clustering is necessary for enucleation and is regulated by Rac GTPases. (A) Staining of control and NSC23766-treated enucleating erythroblasts with CTB-AlexaFluor-594, which labels the lipid raft marker ganglioside GM1, revealed that Rac inhibition inhibits lipid raft clustering in the cleavage furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte (indicated by white arrowheads). Three representative images are shown in each panel from at least 40 cells with similar morphology in each category. Images were obtained with a 60× objective lens by Imagestreamx. (B) The bright detail intensity of lipid raft staining decreased significantly in enucleating WT erythroblasts incubated with the Rac GTPases inhibitor NSC23766 (50μM). Medians and means for bright detail intensity of CTB staining in control WT and NSC23766-inhibited enucleating erythroblasts are shown, and the difference of the 2 samples is statistically significant with P < .001. (C) Effect of pharmacologic inhibitors of actin filament assembly (cytochalasin-D), lipid raft organization (filipin), and Rac GTPase activity (NSC23766) on the enucleating efficiency of WT erythroblasts in a fast enucleation assay as percentile of the control sample. The absolute enucleation efficiency of the control sample in this experiment was 51.5% ± 3.4%. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 6. *P < .05 (vs control). ‡P < .005 (vs control).
Discussion
Erythroblast enucleation is a dynamic, fast-moving process that lasts approximately 10 minutes.4 Because limited synchronization can be attained in either in vitro erythropoiesis cultures or by stress erythropoiesis in vivo, it has been challenging to evaluate morphologically a significant number of enucleating erythroblasts. Using ImagestreamX (Amnis), we developed a novel method to identify a population enriched in enucleating erythroblasts, based on quantifiable morphologic cell parameters. By focusing on the elongated cells with increased distance between the centers of Ter119+ staining and Draq5+ staining, we were able to examine the distribution of cytoskeleton and signaling components in fixed enucleating erythroblasts, collecting images of at least 80 events of interest in each standardized condition studied. From these, we had at least 30 images per experiment, which were at the appropriate enucleation stage and the appropriate focus for the cytoskeleton component in question to be evaluable.
By this method, we were able to visualize clearly F-actin structures concentrated in a ring (CAR) between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte, in agreement with the images previously shown by Koury et al.6 Moreover, we demonstrated that pMRLC colocalized with actin at the same area, indicating that a functional actomyosin ring is being formed during enucleation. Nonmuscle myosin IIB was recently shown to participate in enucleation.34 The exact mechanism of actin-myosin contraction, mediated either by myosin's head,17,35,36 or by a tail-hinge apparatus,37 but in any way regulated by MRLC phosphorylated at Ser19, a target of Rho-kinase (ROCK) or MLCK,38 remains to be elucidated. Using our fast in vitro enucleation assays, we evaluated the action of cytochalasin-D and ML7, inhibitors of actin polymerization and MLCK, respectively. Both inhibited enucleation in a dose-dependent and reversible manner without a synergistic effect when combined, indicating that they both inhibit the same process during enucleation. The inhibition we observed with these inhibitors was not complete, especially for cytochalasin-D,6,8 probably because of the high enucleation efficiency (30%-70%) in our assays, attained by using stroma cells. A more complete inhibition is easier to achieve when control samples have enucleation efficiency of 10% to 18% as previously described6,8 ; however, we observed that experiments terminated at a low enucleation rate gave highly variable results.
We observed that inhibition of Rac GTPases by the pan-Rac inhibitor NSC23766 suppressed enucleation, consistent with previous report by Ji et al,10 and in agreement with our earlier findings that Rac GTPases control F-actin polymerization in erythrocytes.18 Multiparameter high-speed cell imaging in flow revealed that genetic or pharmacologic inhibition of all Rac GTPases was associated with failure to assemble F-actin and pMRLC into creating CAR next to the nucleus that had moved appropriately within the elongated cell (Figures 3A and 4B). Hematopoietic cells with genetic deletion of Rac1 and Rac2 GTPases were able to differentiate in vitro to erythroblasts, enucleating at least as efficiently as WT erythroblasts, because of concurrent Rac3 up-regulation. It is intriguing that Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts exhibited levels of enucleation higher than WT erythroblasts in erythropoiesis cultures. This finding implicates that the pathways regulating enucleation involve multiple signaling and cytoskeletal components. Deletion of some of these components at the genetic level may be associated with up-regulation of other genes at a parallel or downstream level that leads to overcompensation. Such an overcompensation in quantity may happen at the expense of quality, as it is suggested by the small, fragile reticulocytes produced by Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts.18 Erythroblast enucleation is a process necessary for mammalian survival, as indicated by the embryonal lethality of mouse mutants with genetic deletion of erythroblast-macrophage protein or of DNase II, where a significant number of fetal erythroblasts fail to enucleate.39,40 Enucleation in vitro has a significantly decreased efficiency compared with the in vivo process. This superb in vivo efficiency is probably the result of interactions among the erythroblasts and of erythroblasts with the central macrophage and extracellular matrix within the erythroblastic islands.1 Rac GTPases are activated by cell-receptor-mediated signaling,32 and their optimal regulation of enucleation may depend on cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix interaction within the erythroblastic island. Further studies will be required to evaluate the multiple processes collaborating to produce efficient enucleation.
We did observe inhibition of enucleation after incubation of erythroblasts with colchicine, in agreement to the study by Chasis et al,7 but in contrast to 2 other previous studies.6,8 Optimization of our fast enucleation assay by adding stroma cells to achieve enucleation efficiency of higher than 30% in the untreated sample allowed us to observe the inhibitory effect of colchicine consistently. Although we cannot completely exclude the possibility that microtubule inhibition decreased enucleation by effects to the stromal cells, we were able to see altered microtubule distribution in the erythroblasts after incubation with colchicine or taxol (Figure 5B-C). Organized microtubules, labeled with AlexaFluor-488–anti–β-tubulin, were visible in the population of orthochromatic erythroblasts in the untreated sample, inducing cell polarity in preparation for enucleation. In contrast, β-tubulin was diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm in colchicine-treated samples. The distance between the center of the cell as seen in bright-field and the center of the nucleus stained by Draq5, as measured by ImagestreamX, was decreased in colchicine-treated versus control samples, indicating that inhibition of microtubules results in a significant decrease in erythroblast polarity and inhibition of enucleation in the subsequent step.
The essential role of Rac GTPases in enucleation is exerted at least in part via their regulatory role on actin polymerization. However, we noted that NSC23766 caused a more efficient inhibition of enucleation than the maximum inhibitory effect we could attain with cytochalasin-D (Figure 3E). Active Rac is known to bind to low-density, cholesterol-rich membranes identified by the lipid raft marker GM1-ganglioside.32,33 Such lipid domains have been shown to cluster in the cleavage furrow of dividing cells.16 Accordingly, we found that lipid rafts did merge in the furrow between incipient reticulocyte and pyrenocyte, as visualized by ImagestreamX after labeling of GM1-gangliosides with fluorescent CTB. Inhibition of Rac GTPases decreased clustering of lipid rafts. Moreover, inhibition of lipid raft organization by filipin, through cholesterol depletion, inhibited enucleation. The combination of cytochalasin-D with filipin had a synergistic effect in inhibiting enucleation, equivalent to the inhibition attained by Rac inhibition, suggesting that Rac GTPases may regulate enucleation through a combined effect on F-actin and lipid raft assembly. Lipid rafts are important for membrane trafficking,41,42 and it has been proposed that they may target secretory vesicles to the division site at the time of membrane addition during cytokinesis.43 Further work is needed to explore the potential association of these signaling cholesterol-rich lipid platforms with the clathrin-dependent endocytic vesicles identified to contribute to enucleation by Keerthivasan et al.8
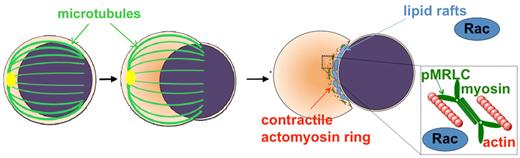
Our data support the concept that erythroblast enucleation is a complex, multistep process that involves numerous cytoskeleton and signaling components and has several similarities with cytokinesis. We propose a coordinated interplay of microtubules at an early stage, with actin and lipid rafts under the regulation of Rac GTPases at a later stage (Figure 7). F-actin interacts with myosin to provide a contractile ring, after phosphorylation of MRLC, probably driven by different signaling pathways. Enucleation is a robust process, necessary for survival, optimal circulation, and oxygen transfer in mammals; therefore, some redundancy may have been developed in the mechanisms involved in vivo, as demonstrated by the up-regulation of Rac3 in Rac1Δ/Δ;Rac2−/− erythroblasts. Further research will be required to identify the detailed molecular events to gain a complete understanding of the enucleation process in erythropoiesis.
Working model of the erythroblast enucleation process. Microtubules assist in the establishment of polarity in orthochromatic erythroblasts. Actin, under the control of Rac GTPases, assembles with myosin to form an actomyosin ring in the “cleavage furrow” between nucleus and incipient reticulocyte. The phosphorylation of MRLC allows the actomyosin complex to contract. Lipid rafts, containing and coordinated by Rac GTPases, coalesce in the cleavage furrow serving possibly to position the actomyosin ring properly and to target secretory vesicles toward creation of new membrane and separation of the nucleus.
Working model of the erythroblast enucleation process. Microtubules assist in the establishment of polarity in orthochromatic erythroblasts. Actin, under the control of Rac GTPases, assembles with myosin to form an actomyosin ring in the “cleavage furrow” between nucleus and incipient reticulocyte. The phosphorylation of MRLC allows the actomyosin complex to contract. Lipid rafts, containing and coordinated by Rac GTPases, coalesce in the cleavage furrow serving possibly to position the actomyosin ring properly and to target secretory vesicles toward creation of new membrane and separation of the nucleus.
There is an Inside Blood commentary on this article in this issue.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Adrienne Cox (University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC) for the generous gift of Rac3-specific antibody, Dr Ivan de Curtis (San Raffaele Scientific Institute, Milano, Italy) for providing Rac3−/− mice, the Flow Cytometry core of Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, and Richard Demarco, Sherree Friend, and Scott Mordecai from Amnis Corporation for expert technical support.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants K08 HL088126, T.A.K.; R01 CA141341, Y.Z.; and 5R01DK062757-11, D.A.W.).
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: T.A.K., D.G.K., and S.P. designed and performed research and analyzed data; J.F.J. and C.E.H. performed research and analyzed data; S.M. performed the statistical analysis; J.A.C., D.A.W., and Y.Z. contributed instrumental suggestions and mentorship on the research design and analysis of data; and all authors wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Theodosia A. Kalfa, Division of Hematology/Oncology, Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, 3333 Burnet Ave, MLC 7015, Cincinnati, OH 45229-3039; e-mail: theodosia.kalfa@cchmc.org.
References
Author notes
D.G.K. and S.P. contributed equally to this study.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal