Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
SPECIAL REPORT
Erdheim-Chester disease: consensus recommendations for evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment in the molecular era
Two articles this week focus on Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD), a rare histiocytosis that mainly affects adults. Clonal somatic mutations primarily involving proteins in the BRAF and MPAK pathways have established ECD as a myeloid neoplasm, with targeted therapies now available for patients. In the first paper, an international panel presents new consensus recommendations for evaluation and treatment of ECD. In the second paper, Pegoraro and colleagues present long-term outcomes of patients with ECD treated with sirolimus, with responses in patients both with and without BRAF mutations.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
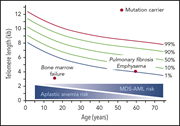
Cancer spectrum and outcomes in the Mendelian short telomere syndromes
Short telomere syndromes are premature aging syndromes associated with a wide range of phenotypes. The authors report on their experience with cancer (predominantly myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia) in persons with these syndromes.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
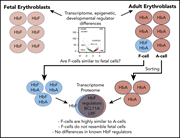
Understanding heterogeneity of fetal hemoglobin induction through comparative analysis of F and A erythroblasts
Increasing fetal hemoglobin expression is an important clinical approach to the treatment of hemoglobinopathies, but the mechanism of upregulation of hemoglobin F (HbF) is still not clear. Khandros et al demonstrated by elegant transcriptional and proteomic profiling studies that F cells and A cells are virtually identical, suggesting that HbF expression and nonexpression reflect isolated transcriptional changes in the β-globin locus.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
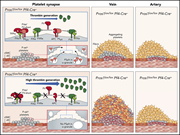
Platelet protein S limits venous but not arterial thrombosis propensity by controlling coagulation in the thrombus
About 2.5% of protein S is synthesized in megakaryocytes and packaged in platelet granules, but its function is not clear. Calzavarini and colleagues demonstrated that platelet protein S is important in limiting venous thrombosis.
TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
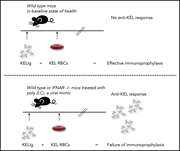
Poly(I:C) causes failure of immunoprophylaxis to red blood cells expressing the KEL glycoprotein in mice
Anti-D therapy prevents hemolytic disease of the newborn in about 98% of Rh-negative women, but the remainder may have breakthrough alloimmunization. The authors demonstrated that inflammation can decrease the efficacy of immunoprophylaxis, suggesting that inflammatory disease or viral infection may lead to failure of Rh immunoglobulin in preventing alloimmunization.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Long-term follow-up of mTOR inhibition for Erdheim-Chester disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Two articles this week focus on Erdheim-Chester disease (ECD), a rare histiocytosis that mainly affects adults. Clonal somatic mutations primarily involving proteins in the BRAF and MPAK pathways have established ECD as a myeloid neoplasm, with targeted therapies now available for patients. In the first paper, an international panel presents new consensus recommendations for evaluation and treatment of ECD. In the second paper, Pegoraro and colleagues present long-term outcomes of patients with ECD treated with sirolimus, with responses in patients both with and without BRAF mutations.
Initiating adjunct low-dose hydroxyurea therapy for stroke prevention in children with SCA during the COVID-19 pandemic
Clinical Trials & Observations
In anticipation of possible blood shortages during the current COVID-19 pandemic, DeBaun proposes rapid initiation of administration of low, fixed doses of hydroxyurea for children with sickle cell anemia (SCA) who receive regular prophylactic transfusions for stroke prevention.
Clonal hematopoiesis evolves from pretreatment clones and stabilizes after end of chemotherapy in patients with MCL
Eskelund et al examined clonal hematopoiesis (CH) in a cohort of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) treated with first-line chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation. In young, good-risk MCL patients, CH after first-line therapy arises almost entirely from preexisting clones, stabilizes after a period of expansion posttransplantation, and does not negatively impact survival.
EBV+ diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation expands the spectrum of breast implant–related lymphomas
Clinical Trials & Observations
Breast implant–associated anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is a rare T-cell lymphoma that arises adjacent to breast implants. The authors describe 3 patients with Epstein-Barr virus–positive (EBV+) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma as a rare subtype of breast implant–related lymphoma.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are the most common cancers of short telomere syndromes. The image shows increased blasts in a marrow aspirate from a patient with a short telomere syndrome who developed hypoplastic AML with MDS changes after lung transplantation for pulmonary fibrosis. See the article by Schratz et al on page 1946.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals



Management of ECD: the era of targeted therapies