Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
Pluripotent stem cell–derived NK cells with high-affinity noncleavable CD16a mediate improved antitumor activity
CD16a, the immunoglobulin G Fc receptor FcγRIIIa, is an important mediator of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Zhu et al engineered induced pluripotent stem cell–derived natural killer (NK) cells with a modified CD16a that provide an off-the-shelf NK cell product with improved antitumor activity for targeting both hematological and solid malignancies.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
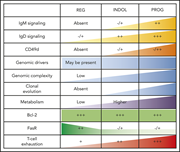
Integrative analysis of spontaneous CLL regression highlights genetic and microenvironmental interdependency in CLL
Clinical Trials & Observations
Spontaneous regression is a rare event in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), estimated to occur in 1 to 2 percent of patients. The authors analyze phenotypic, functional, and genomic features of sequential samples from patients with spontaneous regression, providing insight into the interaction of genetic and microenvironmental features modulating CLL cell proliferation.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
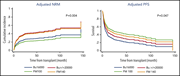
Platelet necrosis mediates ischemic stroke outcome in mice
Ischemia-perfusion injury leads to extension of tissue loss following ischemic stroke. Denorme et al demonstrated in mouse knockout models that platelet cyclophilin D induces platelet necrosis, and necrotic platelet-neutrophil aggregates amplify ischemic injury. Targeting cyclophilin D limits ischemia-reperfusion injury without risking bleeding by inhibiting platelet function.
TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
Lack of the multidrug transporter MRP4/ABCC4 defines the PEL-negative blood group and impairs platelet aggregation
Azouzi et al used combined genomic and proteomic analysis to show that the molecular basis for the rare PEL-negative red cell phenotype is a large deletion of the ABCC4/MRP4 gene, which encodes a widely expressed ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter. ABCC4 negativity alters multidrug resistance and impairs platelet aggregation.
TRANSPLANTATION
Is there an optimal conditioning for older patients with AML receiving allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation?
Brief Report
The authors compare 4 conditioning regimens for older patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, confirming better outcomes with reduced-intensity melphalan-based conditioning.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Erythroferrone lowers hepcidin by sequestering BMP2/6 heterodimer from binding to the BMP type I receptor ALK3
The authors dissect the transcriptional regulatory pathway by which the iron regulatory hormone hepcidin is suppressed by erythroferrone in response to erythropoietin.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Platelet necrosis regulated by cyclophilin D mediates platelet-neutrophil interactions, aggravating ischemic stroke in mice. The image shows platelets (green) and neutrophils (red) interacting and accumulating in the brain after ischemic stroke. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole, blue). See the article by Denorme et al on page 429.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






A dastardly, deadly duo in stroke