Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Recombinant von Willebrand factor prophylaxis in patients with severe von Willebrand disease: phase 3 study results
Clinical Trials & Observations
International guidelines suggest long-term prophylaxis in patients with von Willebrand disease (VWD) and recurrent severe or frequent bleeds. Leebeek and colleagues report on the results of a nonrandomized trial of recombinant von Willebrand factor (rVWF) prophylaxis, finding reductions in spontaneous bleeding rates in patients previously on plasma-derived VWF (pVWF) “on-demand” therapy and similar levels of control over spontaneous bleeding in patients switching from prophylactic pVWF.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
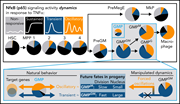
NfκB signaling dynamics and their target genes differ between mouse blood cell types and induce distinct cell behavior
How the fate of offspring from bipotent progenitor cells, such as granulocyte-macrophage progenitors (GMPs), is determined remains contentious. Kull and colleagues elegantly demonstrate using time-lapse imaging and single-cell RNA sequencing that with uniform stimuli, NfκB signaling dynamics vary among GMPs and their progeny. Those destined to become macrophages display oscillating NfκB nuclear-cytoplasmic translocations, and enforced oscillation drives GMPs towards macrophage fate.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
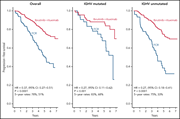
Long-term outcomes for ibrutinib–rituximab and chemoimmunotherapy in CLL: updated results of the E1912 trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Shanafelt et al report on the long-term outcome of the pivotal ECOG-ACRIN E1912 study, detailing the continued superiority of ibrutinib plus rituximab (IR) compared to the prior standard treatment—fludarabine, cyclophosphamide and rituximab (FCR)—for initial treatment of fit patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. The authors demonstrate that IR is superior to FCR irrespective of IGHV mutational state and that outcomes are favorable for the 21% of patients who ceased IR due to adverse events, with the median time to disease progression exceeding 2 years.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
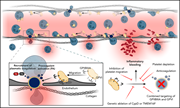
Procoagulant platelet sentinels prevent inflammatory bleeding through GPIIBIIIA and GPVI
Kaiser et al investigated how platelets contribute to vascular integrity during inflammation. They show that single migrating platelets become procoagulant, recruiting the coagulation cascade to prevent pulmonary inflammatory bleeding. This protective action is triggered by encounters with subendothelial collagen and is mediated via glycoprotein (GP) IIBIIIA and GPVI signaling. Blockade of this integrin signaling aggravates inflammatory pulmonary hemorrhage, suggesting relevance to clinical scenarios.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Two SERPINC1 variants affecting N-glycosylation of Asn224 cause severe thrombophilia not detected by functional assays
Antithrombin (AT), encoded by the gene SERPINC1, is a serine protease inhibitor whose deficiency causes a severe form of dominantly inherited thrombophilia. de la Morena-Barrio et al describe 2 novel variants of AT with altered glycosylation profiles that were identified in 4 unrelated families with thrombophilia. This study finds that although these mutations are clearly associated with abnormal thrombosis, carriers are not identified using routine testing for AT deficiency. These discoveries provide insight into the regulation of AT function, and they have implications for the investigation of severe thrombophilia, particularly in families.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Vaccine-induced T-cell responses against SARS-CoV-2 and its Omicron variant in patients with B cell–depleted lymphoma after CART therapy
Clinical Trials & Observations
Patients receiving CD19 CAR T-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory lymphoma experience prolonged and profound B-cell aplasia and hypogammaglobulinemia, placing them at a higher risk for severe COVID-19. Independently, Oh et al and Atanackovic et al demonstrate that despite attenuated humoral response to mRNA-based vaccines, patients demonstrate normal or heightened functional T-cell responses, including antiviral T-cell activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron. Collectively, these data reinforce the importance of COVID-19 vaccination following CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, despite long-term B-cell aplasia.
Enhanced BNT162b2 vaccine-induced cellular immunity in anti-CD19 CAR T cell–treated patients
Clinical Trials & Observations
Patients receiving CD19 CAR T-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory lymphoma experience prolonged and profound B-cell aplasia and hypogammaglobulinemia, placing them at a higher risk for severe COVID-19. Independently, Oh et al and Atanackovic et al demonstrate that despite attenuated humoral response to mRNA-based vaccines, patients demonstrate normal or heightened functional T-cell responses, including antiviral T-cell activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants including Omicron. Collectively, these data reinforce the importance of COVID-19 vaccination following CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, despite long-term B-cell aplasia.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Migrating human platelets (white) on a fibrinogen (green)/albumin/collagen matrix, some of which have turned procoagulant (pink/yellowish) after sensing collagen. See the article by Kaiser et al on page 121.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Incorporating signaling dynamics into fate decision