Abstract
Background
Slow progress has been made in improving induction therapy for patients (pts) with AML. Nucleoside analogues such as cladribine can increase the efficacy of araC by modulating deoxycytidine kinase. Indeed, the addition of cladribine to standard 7+3 chemotherapy has been shown to improve survival in pts with AML (Holowiecki JCO 2012). Additionally, higher doses of araC during induction may have a role in improving outcomes for younger pts (Burnett JCO 2013, Willemze JCO 2013). We conducted a trial to study the efficacy of cladribine combined with higher-dose araC during induction for younger pts with AML.
Methods
The three-drug, induction-consolidation treatment protocol consisted of the combination of cladribine, idarubicin, and araC (CLIA) in pts with AML aged ≤ 65. Two cohorts were enrolled: newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory (R/R). Pts with adequate organ function, a diagnosis of AML (except APL), including secondary- (s-AML) and therapy-related AML (t-AML), and high risk MDS were eligible. Induction consisted of cladribine 5 mg/m2 IV over 30 minutes on days 1-5, followed (3-6 hrs later) by araC 1000 mg/m2 IV on days 1-5, and idarubicin 10 mg/m2 IV days 1-3. Consolidation consisted of up to 5 more cycles of cladribine 5 mg/m2 IV over 30 minutes on days 1-3 with araC 750 mg/m2 IV on days 1-3 and idarubicin 8 mg/m2 IV on days 1-2. One cycle was 4 weeks and up to 2 cycles of induction were allowed. Pts with FLT3-ITD could have sorafenib 400mg PO BID added to CLIA. Pts with FLT3+ disease or presenting WBC count > 100 received prophylactic intrathecal araC at the nadir of their counts during cycle 1. AML mutation screening was performed prior to treatment.
Results
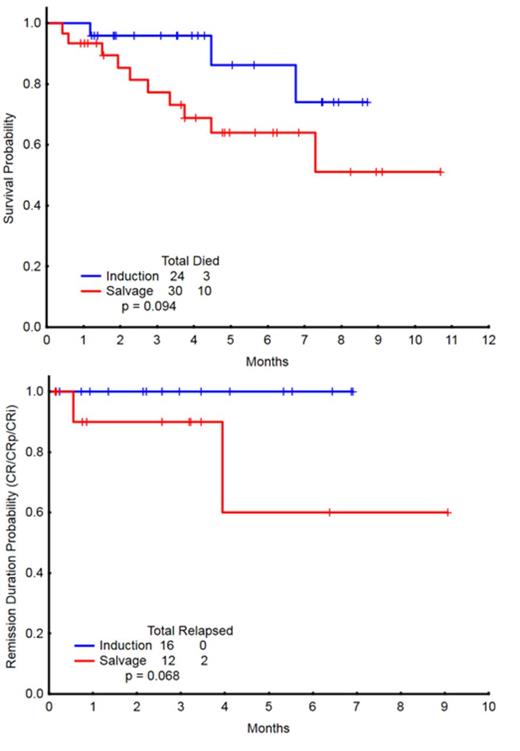
A total of 54 pts were enrolled, with a median age of 51 years (range, 20-65), including 24 pts (44%) in the frontline cohort and 30 (56%) in the R/R cohort. Patient characteristics by cohort are outlined in Table 1. In the frontline cohort, 24 pts, who received a median of 2 (1-6) cycles, were evaluable for response. Sixteen patients achieved CR (67%) after a median of 1 (1-4) cycle. The 4- and 8-week mortality rates were 0% and 4%, respectively. 2/4 (50%) pts with FLT3-ITD, 7/7 (100%) pts with NPM1, and 2/4 (50%) pts with RAS mutations achieved a CR. In the R/R cohort, 29 pts, who received a median of 1 (1-4) cycle, were evaluable for response. Six patients achieved CR (21%), 2 CRp (7%), and 4 CRi (14%), for an overall response rate (ORR) of 41%. A median of 1 (1-2) cycle was required for response. The 4- and 8-week mortality rates were 7% and 10%, respectively. Patients in the R/R cohort had received a median of 2 (1-5) prior therapies. ORR by salvage status is summarized in Table 2. 4/8 (50%) pts with FLT3-ITD, 4/8 (50%) pts with NPM1, and 1/3 (33%) pts with RAS mutations achieved a response (CR/CRp/CRi). With a median follow-up of 6 months (0.9 - 11.9), the 6-month OS estimates were 90% and 67% for the frontline and R/R cohorts, respectively (Figure 1). The 6-month remission durations were 100% and 79% for the frontline and R/R cohorts, respectively (Figure 1).The regimen was well tolerated. The most common ≥ grade 3 non-hematologic adverse events (AEs) were fever/infection (17), tumor lysis syndrome (1), cardiac arrhythmia (1), Rash (1), elevated bilirubin (1) and creatinine (1).
Conclusion
The 3-drug combination, CLIA, is safe and effective in patients with AML. Response rates for patients in the newly-diagnosed, first- and second-salvage settings are particularly interesting and should be explored further in larger studies and compared to current standard regimens.
| Characteristic . | Parameter . | Frontline . | Salvage . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Median (Range) | 52 (30 - 62) | 50 (20 - 65) |
| Diagnosis | AML [N] | 24 | 30 |
| Cytogenetics | Diploid, -Y ; N (%) | 13 (54) | 11 (37) |
| Adverse ; N (%) | 4 (17) | 12 (40) | |
| Misc, other ; N (%) | 6 (25) | 7 (23) | |
| IM/ND ; N (%) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | |
| Bone marrow Blast % | Median (Range) | 50 (8 - 93) | 48 (10 - 94) |
| WBC [x109/L] | Median (Range) | 3.4 (0.7 - 37.9) | 2.9 (0.3 - 75.4) |
| Platelets [x109/L] | Median (Range) | 31 (12 - 584) | 19 (6 - 189) |
| Peripheral Blood Blast % | Median (Range) | 13 (1 - 91) | 48 (3 - 97) |
| Serum Creatinine | Median (Range) | 0.71 (0.4 - 1.3) | 0.8 (0.5 - 1.4) |
| LDH | Median (Range) | 568 (364 - 2449) | 792 (340 - 14159) |
| Characteristic . | Parameter . | Frontline . | Salvage . |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Median (Range) | 52 (30 - 62) | 50 (20 - 65) |
| Diagnosis | AML [N] | 24 | 30 |
| Cytogenetics | Diploid, -Y ; N (%) | 13 (54) | 11 (37) |
| Adverse ; N (%) | 4 (17) | 12 (40) | |
| Misc, other ; N (%) | 6 (25) | 7 (23) | |
| IM/ND ; N (%) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | |
| Bone marrow Blast % | Median (Range) | 50 (8 - 93) | 48 (10 - 94) |
| WBC [x109/L] | Median (Range) | 3.4 (0.7 - 37.9) | 2.9 (0.3 - 75.4) |
| Platelets [x109/L] | Median (Range) | 31 (12 - 584) | 19 (6 - 189) |
| Peripheral Blood Blast % | Median (Range) | 13 (1 - 91) | 48 (3 - 97) |
| Serum Creatinine | Median (Range) | 0.71 (0.4 - 1.3) | 0.8 (0.5 - 1.4) |
| LDH | Median (Range) | 568 (364 - 2449) | 792 (340 - 14159) |
| . | N . | ORR (%) . | CR (%) . | CRp (%) . | CRi (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Salvage | 29 | 12 (41) | 6 (21) | 2 (7) | 4 (14) |
| 1st Salvage | 9 | 6 (67) | 4 (44) | 1 (11) | 1 (11) |
| 2nd Salvage | 8 | 4 (50) | 2 (25) | 0 (0) | 2 (25) |
| 3rd+ Salvage | 12 | 2 (17) | 0 (0) | 1 (8) | 1 (8) |
| . | N . | ORR (%) . | CR (%) . | CRp (%) . | CRi (%) . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Salvage | 29 | 12 (41) | 6 (21) | 2 (7) | 4 (14) |
| 1st Salvage | 9 | 6 (67) | 4 (44) | 1 (11) | 1 (11) |
| 2nd Salvage | 8 | 4 (50) | 2 (25) | 0 (0) | 2 (25) |
| 3rd+ Salvage | 12 | 2 (17) | 0 (0) | 1 (8) | 1 (8) |
Cortes:Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; BerGenBio AS: Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding; Ariad: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astellas: Consultancy, Research Funding; Ambit: Consultancy, Research Funding; Arog: Research Funding; Celator: Research Funding; Jenssen: Consultancy. Pemmaraju:Stemline: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; LFB: Consultancy, Honoraria. DiNardo:Novartis: Research Funding. Konopleva:Novartis: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Stemline: Research Funding; Calithera: Research Funding; Threshold: Research Funding. Wierda:Celgene Corp.: Consultancy; Glaxo-Smith-Kline Inc.: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal