Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a review series on classic myeloproliferative neoplasms
Our knowledge about the biology of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) has exploded in the last 20 years, and this increased knowledge has led to advances in therapy. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series brings readers up to date on our understanding of the natural history of the classical MPNs—polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myelofibrosis—and the approaches to diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment for patients with these conditions.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW SERIES
Genetic basis and molecular profiling in myeloproliferative neoplasms
Our knowledge about the biology of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) has exploded in the last 20 years, and this increased knowledge has led to advances in therapy. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series brings readers up to date on our understanding of the natural history of the classical MPNs—polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myelofibrosis—and the approaches to diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment for patients with these conditions.
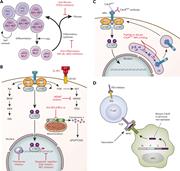
Biology and therapeutic targeting of molecular mechanisms in MPNs
Our knowledge about the biology of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) has exploded in the last 20 years, and this increased knowledge has led to advances in therapy. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series brings readers up to date on our understanding of the natural history of the classical MPNs—polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myelofibrosis—and the approaches to diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment for patients with these conditions.
JAK2V617F allele burden in polycythemia vera: burden of proof
Our knowledge about the biology of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) has exploded in the last 20 years, and this increased knowledge has led to advances in therapy. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series brings readers up to date on our understanding of the natural history of the classical MPNs—polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myelofibrosis—and the approaches to diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment for patients with these conditions.
Essential thrombocythemia: challenges in clinical practice and future prospects
Our knowledge about the biology of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) has exploded in the last 20 years, and this increased knowledge has led to advances in therapy. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series brings readers up to date on our understanding of the natural history of the classical MPNs—polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myelofibrosis—and the approaches to diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment for patients with these conditions.
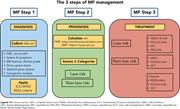
Myelofibrosis
Our knowledge about the biology of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) has exploded in the last 20 years, and this increased knowledge has led to advances in therapy. Introduced by Associate Editor Mario Cazzola, this Review Series brings readers up to date on our understanding of the natural history of the classical MPNs—polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myelofibrosis—and the approaches to diagnosis, prognostication, and treatment for patients with these conditions.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Polatuzumab vedotin in previously untreated DLBCL: an Asia subpopulation analysis from the phase 3 POLARIX trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein for first-time immune tolerance induction: final results of the verITI-8 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Inhibitor development is a major challenge to treatment of severe hemophilia. Malec and colleagues report on the results of the first prospective study of immune tolerance induction (ITI) using a recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein with an extended half-life. The authors found that durable ITI is achieved by a median of 3 months in 10 of 16 patients, setting the stage for further evaluation of this product.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
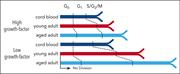
Aging alters the cell cycle control and mitogenic signaling responses of human hematopoietic stem cells
To prevent stem cell exhaustion, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are quiescent and divide rarely; nevertheless, their characteristics change as we age. Hammond et al quantify the proliferation kinetics and cell-cycle progression of single highly purified HSCs isolated from cord blood, young adults, and older healthy donors. The authors show that older HSCs are less sensitive to growth factor stimulation and are more difficult to activate than young HSCs, providing mechanistic insights to explain these changes.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
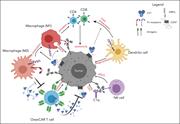
Potentiating antibody-dependent killing of cancers with CAR T cells secreting CD47-SIRPα checkpoint blocker
An immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment is a major barrier to the efficacy of antibody-based therapies. Dacek et al present a novel strategy to overcome this by enhancing the antibody-dependent killing of tumors through additional infusion of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells engineered to locally secrete a small anti-CD47 blocking agent that disrupts antiphagocytic signaling induced by tumor cell CD47 binding to macrophage signal-regulatory protein α. This increases macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis or antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and enables increased tumor cell lysis in a mouse model. Such strategies can now be tested in clinical trials.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
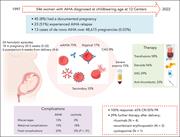
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia during pregnancy and puerperium: an international multicenter experience
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
In this month’s CME article, Fattizzo and colleagues describe the outcomes of the rare problem of autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA) during pregnancy in a multicenter cohort of 33 patients covering 45 pregnancies. The authors report good maternal outcomes despite severe hemolysis and substantial relapse rates but also reveal a higher rate of serious fetal and neonatal complications than seen in controls. These data inform practice when clinicians are faced with AIHA in a pregnant patient.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
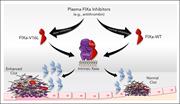
Factor IXa variants resistant to plasma inhibitors enhance clot formation in vivo
Endogenous plasma protein anticoagulants limit clot formation by inhibiting factor IXa activity. Ivanciu and colleagues show that factor-delaying IXa inhibition using novel zymogen-like variants increases the potency of administered factor IX in models of hemophilia B. The authors’ data enhance our understanding of the control of clot formation, and the findings suggest a novel strategy to augment clot formation in hemophilia B.
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
CD61 immunostained bone marrow trephine tissue section showing increased numbers and clustering of megakaryocytes with megakaryocyte pleomorphism; in the context of hypercellular bone marrow and the clinical picture, the morphology favors a diagnosis of iron-deficient polycythemia vera. See the article by Godfrey et al on page 1943.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals







Immune tolerance induction in development
Clinical Trials & Observations