Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
SPECIAL REPORT
Immune effector cell–associated hematotoxicity: EHA/EBMT consensus grading and best practice recommendations
Distinct patterns of cytopenias that are distinguishable from standard chemotherapy-associated cytopenias are seen after chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, displaying a neutropenia predominance and a biphasic nature, often with a prominent recurrence after 30 days or more. Written by Rejeski et al, this Special Report from a panel of Europe-based experts summarizes the data on immune effector cell–associated hematotoxicity (ICAHT) and makes recommendations on predicting, preventing, grading, and managing ICAHT.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Five-year follow-up of KEYNOTE-087: pembrolizumab monotherapy for relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Hodgkin lymphoma cells overexpress programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), and programmed death 1 (PD-1) inhibition with either pembrolizumab or nivolumab is highly active against relapsed, refractory disease. Armand et al describe the long-term outcomes of a 210-patient phase 2 pembrolizumab registration study, finding that in the 58 patients achieving complete response (CR), durable responses continued in half, and allogeneic stem cell transplant may not be required. In patients relapsing from CR, a second course of pembrolizumab frequently reinduced response, further emphasizing the potential of PD-1 blockade in this disease.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
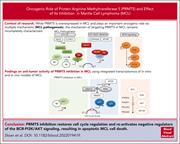
PRMT5 supports multiple oncogenic pathways in mantle cell lymphoma
Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) is an epigenetic regulator of many potentially oncogenic processes and is overexpressed in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Sloan and colleagues used cell lines, primary patient samples, and patient-derived xenografts to reveal that PRMT5 inhibition reverses cell-cycle deregulation, promotes apoptotic cell death, and reactivates negative regulators of B-cell receptor signaling in relapsed MCL. The authors’ data identify potential biomarkers for sensitivity of MCL to PRMT5 inhibition, providing a basis for future clinical trials.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
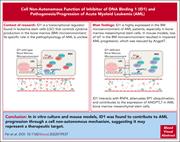
The non-cell-autonomous function of ID1 promotes AML progression via ANGPTL7 from the microenvironment
Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 (ID1) is a transcriptional regulator found in normal and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) stem cells that controls cytokine production in the bone marrow microenvironment (BMM). In a mechanistic study using primary patient samples and murine models, Fei et al identified a regulatory loop in which specific leukemogenic fusion proteins increase BMP6 expression that is then secreted into the BMM, where it upregulates ID1 in mesenchymal stromal cells and increases angiopoietin-like 7 (ANGPTL7) production, which in turn promotes leukemia growth in vitro and in vivo. These findings point to ID1 and the ANGPTL7 axis as therapeutic targets in AML.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
Loss of miR-144/451 alleviates β-thalassemia by stimulating ULK1-mediated autophagy of free α-globin
The locus for microRNA miR-144/451 is highly expressed during terminal erythroid differentiation, and its disruption is detrimental in normal erythroid cells. In contrast, Keith and colleagues show that its disruption is beneficial in β-thalassemia, as increased Unc-51–like autophagy-activating kinase 1 (ULK1) activity degrades the excess-free α-globin, thereby reducing apoptosis triggered by globin imbalance. The authors demonstrate that miR-144/451 loss stimulates ULK1 indirectly by 2 mechanisms, including by inducing erythroblast iron restriction, and they suggest that these pathways are readily amenable to therapeutic manipulation.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Inhibition of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 upregulates protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor-type O truncated (PTPROt) expression (brown) in mantle cell lymphoma patient-derived xenografts infiltrating the spleen. PTPROt is a negative regulator of the B-cell receptor signaling pathway. See the article by Sloan et al on page 887.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





A road map for navigating CAR T hematotoxicity