Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
Potential future direction of measurable residual disease evaluation in multiple myeloma
Mohty and colleagues provide a concise summary of the field of measurable residual disease (MRD) assessment in myeloma. The authors’ expert synthesis of the latest data in both first- and later-line settings identifies key issues that have been resolved and those that remain contentious. They challenge some aspects of the US Food and Drug Administration’s 2020 recommendations for MRD monitoring in myeloma and proffer their guidance on how MRD measurement should be used now and into the future.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Lenalidomide and dexamethasone maintenance with or without ixazomib, tailored by residual disease status in myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Does intensifying or prolonging lenalidomide-based maintenance therapy enhance outcomes for patients with myeloma? In a randomized study, Rosiñol et al found that adding ixazomib, an oral proteosome inhibitor, to lenalidomide and dexamethasone maintenance therapy following autologous stem cell transplantation, does not improve disease control. The trial also prospectively demonstrates that maintenance therapy can be successfully limited to 2 years in patients who reach sustained measurable residual disease negativity.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
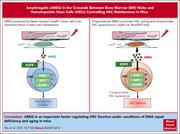
LepR+ niche cell–derived AREG compromises hematopoietic stem cell maintenance under conditions of DNA repair deficiency and aging
Niche-derived paracrine growth factors provide essential support for hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) maintenance. Wu and colleagues reveal that leptin receptor–expressing bone marrow stromal cells in mice upregulate and secrete amphiregulin (AREG) during aging and persistent DNA damage, promoting HSC cycling and a decline in HSC repopulating capacity. These data indicate that AREG has potential as a therapeutic target to improve HSC function.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
CARD11 gain of function upregulates BCL2A1 expression and promotes resistance to targeted therapies combination in B-cell lymphoma
Designing curative regimens for patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) is an important challenge. Combinations targeting Bruton tyrosine kinase, B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL2), and CD20 show promising results, but resistant subclones emerge. Using patient samples, Decombis and colleagues pinpointed CARD11 mutations as drivers of resistance through upregulation of the prosurvival protein BCL2A1. Inhibition of MALT1 reverses this in model systems, suggesting a clinically testable strategy for augmenting targeted therapy regimens for MCL.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
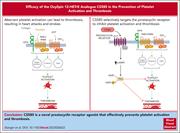
The oxylipin analog CS585 prevents platelet activation and thrombosis through activation of the prostacyclin receptor
Stanger and colleagues report on the synthesis of CS585, a novel analogue of an oxylipin product of 12-lipoxygenase activity in platelets, which acts as a prostacyclin receptor agonist. The authors demonstrate that CS585 selectively inhibits platelet secretion, aggregation, integrin activation, and adhesion and reduces both arterial and venous thrombosis in vivo. This work suggests CS585 has potential as an antiplatelet drug for the prevention of thrombosis without impacting coagulation or bleeding.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BRAFV600E is associated with higher incidence of second cancers in adults with Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Representative image of a CARD11-mutated mantle cell lymphoma tumor mass using a preclinical in ovo model. This patient-derived xenograft is highly vascularized by the chick embryo's chorioallantoic membrane. See the article by Decombis et al on page 1543.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals







Maintain maintenance in multiple myeloma?
Clinical Trials & Observations