Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
Baseline PET as prognostic marker for Hodgkin?
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this issue of Blood, Akhtari et al present a retrospective analysis of baseline positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) in relation to the prognostic significance of the metabolic tumor volume (MTV) in risk classification of early-stage HL.1 These measurements yield estimates of the total tumor burden, which has previously been demonstrated to be one of the most significant prognostic factor in HL.2 A more precise discrimination between low-risk vs high-risk HL using baseline PET-CT characteristics could be clinically useful and might inform treatment decisions.
LEDGF: a leukemia-specific target
In this issue of Blood, El Ashkar et al1 reveal that the lens epithelium-derived growth factor (LEDGF) protein is a key therapeutic target by showing that it is essential for leukemia, but not normal hematopoiesis. Such context-dependent information is important for the development of new targeted therapies.
Off-the-shelf TCR for graft-versus-leukemia without GVHD
In this issue of Blood, Dossa et al report the engineering of T-cell receptor (TCR) transgenic T cells against the human minor histocompatibility antigen HA-1 for the prevention or treatment of leukemia relapse after allogeneic stem cell transplantation.1
CD19 CAR-T therapy and sepsis: dancing with the devil
In this issue of Blood, Hill and colleagues characterized infectious complications in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies after treatment with CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor–modified T (CAR-T) cells in a phase 1/2 study.1 This is the first study that systemically analyzed infectious events in CAR–T-cell–treated patients.
AML: exposed and exploited?
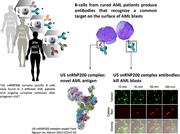
In this issue of Blood, Gillissen and colleagues characterize donor-derived cytotoxic antibodies, isolated from allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HSCT) patients with acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) in sustained remission, that targeted the spliceosome U5 snRNP200 complex expressed on the cell membrane of AML blasts. Mechanistically, in vitro antibody-dependent cytotoxicity did not cause leukemia cell apoptosis, but rather destabilization of the cell membrane cytoskeleton and subsequent pore formation, resulting in cellular swelling and extravasation of intracellular contents (oncosis). In addition, in vivo reduction in AML burden using a U5 snRNP200–specific antibody was demonstrated in a murine SCID xenograft model. Collectively, the authors’ work suggests a potential role for donor-derived antibodies in mediating graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) activity following allogeneic HSCT.1
The delectability of platelets to a phagocyte
In this issue of Blood, Saris et al show that some HLA antigens, namely, B8, B12, and B35, vary in expression on the platelets of some individuals and that this is a constant variant in these people.1
REVIEW SERIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Reclassifying patients with early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma based on functional radiographic markers at presentation
Clinical Trials & Observations
Publisher's Note: There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
Development of T-cell immunotherapy for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation recipients at risk of leukemia relapse
Clinical Trials & Observations
Publisher's Note: There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
Infectious complications of CD19-targeted chimeric antigen receptor–modified T-cell immunotherapy
Clinical Trials & Observations
Publisher's Note: There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
AML-specific cytotoxic antibodies in patients with durable graft-versus-leukemia responses
Publisher's Note: There is a Blood Commentary on this article in this issue.
TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
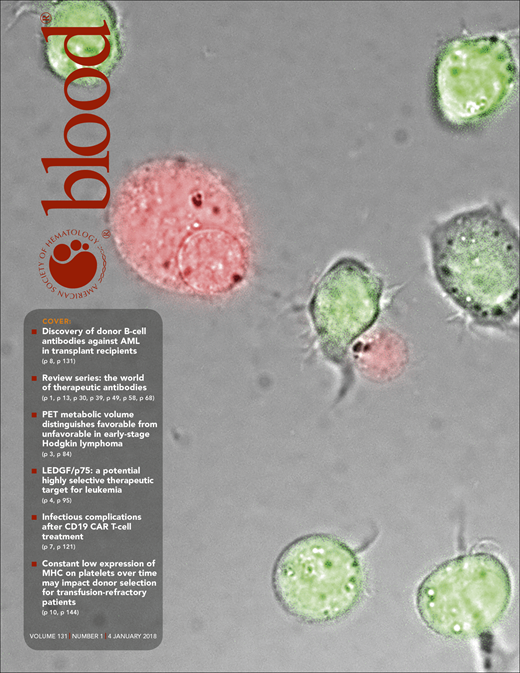
Donor-derived antibodies from patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in durable remission after allogeneic stem cell transplantation are cytotoxic to blasts in the absence of effector cells or complement. The image shows a live-cell visualization of antibody-mediated cytotoxicity of the AML cell line THP-1. Live cells contain a green fluorescent dye in their lumen, whereas dead cells lose the green dye and become red fluorescent (a wide-field image is superimposed for clarity). See the article by Gillissen et al on page 131.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals