Issue Archive
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
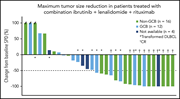
Ibrutinib and lenalidomide: when 1+1 = >2
Clinical Trials & Observations
Ibrutinib plus lenalidomide and rituximab has promising activity in relapsed/refractory non–germinal center B-cell–like DLBCL
Clinical Trials & Observations
The investigators report on the promising activity of a phase 1b trial of the targeted therapy triplet rituximab, ibrutinib, and lenalidomide in patients with relapsed non–germinal center diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
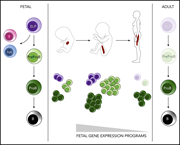
Origins of the human B-cell lineage
Discovery of a CD10-negative B-progenitor in human fetal life identifies unique ontogeny-related developmental programs
By comparing fetal and adult B-lymphopoiesis, the authors identify a prepro–B-cell subset in humans that marks the origin of B-cell lineage commitment in utero.
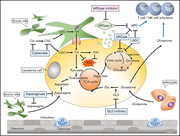
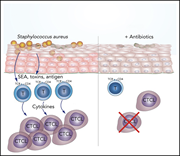
Antibiotics can improve CTCL
Antibiotics inhibit tumor and disease activity in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
This paper reports that aggressive antibiotic treatment inhibits disease activity and lymphocyte proliferation in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). The study offers important evidence for a link between bacterial infection, activation of the immune system, and CTCL progression.
PLENARY PAPER
Effect of donor, component, and recipient characteristics on hemoglobin increments following red blood cell transfusion
This study furnishes evidence that both confirms and refutes a long-standing maxim that a one-unit transfusion of red blood cells should yield a posttransfusion hemoglobin increment of 1 g/dL.
REVIEW ARTICLE
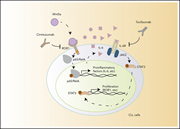
Amino acid metabolism in hematologic malignancies and the era of targeted therapy
The authors review the latest knowledge of amino acid metabolism in hematologic malignancies and the clinical relevance and potential of amino acid therapeutic targeting.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Ibrutinib plus lenalidomide and rituximab has promising activity in relapsed/refractory non–germinal center B-cell–like DLBCL
Clinical Trials & Observations
The investigators report on the promising activity of a phase 1b trial of the targeted therapy triplet rituximab, ibrutinib, and lenalidomide in patients with relapsed non–germinal center diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
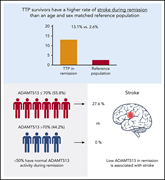
Reduced ADAMTS13 activity during TTP remission is associated with stroke in TTP survivors
Clinical Trials & Observations
This study shows that the increased occurrence of stroke in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) during remission is associated with low ADAMTS13 values.
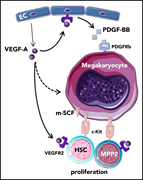
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
Discovery of a CD10-negative B-progenitor in human fetal life identifies unique ontogeny-related developmental programs
By comparing fetal and adult B-lymphopoiesis, the authors identify a prepro–B-cell subset in humans that marks the origin of B-cell lineage commitment in utero.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Antibiotics inhibit tumor and disease activity in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
This paper reports that aggressive antibiotic treatment inhibits disease activity and lymphocyte proliferation in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). The study offers important evidence for a link between bacterial infection, activation of the immune system, and CTCL progression.
Cirmtuzumab blocks Wnt5a/ROR1 stimulation of NF-κB to repress autocrine STAT3 activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
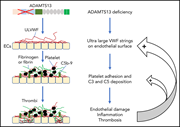
Synergistic effects of ADAMTS13 deficiency and complement activation in pathogenesis of thrombotic microangiopathy
This study in mice suggests a synergistic role of ADAMTS13 deficiency and complement “hyperactivatability” in the pathogenesis of thrombotic microangiopathy.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Adjuvant low-dose rituximab and plasma exchange for acquired TTP
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Weak tyrosine-phosphorylated STAT3 staining (brown) in keratinocytes and lymphocytes in skin lesions from cutaneous T-cell lymphoma following aggressive antibiotic treatment, indicating that eradication of Staphylococcus aureus is associated with inhibition of tumor and disease activity. See the article by Lindahl et al on page 1072.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon AdvertisingAdvertising
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals


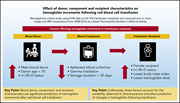

Effect of donor, component, and recipient characteristics on hemoglobin increments following red blood cell transfusion
This study furnishes evidence that both confirms and refutes a long-standing maxim that a one-unit transfusion of red blood cells should yield a posttransfusion hemoglobin increment of 1 g/dL.