Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
SPECIAL REPORT
Primary cutaneous lymphoma: recommendations for clinical trial design and staging update from the ISCL, USCLC, and EORTC
Clinical Trials & Observations
Olsen and colleagues present updated recommendations from a large international consortium for the clinical trial design and staging of primary cutaneous lymphoma. They propose that this will provide a basis for standardized methodology for collaborative clinical investigations of new therapies.
HOW I TREAT
How I treat immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after hospital discharge
Cataland and colleagues describe a clinical approach to the follow-up of patients with immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (iTTP) following acute hospitalization. The authors provide valuable recommendations for frequency of laboratory testing, timing of intervention with further immunosuppression, and monitoring for the known complications of iTTP.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
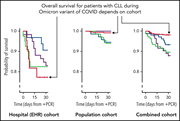
Patients with CLL have a lower risk of death from COVID-19 in the Omicron era
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Niemann and colleagues used the Danish clinical registry to provide a longitudinal view of the outcomes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who become infected with COVID-19. Overall, outcomes have improved during the era of the Omicron variants, with 30-day mortality across all patients with CLL declining from 23% to 2%. However, patients requiring hospital care continue to have 30-day mortality as high as 23%, suggesting that this population should be considered for close monitoring and preemptive antiviral therapy.
GENE THERAPY
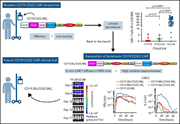
CD19/22 CAR T cells in children and young adults with B-ALL: phase 1 results and development of a novel bicistronic CAR
Clinical Trials & Observations
Shalabi et al report on a phase 1 trial of a bivalent chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell product targeting both CD19 and CD22, including some patients whose CAR T-cell therapy had failed. The complete response rate was 60% in all patients and 71% in those without prior CAR T-cell therapy. However, expansion and persistence of the CAR T cells are limited, and the investigators developed a new vector based on laboratory studies that may optimize the persistence of the bivalent vector in the future. Until then, proceeding to stem cell transplantation in responding patients is advised.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
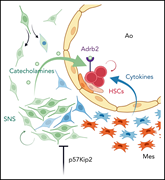
p57Kip2 regulates embryonic blood stem cells by controlling sympathoadrenal progenitor expansion
Kapeni et al report that the cell-cycle inhibitor p57Kip2/Cdkn1c regulates murine embryonic stem cell numbers by modulating the sympathetic nervous system cell pool and decreasing hematopoietic stem cell (HSC)-supportive catecholamine secretion. This is in contrast to its role in supporting adult mesenchymal cell production to maintain adult HSCs.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
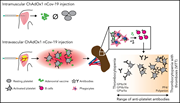
Thrombocytopenia and splenic platelet-directed immune responses after IV ChAdOx1 nCov-19 administration
Nicolai and colleagues studied vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) and immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) following adenovirus-based COVID-19 vaccine administration. They isolated and characterized antiplatelet antibodies from 27 patients with VITT and 26 patients with isolated thrombocytopenia following ChAdOx1 n-Cov-19 vaccination and modeled antibody formation in mice. Intravenous rather than intramuscular injection triggers platelet-adenovirus aggregates that are phagocytosed by splenic macrophages, leading to B-cell responses, suggesting that avoiding intravenous administration could obviate this complication.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
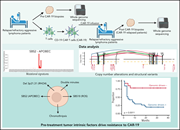
Whole-genome sequencing reveals complex genomic features underlying anti-CD19 CAR T-cell treatment failures in lymphoma
Two articles investigate tumor characteristics that predict the failure of CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in the treatment of large B-cell lymphoma. In the first article, Jain et al report on the results of whole-genome sequencing of 51 tumor samples; they confirm that pretreatment complex structural variants, APOBEC mutational signature, reactive oxygen species-related genomic changes, and recurrent 3p21.31 chromosomal deletion predict CAR T failure. In the second article, Cherng et al sequenced cell-free DNA from the blood of 122 CAR T-cell recipients evaluating for DNA copy number alterations (CNAs). High level CNA predicts poor outcomes, and they identified specific CNAs that are frequent in these patients. Using these observations, they built a risk model to stratify patients. Such studies promise to improve prognostic predictions for these patients and define a population of those requiring additional or alternative therapy.
Risk assessment with low-pass whole-genome sequencing of cell-free DNA before CD19 CAR T-cell therapy for large B-cell lymphoma
Two articles investigate tumor characteristics that predict the failure of CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells in the treatment of large B-cell lymphoma. In the first article, Jain et al report on the results of whole-genome sequencing of 51 tumor samples; they confirm that pretreatment complex structural variants, APOBEC mutational signature, reactive oxygen species-related genomic changes, and recurrent 3p21.31 chromosomal deletion predict CAR T failure. In the second article, Cherng et al sequenced cell-free DNA from the blood of 122 CAR T-cell recipients evaluating for DNA copy number alterations (CNAs). High level CNA predicts poor outcomes, and they identified specific CNAs that are frequent in these patients. Using these observations, they built a risk model to stratify patients. Such studies promise to improve prognostic predictions for these patients and define a population of those requiring additional or alternative therapy.
LETTER TO BLOOD
An LSC-based MRD assay to complement the traditional MFC method for prediction of AML relapse: a prospective study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Li et al delineate a novel technique for assessing measurable residual disease (MRD) by the assessment of isolated leukemia stem cells (LSCs). They report that assessment of MRD in LSCs provides a better prediction of outcome than standard multiparameter flow cytometry.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunohistochemistry staining on an E11 mouse embryo section in the area of the dorsal aorta, showing onset of p57Kip2 expression (red) as Sox10+ neural crest cells (green) commit to the sympathoadrenal fate. These cells regulate stem cell numbers as part of the aorta-gonads-mesonephros region hematopoietic stem cell niche. See the article by Kapeni et al on page 464.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






CLL and COVID-19: light at the end of the tunnel?
Clinical Trials & Observations