Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
Richter syndrome: novel insights into the biology of transformation
The transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to aggressive lymphoma, or Richter syndrome, has not been well-characterized. Parry and colleagues review how computational methods and extended genetic, transcriptomic, and epigenetic analysis have provided greater insight into the biology and clonal origins of Richter syndrome.
GENE THERAPY
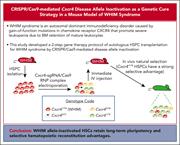
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Cxcr4 disease allele inactivation for gene therapy in a mouse model of WHIM syndrome
Gao et al report on a novel gene therapy approach to WHIM (warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, recurrent infections, and myelokathexis) syndrome, an immunodeficiency disorder caused by gain-of-function mutations in CXCR4 leading to bone marrow retention of mature leukocytes. Citing a spontaneous cure of WHIM syndrome reported to arise from spontaneous deletion of the mutant allele in a hematopoietic stem cell, the authors report that random inactivation of CXCR4 by CRISPR/Cas9 editing allowed outgrowth of WHIM allele–inactivated cells and selective marrow reconstitution in a mouse model. If successful in clinical trials, this could provide a general approach for autosomal dominant gain-of-function diseases.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
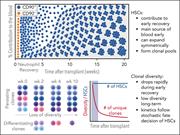
Stochastic fate decisions of HSCs after transplantation: early contribution, symmetric expansion, and pool formation
Radtke and colleagues challenge the dogma that hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) are rare, infrequently dividing, and do not contribute to early mature cell production following hematopoietic cell transplantation. The authors demonstrate using high-density clonal tracking that HSC clones appear early after transplant and are the main source of early blood cell production. Furthermore, the number of individual HSC clones rapidly declines with time, with long-term reconstitution resulting from a smaller number of expanding HSC clones.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Oncogenic role and target properties of the lysine-specific demethylase KDM1A in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Epigenetic changes in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are thought to be key contributors to disease progression, but what regulates CLL epigenetics is not well understood. Jiang and colleagues demonstrate that the lysine-specific histone demethylase KDM1A is a central player in epigenetic regulation, and elevated KDM1A correlates with aggressive disease and adverse outcomes in CLL. Knockdown of KDM1A expression in a murine CLL model reduced CLL survival and synergized with other anti-CLL therapies, suggesting it might be a novel target for improved CLL therapy.
Preclinical characterization of pirtobrutinib, a highly selective, noncovalent (reversible) BTK inhibitor
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
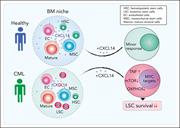
Characterization of the bone marrow niche in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia identifies CXCL14 as a new therapeutic option
A noncanonical enzymatic function of PIWIL4 maintains genomic integrity and leukemic growth in AML
RNA-binding proteins facilitate messenger RNA metabolism and prevent or resolve DNA:RNA hybrids or R-loops. Bamezai and colleagues report that PIWIL4, a germ cell–associated RNA binding protein, is overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and is essential for leukemic stem cell function but not for normal stem cells. The authors show that PIWIL4 resolves R-loops in AML cells, preventing DNA damage and replication stress. PIWIL4 depletion downregulates these processes, impairs AML stem cell function, and increases sensitivity to therapeutic agents, suggesting that this pathway may be a target for therapy.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
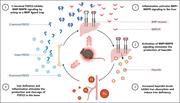
Bone-derived C-terminal FGF23 cleaved peptides increase iron availability in acute inflammation
Inflammation is associated with increased hepcidin expression, which leads to functional iron deficiency. Inflammation also stimulates expression of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), although much of FGF23 is cleaved and does not function as an intact hormone. Courbon et al link these 2 observations by demonstrating that FGF23 fragments bind to bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) receptors, blocking BMP induction of hepcidin expression. In this way, FGF23 fragments act as a negative feedback loop to moderate the induction of hepcidin.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunohistochemical staining for myeloperoxidase showing the accumulation of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) blasts in the bone marrow of a mouse transplanted with ckit+ MLL-AF9+ primary AML cells. Loss of PIWIL4 expression in ckit+ MLL-AF9+ AML diminishes leukemia stem cell frequency and delays AML progression. See the article by Bamezai et al on page 90.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals







Gene silencing on a WHIM