Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
Prevalence and significance of DDX41 gene variants in the general population
Clinical Trials & Observations
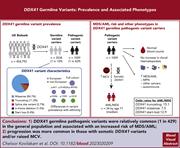
Germline pathogenic variants (GPVs) in the DEAD-box RNA helicase 41 gene (DDX41) are an inheritable risk factor for myelodysplasia and acute myeloid leukemia (MDS/AML) in adults. In this Plenary Paper, Cheloor Kovilakam and colleagues report on a comprehensive analysis of >450,000 adults in the United Kingdom Biobank, assessing the epidemiologic characteristics, clinical features, and malignancy risk associated with various DDX41 GPVs. They are common (1 in 450 people), and while they increase the probability of MDS/AML occurring by 12-fold, the absolute risk remains low at 3.21%. These data inform counselling for patients and their families, including potential related hematopoietic stem cell donors.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Single-cell genomics in acquired bone marrow failure syndromes
Bone marrow failure (BMF) syndromes include aplastic anemia, hypoplastic myelodysplastic syndrome, clonal T-cell–mediated hypoplasia, and monogenic constitutional disorders. Wu and Young review recent studies of BMF using single-cell genomic analyses. The authors identify advances and challenges in applying this technology and set the scene for its future use in dissecting the pathophysiology of BMF syndromes and therapeutic effects.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Birtamimab plus standard of care in light-chain amyloidosis: the phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled VITAL trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Birtamimab is a humanized antibody designed to eliminate the toxic light chain oligomers and deposits in amyloidosis. In the VITAL trial, it was combined with bortezomib-based chemotherapy, but the trial was ceased prematurely after an interim analysis suggested futility. Gertz et al report on a post hoc analysis revealing reduced all-cause mortality at 9 months for the subset of patients with Mayo stage IV cardiac light chain amyloidosis receiving birtamimab compared to the placebo group.
Birtamimab: a new amyloidosis treatment?
Clinical Trials & Observations
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
MYD88L265P augments proximal B-cell receptor signaling in large B-cell lymphomas via an interaction with DOCK8
One molecular subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) with an inferior prognosis carries concurrent alterations of the toll-like receptor and B-cell receptor (BCR) pathway members, MYD88L265P and CD79BY196F. Mandato and colleagues used genetically engineered cell lines to reveal that MYD88L265P selectively increases proximal BCR signaling and survival via the adaptor protein dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8). These data likely explain the increased sensitivity of MYD88L265P/CD79BY196F DLBCLs to Bruton tyrosine kinase blockade in patients.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
Cryo-EM structures of human arachidonate 12S-lipoxygenase bound to endogenous and exogenous inhibitors
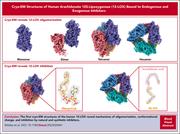
The enzyme human arachidonate 12S-lipoxygenase (12-LOX) is expressed in platelets where it promotes activation of αIIbβ3, glycoprotein VI, and protease-activated receptor 4. Mobbs et al report on high resolution structures of 12-LOX obtained by cryogenic electron microscopy. The authors elucidate oligomeric states, conformational plasticity, and binding interactions, providing new knowledge that may accelerate the development of antithrombotic structure–based inhibitors.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Neurologic toxicities following adoptive immunotherapy with BCMA-directed CAR T cells
Clinical Trials & Observations
In 2 complementary Letters to Blood, Karschnia et al and Graham et al provide new insights into the neurological toxicities that are observed with B-cell maturation antigen–directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell treatment for multiple myeloma, identifying a frequency of immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) that exceeds 40%. Severe ICANS is identified in 8% of patients in this real-world series. Outcomes were generally favorable, although the authors describe rare, late Parkinsonism-like hypokinetic movement disorders (also known as movement and neurocognitive toxicities) post-ICANS in 2 patients.
Chemotherapy-induced reversal of ciltacabtagene autoleucel–associated movement and neurocognitive toxicity
Clinical Trials & Observations
In 2 complementary Letters to Blood, Karschnia et al and Graham et al provide new insights into the neurological toxicities that are observed with B-cell maturation antigen–directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell treatment for multiple myeloma, identifying a frequency of immune effector cell–associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) that exceeds 40%. Severe ICANS is identified in 8% of patients in this real-world series. Outcomes were generally favorable, although the authors describe rare, late Parkinsonism-like hypokinetic movement disorders (also known as movement and neurocognitive toxicities) post-ICANS in 2 patients.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Merged confocal image of DOCK8:MYD88 proximity ligation assay signals (green) in MYD88L265P/CD79BY196F diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. In these genetically defined tumors, MYD88L265P increases proximal B-cell receptor signaling and survival via DOCK8. Stains: nuclei, DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue); cytoplasm, BioTracker 555 (red). See the article by Mandato et al on page 1219.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






DDX41: here, there…and everywhere