Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
CAR T cells as a second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: a paradigm shift?
Clinical Trials & Observations
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is standard for patients with large B-cell lymphoma following failure of autologous stem cell transplant (SCT). Now, 3 prospective randomized trials provide comparisons of CAR T cells with SCT as second-line therapy. Westin and Sehn review the design, key findings, and caveats for each trial and provide an insightful summary of how CAR T-cell therapy is changing our standard approach to patients when first-line therapy is not curative.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Bortezomib and high-dose melphalan conditioning regimen in frontline multiple myeloma: an IFM randomized phase 3 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Roussel and colleagues report on a large, highly anticipated randomized trial of adding bortezomib to melphalan as autologous stem cell transplantation conditioning for patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. While the phase 2 data had suggested improved efficacy, no differences were observed in the rates of complete remission, minimal residual disease negativity, progression-free survival or overall survival. These data reaffirm high-dose melphalan as the standard conditioning regimen in myeloma.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
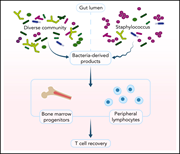
Early intestinal microbial features are associated with CD4 T-cell recovery after allogeneic hematopoietic transplant
Clinical Trials & Observations
Perturbations in the gastrointestinal microflora are common following allogeneic stem cell transplants (SCTs). Miltiadous et al report on the association between early posttransplant gut microbiome and immune cell reconstitution in 894 patients post-SCT, finding fecal microbial diversity to be predictive of CD4+ T-cell counts at 3 months. Higher relative abundance of Staphylococcus in the early post-HCT period independently predicts worse CD4+ T-cell recovery, suggesting a new modifiable factor for optimization of immune recovery.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
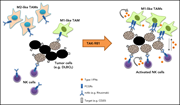
The SUMOylation inhibitor subasumstat potentiates rituximab activity by IFN1-dependent macrophage and NK cell stimulation
Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies are a mainstay of therapy for B-cell lymphomas, but efficacy is not uniform and resistance may develop. Nakamura and colleagues revealed that the SUMOylation inhibitor subasumstat is able to augment the ability of rituximab to evoke macrophage phagocytosis and natural killer cell cytotoxicity, thereby delivering improved antitumor activity in murine lymphoma models. These data highlight the potential for small molecule drugs to potentiate existing monoclonal antibody-based regimens.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
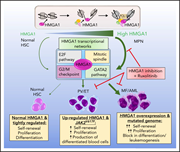
HMGA1 chromatin regulators induce transcriptional networks involved in GATA2 and proliferation during MPN progression
A major cause of mortality for patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) is progression to myelofibrosis and acute leukemia. Li et al identified that High Mobility Group A1 (HMGA1) acts as an epigenetic switch during MPN progression and that HMGA1 deficiency prevents myelofibrosis and enhances sensitivity to ruxolitinib, prolonging survival in murine models of JAK2 mutant secondary acute myeloid leukemia. These data suggest HMGA1 is a therapeutic target to treat or prevent progression.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
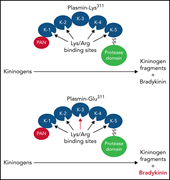
A mechanism for hereditary angioedema caused by a lysine 311–to–glutamic acid substitution in plasminogen
Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a genetic condition causing episodic bradykinin-induced swelling of skin and mucosal membranes. Dickeson and colleagues revealed a new mechanism for HAE in patients whose disease is associated with a lysine-311 to glutamic acid substitution in plasminogen. The authors' detailed biochemical studies linked fibrinolysis and bradykinin formation in this condition.
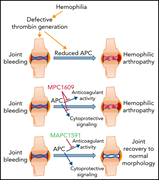
Selective inhibition of activated protein C anticoagulant activity protects against hemophilic arthropathy in mice
Arthropathy is the most common clinical sequela of bleeding in severe hemophilia. Magisetty et al report that an antibody that selectively inhibits the anticoagulant activity of activated protein C (APC), but not its anti-inflammatory activity, prevents bleeding-induced arthropathy in a mouse model, whereas an antibody that inhibits both APC functions does not. These data argue for the clinical development of anti-APC antibodies with highly selective actions for prevention of hemophilic arthropathy.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Myelofibrosis in transgenic mice overexpressing JAK2V617F in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. The marrow is characterized by megakaryocyte hyperplasia, marked fibrosis, and osteosclerosis, all of which closely model human myelofibrosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Hmga1 heterozygous deficiency prevents progression to myelofibrosis. See the article by Li et al on page 2797.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






A gut-graft axis mediated by microbiota