Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
CAR T-cell therapy in multiple myeloma: mission accomplished?
In this Blood Spotlight, Rasche and colleagues summarize recent progress in cellular immunotherapy for multiple myeloma using anti–B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. The authors address the clinically critical issues of patient selection, sequencing with respect to anti-BCMA T-cell–engaging antibody therapy, toxicity, and the high probability of relapse. Given the potency of these treatments, they emphasize the importance of increasing patient access and exploring use in early lines of therapy.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
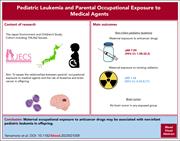
Pediatric leukemia and maternal occupational exposure to anticancer drugs: the Japan Environment and Children’s Study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Using a large birth cohort with data collected prospectively from the Japan Environment and Children’s Study, Yamamoto and colleagues investigated the associations between parental occupational exposure to anticancer agents, anesthetics, or ionizing radiation and childhood cancer in their offspring. The authors report a nearly eightfold increased risk of leukemia among children aged 1 to 3 years whose mothers were occupationally exposed to anticancer agents during pregnancy but no increased risk from radiation or anesthetics. These data have important implications for occupational safety.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Clonal evolution dissection reveals that a high MSI2 level promotes chemoresistance in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
While treatment outcomes in pediatric T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) are improving, resistance and relapse remain the major barriers to a cure. Zhang et al utilized bulk and single-cell sequencing analyses of paired diagnosis-relapse patient samples to describe 2 different patterns of leukemia clonal evolution with treatment. The authors’ work also identified the RNA-binding protein Musashi-2 (MSI2) as a key player in T-ALL therapy–induced clonal evolution and its resistance to chemotherapy.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Molecular MRD is strongly prognostic in patients with NPM1-mutated AML receiving venetoclax-based nonintensive therapy
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Measurable residual disease (MRD) monitoring in patients with nucleophosmin (NPM1)-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) undergoing intensive chemotherapy has established clinical utility. Othman and colleagues now show the utility of MRD monitoring of patients with NPM1-mutated AML treated with venetoclax-based regimens. On multivariable analysis, the authors report that bone marrow MRD negativity at the end of 4 cycles of treatment was associated with improved survival and durable treatment-free remission.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
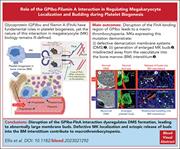
GPIbα–filamin A interaction regulates megakaryocyte localization and budding during platelet biogenesis
Macrothrombocytopenia is a disease characterized by low platelet count but with enlarged platelet size. By studying platelet formation in a murine model of human macrothrombocytopenia caused by a specific mutation in glycoprotein Ibα (GPIbα) that abolishes interaction with the cytoskeletal linker protein filamin A, Ellis et al discovered that the macrothrombocytopenia phenotype is due to aberrant megakaryocyte membrane budding but with unaffected proplatelet formation. These data highlight the importance of the GPIbα-cytoskeleton interaction in determining platelet size and increase the evidence that platelets do arise through megakaryocyte membrane budding.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
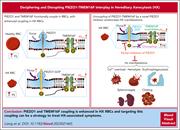
Deciphering and disrupting PIEZO1-TMEM16F interplay in hereditary xerocytosis
Hereditary xerocytosis (HX) is a red cell disorder caused by a gain-of-function mutation in PIEZO1, which manifests clinically as anemia, splenomegaly, and postsplenectomy thrombosis. Liang et al discovered that the elevated exposure of cell surface phosphatidylserine (PS) that underpins the clinical phenotype is dependent upon TMEM16F, a calcium-activated phospholipid scramblase in the red cell membrane whose activity is enhanced by PIEZO1 in HX. The antigout drug benzbromarone blocks PIEZO1 and decouples PIEZO1-TMEM16F, preventing PS exposure, echinocytosis, and hemolysis in HX erythrocytes, suggesting a potential therapy for testing in clinical trials.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Characterization of reverse-engineered anti-PF4 stereotypic antibodies derived from serum of patients with VITT
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A 3-dimensional Airyscan image showing branched intrapulmonary proplatelets from GPIbαFW mice, with proplatelets in green (CD41), endothelium in red (laminin), and large intravascular platelets. See the article by Ellis et al on page 342.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






Anticancer drug exposure in utero and leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations