Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
New frameworks for hematopoiesis derived from single-cell genomics
How the development of multiple lineages of mature blood cells from stem cells is regulated remains a fundamental question in hematology research, with a new understanding often revealed through advances in technology. Safina and van Galen provide an insightful review on how single-cell genomics is allowing new ground to be broken on this enduring question, enabling better resolution of stem- and progenitor-cell plasticity during steady-state and stressed hematopoiesis.
HOW I TREAT
How I diagnose and treat organizing pneumonia in hematopoietic cell transplant recipients
Organizing pneumonia (OP) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT OP) is a major cause of severe morbidity and mortality and is usually associated with graft-versus-host disease. However, improving outcomes has been hindered by the absence of a uniform definition or validated diagnostic criteria and by generalization from the presentation and clinical course of non-HCT OP. Lai et al examine 4 informative cases that illustrate the challenges of this disease and outline their practical approach to clinical management, emphasizing multidisciplinary input.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
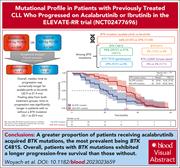
Mutational profile in previously treated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia progression on acalabrutinib or ibrutinib
Clinical Trials & Observations
Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKis) have revolutionized therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), with ibrutinib leading the way. With other BTKis now available, it is not known whether the almost inevitable resistance that emerges with long-term continuous therapy is driven by the same mutations as observed with ibrutinib. Woyach and colleagues report clonal evolution data for patients progressing after a median of 3.5 years in a prospective randomized trial of ibrutinib and acalabrutinib, finding that the BTK C481S mutation is common with either therapy, while PLCG2 mutations are more prevalent with ibrutinib, and some uncommon mutations are associated with only 1 of the BTKis.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
HA-1–targeted T-cell receptor T-cell therapy for recurrent leukemia after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Clinical Trials & Observations
The holy grail of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) is the generation of graft-versus-leukemia (malignancy) effect without graft-versus-host-disease. Krakow et al explored the use of T cells transduced with T-cell receptors targeting the hematopoiesis-specific minor histocompatibility antigen HA-1 to control leukemia following HCT in HA-1–mismatched patients. In this small phase 1 clinical trial, the transduced T cells expanded and persisted in vivo, and safety and feasibility were demonstrated with preliminary evidence of durable responses in some patients.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Randomized study of induction with bendamustine-rituximab ± bortezomib and maintenance with rituximab ± lenalidomide for MCL
Clinical Trials & Observations
While novel agents that do not damage DNA are changing the landscape for treatment of relapsed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), chemoimmunotherapy remains the standard first-line therapy for most patients. Smith and colleagues report on mature results of a 4-arm randomized trial exploring whether the addition of bortezomib during induction and/or lenalidomide in maintenance improves outcomes over a bendamustine-rituximab plus rituximab (BR-R) maintenance regimen. The results indicate no prolongation of progression-free survival (PFS) and increased toxicity with the augmented regimens, while the median PFS is 5.5 years with BR-R, highlighting its acceptability as a standard of care.
Rapid tumor DNA analysis of cerebrospinal fluid accelerates treatment of central nervous system lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
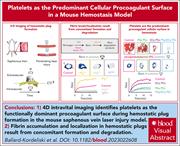
4D intravital imaging studies identify platelets as the predominant cellular procoagulant surface in a mouse hemostasis model
Using 4-dimensional intravital imaging, Ballard-Kordeliski and colleagues explored the intricate balance of procoagulant and fibrinolytic activities during hemostasis in vivo. In a murine hemostasis model, the authors showed that while both endothelial cells and platelets exposed phosphatidylserine at sites of vascular injury, platelet procoagulant activity was most critical for fibrin formation within the nascent hemostatic plug. They further showed that rapid fibrinolysis prevented fibrin accumulation from spreading along the vessel wall. These data refine our understanding of clot formation in vivo and reinforce the centrality of platelets as the key procoagulant cellular surface.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Accumulation of phosphatidylserine (PS, red) and platelets (gray) during hemostatic plug formation following laser injury to the saphenous vein. This study identifies platelets as the functionally predominant source of PS during hemostatic plug formation. See the article by Ballard-Kordeliski et al on page 1116.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals