Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Daratumumab for systemic AL amyloidosis: prognostic factors and adverse outcome with nephrotic-range albuminuria
Clinical Trials & Observations
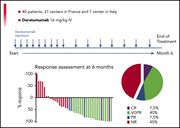
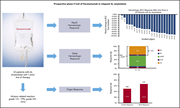
Three articles in this week’s issue report phase 2 studies of daratumumab for the treatment of relapsed/refractory AL amyloidosis. Although their results vary widely, reflecting differences in inclusion criteria, study size, and duration of therapy, all three confirm that daratumumab is a highly effective agent for the treatment of this advanced disease in some patients.
A prospective phase 2 trial of daratumumab in patients with previously treated systemic light-chain amyloidosis
Clinical Trials & Observations
Three articles in this week’s issue report phase 2 studies of daratumumab for the treatment of relapsed/refractory AL amyloidosis. Although their results vary widely, reflecting differences in inclusion criteria, study size, and duration of therapy, all three confirm that daratumumab is a highly effective agent for the treatment of this advanced disease in some patients.
Safety, tolerability, and response rates of daratumumab in relapsed AL amyloidosis: results of a phase 2 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Three articles in this week’s issue report phase 2 studies of daratumumab for the treatment of relapsed/refractory AL amyloidosis. Although their results vary widely, reflecting differences in inclusion criteria, study size, and duration of therapy, all three confirm that daratumumab is a highly effective agent for the treatment of this advanced disease in some patients.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
Clonal hematopoiesis in donors and long-term survivors of related allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Boettcher and colleagues analyzed clonal hematopoiesis (CH) in 42 donor-recipient pairs of long-term survivors of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. CH is prevalent among both donors and recipients, including a small number of recipients with engraftment of donor CH; these clones variably expand between donor and recipient.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
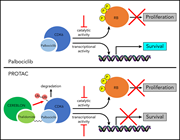
Selective inhibition of Ph-positive ALL cell growth through kinase-dependent and -independent effects by CDK6-specific PROTACs
CDK6 is overexpressed in Philadelphia chromosome–positive acute lymphocytic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) and is required for leukemia cell growth and survival. De Dominici et al demonstrated that a novel proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) that binds CDK6 and a proteasome-targeting E3 ubiquitin ligase has impressive activity against Ph-positive ALL cells in vitro and in vivo.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
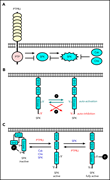
Interplay between the tyrosine kinases Chk and Csk and phosphatase PTPRJ is critical for regulating platelets in mice
Nagy et al elucidate the role of Src family kinases (SFKs) and their regulating tyrosine kinases Chk, Csk, and PTPRJ in determination of platelet number. Through a series of knockout experiments, they demonstrated an intricate interplay among the three kinases and SFKs themselves in inhibiting megakaryocyte proliferation.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
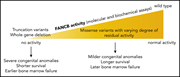
Association of clinical severity with FANCB variant type in Fanconi anemia
Jung and colleagues performed a thorough genotype-phenotype analysis of FANCB, the only X-linked variant of Fanconi anemia. FANCB patients are generally characterized by early-onset bone marrow failure and severe congenital abnormalities. However, variations in causative mutations lead to different functional properties that modulate clinical severity.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Prognostic impact of CSF3R mutations in favorable risk childhood acute myeloid leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Truncation mutations in the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor gene (CSF3R) are a rare abnormality in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia, and are usually associated either with mutations in CEBPA or with t(8;21). Through sequencing of over 2000 patients, the authors demonstrated that, although CSF3R mutations with associated t(8;21) still had an excellent response, CSF3R mutation abrogated the favorable risk of CEBPA mutation alone.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Reticulin-stained bone marrow of a Chk;Csk double knockout mouse. Ablation of the tyrosine kinases Chk and Csk from megakaryocytes leads to severe macrothrombocytopenia and myelofibrosis. See the article by Nagy et al on page 1574.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





AL patients don’t dare go without dara
Clinical Trials & Observations