Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
An integrative model of pathway convergence in genetically heterogeneous blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia
In a study reported in this Plenary Paper, Ko et al used a multi-“omic” analysis of paired chronic phase and blast crisis (BC) chronic myeloid leukemia samples to demonstrate strikingly convergent patterns of gene expression underlying BC. Diverse genetic changes occurring with progression converged on modifications of the polycomb repressor complex that induce epigenetic changes, favoring stem cell proliferation and survival at the expense of differentiation.
HOW I TREAT
How I treat pain in hematologic malignancies safely with opioid therapy
Using 3 illustrative cases, Geyer and colleagues explore issues surrounding the use of opioids to manage pain in patients with hematologic malignancies.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Stage I-II nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: a multi-institutional study of adult patients by ILROG
Clinical Trials & Observations
A multicenter retrospective study of patients with stage I-II nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma confirmed excellent overall survival regardless of treatment by observation, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or combined modality therapy.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
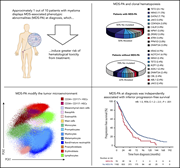
Biological and clinical significance of dysplastic hematopoiesis in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma
Maia et al prospectively analyzed marrow biopsies of 285 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients for flow and DNA evidence of dysplastic hematopoiesis, revealing 33 patients with evidence of dysplasia, half with clonal hematopoiesis (CH). CH was independently associated with inferior survival in this group and in a retrospective analysis including over 1000 patients on previous protocols.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
An intestinal organoid–based platform that recreates susceptibility to T-cell–mediated tissue injury
The authors used a preclinical animal model to examine the determinants of graft-versus-host disease that can predict potential therapies for treating this major complication of allogeneic stem cell transplantation. They elucidated the role of ATG16L1, a polymorphic gene in humans, in T-cell attack on intestinal organoids and demonstrated that it can be inhibited by blocking necroptosis.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
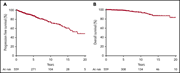
Prognostic and predictive impact of genetic markers in patients with CLL treated with obinutuzumab and venetoclax
Clinical Trials & Observations
Tausch et al assessed the prognostic impact of IGHV mutational status and genomic mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) for treatment-naïve patients in a trial comparing obinutuzumab and chlorambucil (GClb) vs obinutuzumab and venetoclax (VenG). With the exception of del(17p), mutations associated with decreased progression free survival (PFS) with GClb treatment do not confer worse PFS upon treatment with VenG.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
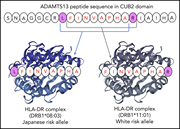
HLA loci predisposing to immune TTP in Japanese: potential role of the shared ADAMTS13 peptide bound to different HLA-DR
HLA loci predisposing to immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) in the white population have been described. In this study, analysis of the HLA haplotypes in 52 Japanese immune TTP patients identifies a different predisposing haplotype from that in whites. Interestingly, modeling different predisposing DRB1 alleles in the Japanese and white populations predicts binding to the same ADAMTS13 peptide.
TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
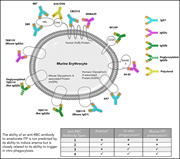
Inhibition of platelet phagocytosis as an in vitro predictor for therapeutic potential of RBC antibodies in murine ITP
Polyclonal anti-D is thought to successfully treat immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) by blocking the reticuloendothelial system through opsonization and phagocytosis of red blood cells (RBCs). Khan et al demonstrated by a combination of in vitro and in vivo studies that successful targeting of RBCs is necessary but insufficient to predict successful interruption of platelet phagocytosis.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
A homozygous deletion in the SLC19A1 gene as a cause of folate-dependent recurrent megaloblastic anemia
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Live culture microscopy image of allogeneic T cells (green) cocultured with intestinal organoids in the presence of the cell death dye propidium iodide stained red to model immune-mediated attack observed in graft-versus-host disease. See the article by Matsuzawa-Ishimoto et al on page 2388.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals







CML: new tools to answer old questions