Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
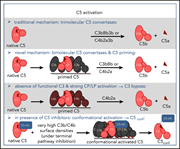
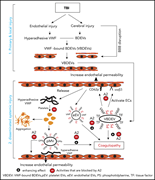
Complement inhibition at the level of C3 or C5: mechanistic reasons for ongoing terminal pathway activity
The C5 inhibitor eculizumab has opened the door to therapeutic blockade of the terminal complement pathway in practice and raised questions about its regulation. In a Plenary Paper, Mannes and colleagues describe potentially paradigm-shifting research related to the complement cascade with important translational implications for complement-driven diseases such as paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome, and antiphospholipid syndromes.
PERSPECTIVE
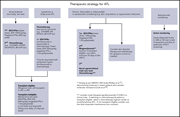
Persistent challenges with treating multiple myeloma early
Goodman et al provide a provocative Perspective on whether the evidence base is sufficient for widespread treatment of patients with multiple myeloma that is not yet causing end-organ damage.
HOW I TREAT
How I treat adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma
Cook and Phillips provide their expert views on how to treat patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL), an uncommon complication of long-term infection with human T-lymphotropic virus type 1. Using 4 cases to orient clinicians to the diversity of presentation and management strategies of ATL, they highlight current treatment outcomes and potential areas for future progress.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Tumor-intrinsic and -extrinsic determinants of response to blinatumomab in adults with B-ALL
Clinical Trials & Observations
Zhao and colleagues report detailed genomic analyses of 44 adult patients with relapsed CD19-positive B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) treated with blinatumomab. They reveal that while specific leukemogenic genetic mutations do not predict response, a tumor-intrinsic transcriptomic signature of heightened immune signaling is associated with response; furthermore, pretreatment identification of a specific CD19 alternative splicing variant is associated with subsequent blinatumomab treatment resistance or failure.
ALL in escape room
Clinical Trials & Observations
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
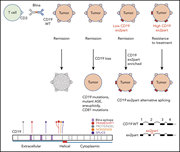
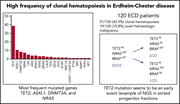
High frequency of clonal hematopoiesis in Erdheim-Chester disease
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
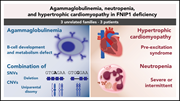
Absent B cells, agammaglobulinemia, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in folliculin-interacting protein 1 deficiency
Brief Report
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
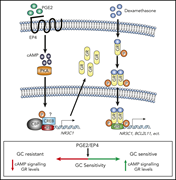
Prostaglandin E2 stimulates cAMP signaling and resensitizes human leukemia cells to glucocorticoid-induced cell death
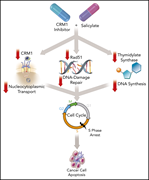
Salicylates enhance CRM1 inhibitor antitumor activity by induction of S-phase arrest and impairment of DNA-damage repair
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
A personalized approach to guide allogeneic stem cell transplantation in younger adults with acute myeloid leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
Fenwarth et al tackled the challenge of how to choose which patients should be selected for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant in first remission. By incorporating genomic data via the the “knowledge bank” of Gerstung et al, minimal residual disease data, and the existing standard recommendations (European LeukemiaNet 2017), they demonstrate enhanced predictive power for benefit and for harm in a cohort of 656 patients prospectively enrolled in a French national trial.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
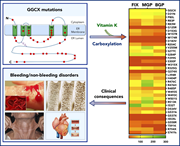
γ-Glutamyl carboxylase mutations differentially affect the biological function of vitamin K–dependent proteins
Hao et al describe how the known natural mutations of the enzyme γ-glutamyl carboxylase (GGCX) affect the differential γ-carboxylation of 3 major vitamin K–dependent proteins with widely different functions in coagulation and noncoagulation functions such as vascular calcification and bone metabolism. Their data explain why vitamin K administration is beneficial for correcting phenotypes of GGCX mutations associated with bleeding but has minimal impact when mutations are present with nonbleeding phenotypes.
TRANSPLANTATION
Neighborhood poverty and pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes: a CIBMTR analysis
Clinical Trials & Observations
This retrospective analysis of data on cohorts of pediatric patients receiving hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is an important step towards understanding the interactions between social determinants of health, insurance coverage, and outcomes of high-complexity therapy for hematological disease. Using postal codes as a surrogate for economic disadvantage and insurance data, Bona and colleagues found that neighborhood poverty is associated with higher transplant-related mortality (TRM) for patients with malignant disease but not those with nonmalignant disease and that survival and TRM appear worse for those with Medicaid rather than private insurance.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunofluorescence staining by confocal microscopy (Zeiss LSM 780; original magnification ×60) showing subcellular localization of transfected nuclear export green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter (green), endogenous CRM1 (red), and DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; blue) in choline salicylate–treated (3 mM, 24 hours) U2OS cells. Choline salicylate treatment augments the activity of the CRM1 inhibitor KPT-330, reducing CRM1 expression and nuclear export of the GFP reporter in these cells. See the article by Abeykoon et al on page 513.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Terminal complement without C5 convertase?