Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a Blood Spotlight series on acute myeloid leukemia
Recent molecular and diagnostic advances in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have led investigators and clinicians to further categorize patients in different subgroups, guiding therapeutic interventions. Associate Editor Selina Luger introduces this 4-piece Blood Spotlight series that she commissioned from leaders in the field and that focuses on these specific patients’ subgroups, not only on recent therapeutic advances but also on identifying areas of unmet need. Sallman and Stahl discuss TP53-mutated myelodysplastic syndrome and AML, proposing a new treatment algorithm. Perl provides a comprehensive spotlight on the use of cytotoxic chemotherapy, FLT3 inhibitors, and transplantation for FLT3-mutated AML. Abedin et al focus on the treatment of AML in fit older patients, making a case for enrollment of such individuals in clinical trials. Last, Walter et al provide a thoughtful discussion of the state of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with AML who are at least 70 years old.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
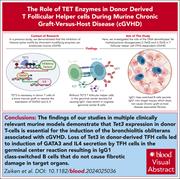
Deficiency of T follicular helper cell Tet3 DNA demethylation inhibits pathogenic IgG2c class switching and chronic GVHD
Treatment for chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) remains a major clinical challenge. In this Plenary Paper, Zaiken and colleagues show that DNA demethylase Tet (ten-eleven translocase) methylcytosine dioxygenase 3 (Tet3) deficiency in donor T cells is critical for differentiation of GATA3+ T follicular helper cells after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in mice. These cells drive B-cell class switching toward less-inflammatory immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) plasma cells, inhibiting the pathogenic IgG2c-producing ones and therefore significantly reducing IgG2c deposition and fibrosis in cGVHD target organs. This epigenetic silencing approach lays the groundwork for potential novel therapeutics for cGVHD.
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT SERIES
TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: how can we improve outcomes?
Clinical Trials & Observations
Recent molecular and diagnostic advances in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have led investigators and clinicians to further categorize patients in different subgroups, guiding therapeutic interventions. Associate Editor Selina Luger introduces this 4-piece Blood Spotlight series that she commissioned from leaders in the field and that focuses on these specific patients’ subgroups, not only on recent therapeutic advances but also on identifying areas of unmet need. Sallman and Stahl discuss TP53-mutated myelodysplastic syndrome and AML, proposing a new treatment algorithm. Perl provides a comprehensive spotlight on the use of cytotoxic chemotherapy, FLT3 inhibitors, and transplantation for FLT3-mutated AML. Abedin et al focus on the treatment of AML in fit older patients, making a case for enrollment of such individuals in clinical trials. Last, Walter et al provide a thoughtful discussion of the state of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with AML who are at least 70 years old.
Approaching a therapeutic inflection point for FLT3-mutated AML
Clinical Trials & Observations
Recent molecular and diagnostic advances in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have led investigators and clinicians to further categorize patients in different subgroups, guiding therapeutic interventions. Associate Editor Selina Luger introduces this 4-piece Blood Spotlight series that she commissioned from leaders in the field and that focuses on these specific patients’ subgroups, not only on recent therapeutic advances but also on identifying areas of unmet need. Sallman and Stahl discuss TP53-mutated myelodysplastic syndrome and AML, proposing a new treatment algorithm. Perl provides a comprehensive spotlight on the use of cytotoxic chemotherapy, FLT3 inhibitors, and transplantation for FLT3-mutated AML. Abedin et al focus on the treatment of AML in fit older patients, making a case for enrollment of such individuals in clinical trials. Last, Walter et al provide a thoughtful discussion of the state of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with AML who are at least 70 years old.
The fit older adult with acute myeloid leukemia: clinical challenges to providing evidence-based frontline treatment
Recent molecular and diagnostic advances in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have led investigators and clinicians to further categorize patients in different subgroups, guiding therapeutic interventions. Associate Editor Selina Luger introduces this 4-piece Blood Spotlight series that she commissioned from leaders in the field and that focuses on these specific patients’ subgroups, not only on recent therapeutic advances but also on identifying areas of unmet need. Sallman and Stahl discuss TP53-mutated myelodysplastic syndrome and AML, proposing a new treatment algorithm. Perl provides a comprehensive spotlight on the use of cytotoxic chemotherapy, FLT3 inhibitors, and transplantation for FLT3-mutated AML. Abedin et al focus on the treatment of AML in fit older patients, making a case for enrollment of such individuals in clinical trials. Last, Walter et al provide a thoughtful discussion of the state of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with AML who are at least 70 years old.
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia in adults over 70 years old
Recent molecular and diagnostic advances in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have led investigators and clinicians to further categorize patients in different subgroups, guiding therapeutic interventions. Associate Editor Selina Luger introduces this 4-piece Blood Spotlight series that she commissioned from leaders in the field and that focuses on these specific patients’ subgroups, not only on recent therapeutic advances but also on identifying areas of unmet need. Sallman and Stahl discuss TP53-mutated myelodysplastic syndrome and AML, proposing a new treatment algorithm. Perl provides a comprehensive spotlight on the use of cytotoxic chemotherapy, FLT3 inhibitors, and transplantation for FLT3-mutated AML. Abedin et al focus on the treatment of AML in fit older patients, making a case for enrollment of such individuals in clinical trials. Last, Walter et al provide a thoughtful discussion of the state of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for patients with AML who are at least 70 years old.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
A first-in-class JAK/ROCK inhibitor, rovadicitinib, for glucocorticoid-refractory or -dependent chronic GVHD
Clinical Trials & Observations
Chronic graft-versus-host (cGVHD) disease is a significant complication for patients after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation, and its effective treatment options are limited. Zhao et al report the results of a phase 1b/2a trial that investigated the safety of the oral dual JAK1/2 and ROCK1/2 inhibitor rovadicitinib for glucocorticoid-refractory or -dependent cGVHD. Rovadicitinib was well tolerated, with an overall response rate of over 80%, and improved patients’ quality of life. These promising results form the basis for the ongoing phase 3 trial to fully assess the place of rovadicitinib in management of cGVHD.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
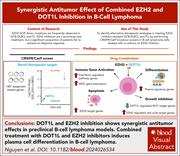
Synergistic antitumor effect of combined EZH2 and DOT1L inhibition in B-cell lymphoma
Gain-of-function somatic mutations in EZH2 are frequently found in germinal center B-cell (GCB) lymphomas, and pharmacological EZH2 inhibition has yielded durable responses in some but not all patients with the disease. To find additional therapeutic targets, Nguyen et al developed an unbiased CRISPR knockout screening in the presence of EZH2 inhibitors, demonstrating the synthetic vulnerability of GCB-derived lymphomas to combined inhibition of EZH2 and DOT1L. Since inhibitors of EZH2 and DOT1L are in the clinic, this study provides strong preclinical rationale for near-term clinical testing of this combination.
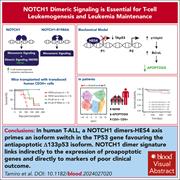
NOTCH1 dimeric signaling is essential for T-cell leukemogenesis and leukemia maintenance
Fifty percent of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) cases are associated with activating mutations in NOTCH1. Tamiro and colleagues provide evidence that human T-ALL cells depend on the formation of dimeric NOTCH1 transcriptional complexes and that this dependency unexpectedly relies on the ability of the dimeric Notch targeting HES4 to upregulate alternative TP53 transcripts, which in turn encode truncated TP53 isoforms that increase expression of antiapoptotic target genes. These novel findings provide new insight into the molecular pathogenesis of human T-ALL while also pointing to divergent functions among HES family members.
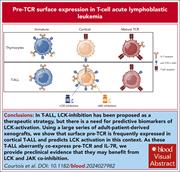
Surface pTα expression predicts LCK activation and preclinical synergy of LCK and JAK coinhibition in adult T-ALL
Relapsed/refractory T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) remains a significant therapeutic challenge. Courtois et al present compelling preclinical data in support of a therapeutic role for coinhibition of the interleukin-7 receptor and pre–T-cell receptor (TCR) pathways for a subset of T-ALL and identify surface expression of the pre-TCR α chain (pTα) as a biomarker predictive of pre-TCR–directed treatment response. Their findings point towards potential benefit for patients with relapsed/refractory T-ALL and provide a rationale for clinical validation.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
Safety and efficacy of rilzabrutinib vs placebo in adults with immune thrombocytopenia: the phase 3 LUNA3 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Despite recent advances in the treatment of immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), many patients’ platelet counts fail to increase. Kuter and colleagues present the results of a large phase 3 trial (LUNA3) evaluating the efficacy and safety of rilzabrutinib, a selective and reversible Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, for the treatment of patients with persistent/chronic ITP. Rilzabrutinib treatment increases platelet counts, reduces bleeding, and improves fatigue in this heavily pretreated patient population, while showing an acceptable safety profile with few adverse effects. This is important information for regulatory agencies assessing rilzabrutinib for approval as a therapeutic option for ITP.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Diabetes mellitus and APOL1 genotype increase the risk for chronic kidney disease progression in sickle cell disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a known risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD), both of which are more common in African Americans. In this Letter to Blood, Sun and colleagues present robust observational data demonstrating that patients with sickle cell disease who have a diagnosis of DM are at a much higher risk of progressing rapidly to ESKD independently of the known genetic risk factor conferred by variants in APOL1. These results emphasize the importance of DM screening for patients with sickle cell disease.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Lung tissue from a mouse with chronic graft-versus-host disease. The section is stained for the detection of immunoglobulin (Ig) subtype deposited in the tissue and DNA (blue). For this mouse, transplanted with wild-type T cells, IgG2c (yellow) was found to be the dominant isotype deposited. Red indicates non-isotype-specific IgG. See the article by Zaiken et al on page 2813.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals









TET3 stirs up trouble via pathogenic Ig class switching