Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
Clonal hematopoiesis and measurable residual disease assessment in acute myeloid leukemia
Molecular analysis has modified the view of complete remission in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) to include consideration of measurable residual disease. In this Perspective, the authors highlight the complexity of interpreting clonal hematopoiesis to distinguish residual AML from ancestral clones of uncertain significance, new or emerging clones, or donor-derived clones in patients undergoing stem cell transplantation.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
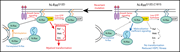
Ruxolitinib for the treatment of steroid-refractory acute GVHD (REACH1): a multicenter, open-label phase 2 trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Steroid-resistant graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) has a dismal prognosis. Jagasia et al report that, in a phase 2 study of the JAK1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib to treat 71 patients with steroid-resistant GVHD, over half of patients responded (including 27% of patients with a complete response), leading to markedly improved survival.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
Immunoglobulin variable domain high-throughput sequencing reveals specific novel mutational patterns in POEMS syndrome
POEMS syndrome is a rare plasma cell dyscrasia with variable manifestations. Bender and colleagues used a novel high-throughput sequencing technique to demonstrate that monoclonal λ light-chain clones are detectable in the vast majority of patients with POEMS syndrome and that they show highly restricted VJ region usage that can help define and diagnose the disease.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: a Haematological Malignancy Research Network report
Using sequencing of over 900 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), the authors used model clustering of mutations to define DLBCL subtypes that provide important prognostic information.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Genetic disruption of N-RasG12D palmitoylation perturbs hematopoiesis and prevents myeloid transformation in mice
RAS gene mutations are challenging to target therapeutically. Zambetti et al investigated the role of posttranslational modification in the pathogenesis of N-Ras–mediated transformation. “Knock-in” of a mutation to block palmitoylation of mutant N-Ras abolishes its transforming ability, identifying a potential therapeutic target for NRAS-mutant cancers.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
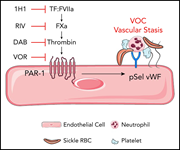
Thrombin activation of PAR-1 contributes to microvascular stasis in mouse models of sickle cell disease
Brief Report
Sparkenbaugh and colleagues demonstrate that inhibition of tissue factor or inhibition of protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1), the major receptor for thrombin, reduces microvascular stasis in mouse models of sickle cell disease (SCD). These results suggest that activation of coagulation is a direct contributor to vaso-occlusive crisis in SCD and support a potential trial of anticoagulation to reduce SCD-related crises.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
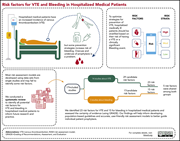
Prognostic factors for VTE and bleeding in hospitalized medical patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Numerous studies have elucidated risk factors for venous thromboembolism (VTE) and bleeding in hospitalized medical patients, leading to complex algorithms to assess risks and benefits of anticoagulation. From these studies, this systematic review identifies 23 risk factors for VTE and 15 for bleeding that can help inform future, and perhaps better, algorithms for risk assessment.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Temozolomide is effective and well tolerated in patients with primary vitreoretinal lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Baron et al report excellent responses to temozolomide in 21 patients (19 relapsed/refractory) with primary vitreoretinal lymphoma. Treatment is well tolerated, even in elderly patients.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Endothelial cell (blue) expression of P-selectin (green) and von Willebrand factor (VWF; red) in the lungs of sickle cell mice 1 hour after IV injection of stroma-free hemoglobin. Colocalization of P-selectin and VWF is visualized in yellow. See the article by Sparkenbaugh et al on page 1783.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Ruxolitinib for steroid-resistant acute GVHD
Clinical Trials & Observations