Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
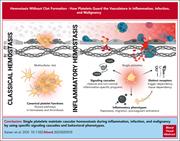
Hemostasis without clot formation: how platelets guard the vasculature in inflammation, infection, and malignancy
Kaiser and colleagues provide a state-of-the-art review of the complex role of platelets in maintaining vascular integrity. The authors describe the processes by which platelets are recruited to the vessel wall, how they prevent hemorrhage, where they facilitate clot formation, and how the processes differ in the setting of inflammatory stresses, where platelets can function as single cells to protect vascular integrity without clot formation.
HOW I TREAT
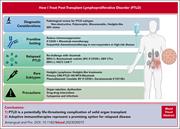
How I treat posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder
Amengual and Pro present their approach to posttransplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD), complicating solid organ transplant and hematopoietic cell transplant. Using 3 illustrative cases, the authors discuss the heterogeneity of PTLD and their approach to treatment using risk-adapted strategies. These strategies include reduction of immunosuppression, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Lenalidomide plus rituximab for the initial treatment of frail older patients with DLBCL: the FIL_ReRi phase 2 study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Gini et al report on the results of a phase 2 study of rituximab and lenalidomide in 65 frail patients over 70 years of age with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Use of this chemotherapy-free combination yielded an overall response rate of 50.8% with 27.7% of patients achieving complete remission. Median progression-free survival was 14 months, and duration of response was 64% at 2 years. Toxicity of grade ≥ 3 occurred in 34 of 65 patients. This chemotherapy-free combination has significant activity and merits further study.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
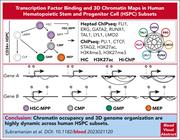
Genome-wide transcription factor–binding maps reveal cell-specific changes in the regulatory architecture of human HSPCs
Subramanian and colleagues report on a map of genome-wide chromatin contacts of canonical transcription factor complexes that elucidates the determinants of cell-type–specific gene expression and maturation. This represents a valuable resource database for analysis of the regulatory networks of normal hematopoietic stem cell maturation and their disruption in leukemic cells.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
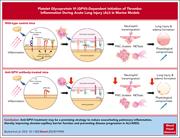
A key role for platelet GPVI in neutrophil recruitment, migration, and NETosis in the early stages of acute lung injury
Acute lung injury (ALI) involves a complex interaction of platelets and neutrophils to promote thrombo-inflammation. Burkard et al further elucidate the pathophysiology by examining the mechanism of neutrophil recruitment to the lung and neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation. Inhibition of glycoprotein VI (GPVI) through genetic knockout or antibody treatment reduced neutrophil recruitment, neutrophil activation, and NET formation, suggesting a possible strategy to reduce acute inflammation leading to ALI.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Inhibition of a new AXL isoform, AXL3, induces apoptosis of mantle cell lymphoma cells
Gelebart et al report on the identification and expression of a novel AXL isoform, AXL3, that is constitutively active in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) cells. Knockdown of AXL3 caused apoptosis in MCL cell lines, as did pharmacological inhibition in primary MCL cells in vitro and mouse xenografts in vivo, suggesting a novel therapeutic target for treating MCL.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Lung intravital confocal microscopy shows platelets (cyan) and neutrophils (yellow) forming clusters in the pulmonary vasculature (magenta) in a model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Anti-glycoprotein VI treatment significantly reduces this cluster formation, pulmonary inflammation, and tissue damage. See the article by Burkard et al on page 1463.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





All wired up: heptads in hematopoiesis