Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
Emerging genetic technologies informing personalized medicine in Shwachman-Diamond syndrome and other inherited BMF disorders
Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) is a rare bone marrow failure (BMF) syndrome associated with abnormal ribosome assembly leading to BMF and carrying a markedly increased risk of myeloid malignancy. Cull and coauthors provide a state-of-the-art review of the impact of new single-cell technologies on monitoring and treatment of patients with SDS, allowing personalized assessment of leukemia risk and influencing decisions around interventions including stem cell transplantation.
HOW I TREAT
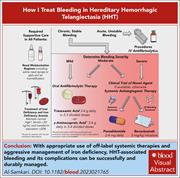
How I treat bleeding in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
Al-Samkari presents a therapeutic approach to bleeding in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasis. Using 4 illustrative cases covering the spectrum of bleeding severity, the author discusses the decreasing role of local interventions that usually provide only temporary control, emphasizes the importance of treating iron deficiency, and outlines the role of antifibrinolytic and antiangiogenic therapies in the management of this chronic disease.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Mass spectrometry–based assessment of M protein in peripheral blood during maintenance therapy in multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a sensitive method for detecting myeloma-derived monoclonal proteins in the peripheral blood to assess measurable residual disease (MRD). Kubicki et al investigated the predictive value of peripheral blood negativity by MS in 138 patients in a phase 3 trial of posttransplant maintenance therapy. MS assessment was feasible and correlated well with bone marrow MRD by next-generation sequencing or multiparameter flow cytometry, though the combination of the 2 provided slightly better predictive value. This raises the possibility that prospective MRD assessment can be obtained without frequent bone marrow assessment.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
Inducible CXCL12/CXCR4–dependent extramedullary hematopoietic niches in the adrenal gland
Schyrr and colleagues report a novel murine model of extramedullary hematopoiesis induced in the adrenal gland, inspired by the observation that some retroperitoneal tumors in the adrenal gland incorporate hematopoietic elements. The authors induced adrenal hematopoiesis in splenectomized mice with hormonal stimulation with homing of transplantable stem cells and formation of stroma.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
In vivo CAR T-cell generation in nonhuman primates using lentiviral vectors displaying a multidomain fusion ligand
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell administration has become an important modality for therapy for B-cell lymphoma, but it is hampered by the inherent delay of individual product manufacture. Nicolai et al report the development of a viral vector expressing surface T-cell activation and costimulatory signals for in vivo transduction of CAR T cells. Administration of the vector to nonhuman primates led to anti-CD20 CAR T cells and B-cell depletion, suggesting this may offer a new paradigm for CAR T-cell therapy.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Genomic imbalance analysis provides new insight into prognostic factors in adult and pediatric T-ALL
Balducci et al used single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array analysis to define genomic imbalances in 317 pediatric and adult patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL). Over 95% of the patients had at least 1 genomic imbalance by SNP array analysis. The authors define the landscape of genomic imbalances in the population and determined that a threshold of 15 genomic imbalances correlated to a high-risk population. They also identified several rare variants that also convey poor prognosis. The incorporation of whole genomic imbalance assessment may refine T-ALL risk stratification.
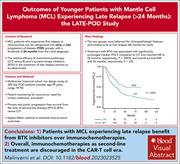
Outcomes of younger patients with mantle cell lymphoma experiencing late relapse (>24 months): the LATE-POD study
Malinverni and colleagues compared outcomes of second-line therapy with Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKis) vs chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) relapsing >24 months after first-line CIT. In an international cohort study including 10 countries, the evaluation of 385 patients with MCL with late-disease progression demonstrated that BTKi therapy was associated with significantly improved progression-free survival (median not reached [NR] vs 26 months) and overall survival (median NR vs 56 months), suggesting that BTKi is the preferred second-line therapy in the late-relapse setting.
TRANSPLANTATION
Novel MAGIC composite scores using both clinical symptoms and biomarkers best predict treatment outcomes of acute GVHD
Clinical Trials & Observations
Current grading systems for acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) assessment are based on clinical symptoms at the time of initiating therapy and distinguish only standard-risk from high-risk GVHD. Akahoshi et al incorporated biomarkers into an algorithm for better predicting treatment response and nonrelapse mortality by defining a low-risk group (about 40% of patients) that can likely avoid long-term steroid therapy and its attendant complications.
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunofluorescence stain of a murine adrenal gland hormonally induced to host extramedullary hematopoiesis showing a focus of hematopoietic cells (CD45, green) embedded in the remodeled stromal niche (PDGFRα, orange) with DAPI (4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole) as nuclear stain (white). See the article by Schyrr et al on page 964.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals