Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
Inflammation and myeloid malignancy: quenching the flame
In this Blood Spotlight review, Stubbins and colleagues summarize recent data showing that the effect inflammation has on leukemic and normal myeloid cells in the marrow is pathway-, cytokine-, and cell context–dependent. They suggest how understanding this heterogeneity should influence the choice of anti-inflammatory agents for preclinical testing and clinical trials in various myeloid neoplasms.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Immune complications and their management in inherited and acquired bleeding disorders
Arruda et al review the alloimmune and autoimmune responses to procoagulant factors that cause serious bleeding and the important, unresolved problems of how to prevent and treat these conditions. They integrate the underlying pathophysiology with relevant clinical findings and outcomes with current treatment approaches while highlighting preclinical developments that are being explored and that may lead to new treatments.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
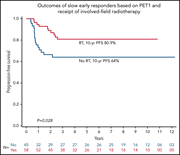
Targeted radiotherapy for early-stage, low-risk pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma slow early responders: a COG AHOD0431 analysis
Clinical Trials & Observations
Parekh et al report on secondary analyses of a frontline pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma phase 3 trial to investigate how speed of response may predict outcome and the impact of radiation therapy. They demonstrated that early positron emission tomography (PET) response after 1 cycle of chemotherapy is associated with a favorable outcome and that involved-field radiotherapy mitigates the relapse risks in those without an early PET response. These data help inform the next generation of trials in this disease.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
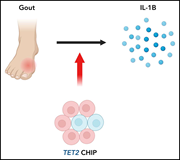
TET2-mutant clonal hematopoiesis and risk of gout
Clinical Trials & Observations
Gout is a common inflammatory arthritis defined by NLRP3 inflammasome– and IL1β-dependent innate immune responses to monosodium urate (MSU) crystals. Agrawal et al identified clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) as a risk factor for gout by analyzing data from 2 large biobanks. In mechanistic studies, they showed that Tet2-knockout mice experienced increased MSU-induced inflammation in an NLRP inflammasome–dependent manner due to the greater production of IL1β by macrophages. These data explain why gout is more common in people with TET2-mutant CHIP.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
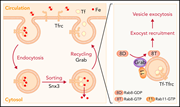
T-cell exhaustion induced by continuous bispecific molecule exposure is ameliorated by treatment-free intervals
Bispecific antibodies that direct T-cell engagement with malignant blood cells are showing exciting potential in many relapsed hematological malignancies, but their optimal use remains undefined. Philipp et al show for the first time that continuous engagement of T cells by bispecific antibodies leads to their exhaustion, whereas including treatment-free intervals in the schedule helps preserve the fitness of immune effectors and can improve long-term results in model systems. These data call for clinical trials comparing current continuous schedules to ones that include treatment-free intervals.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
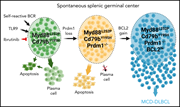
Aberrant expansion of spontaneous splenic germinal centers induced by hallmark genetic lesions of aggressive lymphoma
Through genomic profiling, activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is now recognized to have distinct subgroups that may have distinct cells-of-origin. Pindzola et al generated immunocompetent mice carrying 4 hallmark genetic alterations associated with the MYD88/CD79B-mutated (MCD) genetic subgroup. The mice showed a massive expansion of splenic germinal centers and developed DLBCL with age, revealing splenic germinal center B cells as a likely cell of origin for this subgroup.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
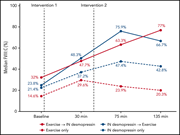
Moderate-intensity aerobic exercise vs desmopressin in adolescent males with mild hemophilia A: a randomized trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
Mild hemophilia is not always a benign disease and may present an increased bleeding risk with intense physical activities. In a randomized trial, Kumar and colleagues compared the effects of exercise versus intranasal desmopressin versus the combination of both on the rise in factor VIII:C (FVIII:C) in patients with mild hemophilia A. They demonstrated substantial rises with exercise, similar to that achieved with desmopressin, and showed that the combination generated more sustained increases in FVIII:C, with normalization in more than half the subjects.
TRANSPLANTATION
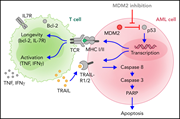
Targeting MDM2 enhances antileukemia immunity after allogeneic transplantation via MHC-II and TRAIL-R1/2 upregulation
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) relapse after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is common. Ho and colleagues report that inhibition of mouse-double-minute-2 (MDM2) increases the potency of T-cell responses to AML and facilitates the “graft-versusleukemia” effect in murine models of HCT. This strategy is being tested in a clinical trial and could also be evaluated in the future in the context of targeted T-cell therapies, such as chimeric antigen receptor T cells.
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Radiotherapy is here to stay
Clinical Trials & Observations