Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
SPECIAL REPORT
Moving toward disease modification in polycythemia vera
Polycythemia vera is a BCR-ABL1–negative myeloproliferative neoplasm that reduces life expectancy through thrombosis, marrow failure, and transformation to leukemia. While thrombosis-reduction management is well established, there is a need for disease-modifying therapies to reduce the risks of the other 2 terminal events. In this Special Report, Bewersdorf and colleagues review current data about disease-modifying therapies and overview ongoing clinical trials of new agents and new combinations.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
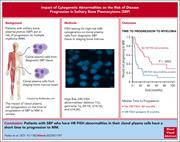
Impact of cytogenetic abnormalities on the risk of disease progression in solitary bone plasmacytomas
Clinical Trials & Observations
Solitary bone plasmacytoma (SBP) is generally considered a low-risk disease condition, and radiation therapy is curative for roughly half of the patients. However, Yadav and colleagues show that this paradigm does not hold true for SBP presenting with 1 or more high-risk cytogenetic markers: +1q or del(17p). Despite radiation therapy, median time to progression to symptomatic myeloma was only 8 months, demonstrating that there is a group of patients who need immediate systemic treatment to prevent further end-organ damage.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
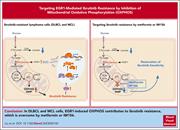
EGR1-mediated metabolic reprogramming to oxidative phosphorylation contributes to ibrutinib resistance in B-cell lymphoma
Resistance to ibrutinib is a cause of treatment failure in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Liu et al describe a new route to acquired ibrutinib resistance via the transcription factor early growth response gene 1 (EGR1) which induces metabolic changes towards oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in MCL and also activated B-cell–like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Targeting OXPHOS with IM156, a novel chemical derivative of metformin, overcomes ibrutinib resistance, suggesting a future strategy for testing in clinical trials.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
A signature of platelet reactivity in CBC scattergrams reveals genetic predictors of thrombotic disease risk
Genetically determined platelet reactivity is postulated to modulate the risk of thrombotic diseases, including coronary artery disease, ischemic stroke, and venous thromboembolism, but assessing this at population-scale has not been possible. Verdier et al pioneered a novel method to predict platelet reactivity from complete blood count (CBC) data and applied it to identify associated genetic variants and find associations with thrombotic diseases. This new approach has exciting potential to discover novel targets to reduce thrombosis.
TRANSFUSION MEDICINE
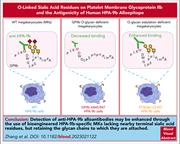
O-linked sialic acid residues on platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb mask the human HPA-9b alloepitope
Accurate diagnosis of fetal/neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia is important and requires the presence of both fetomaternal (parental) platelet antigen incompatibility and maternal antibodies specific to the incompatible antigen. Using induced pluripotent stem cells, Zhang and colleagues show that maternal alloantibodies in sera can be either sialylation-dependent or independent. This opens new ways to enhance antibody detection and reveal alloantibodies that would otherwise be missed.
VASCULAR BIOLOGY
Cold exposure induces vaso-occlusion and pain in sickle mice that depend on complement activation
Patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) may have more severe symptoms, especially pain, after cold exposure, but this has not been well explained. Ivy et al show that the alternative complement pathway drives vaso-occlusion and pain after cold exposure in a mouse model of SCD. Inhibition of C5a generation with anti-C5 or signaling with anti-C5aR antibody inhibits cold-induced vaso-occlusive episodes and hyperalgesia, suggesting therapeutic avenues for clinical evaluation.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A confocal microscopy image of fluorescent staining with the mitochondrial tracker Deep Red shows mitochondrial localization in OCI-Ly10 cells. Blue indicates cell nuclear staining with DAPI. See the article by Liu et al on page 1879.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





When a solitary plasmacytoma is just the beginning…
Clinical Trials & Observations