Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW ARTICLE
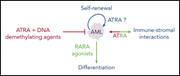
Retinoids in hematology: a timely revival?
Retinoids are ligands for nuclear receptors that act as transcriptional switches. Geoffroy et al contribute an authoritative and timely review of retinoids in leukemia and hematopoiesis. They describe the scientific basis upon which these agents may be used in combination with established therapies for treatment of leukemias other than acute promyelocytic leukemia.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
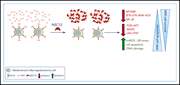
Eculizumab discontinuation in children and adults with atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome: a prospective multicenter study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Fakhouri and colleagues report the first prospective study of treatment discontinuation in 55 patients with atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome (aHUS) who had achieved remission with eculizumab. Relapse is more likely if there is a complement gene variant; however, most patients (77%) remain relapse free and eculizumab resumption reestablishes baseline renal function in the majority of relapsers. Cessation in remission is a safe and effective strategy associated with improved quality of life and cost savings.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY

Some images in the graphical abstract were adapted from Servier Medical Art (https://smart.servier.com), provided by Les Laboratoires Servier. They are available for reuse under the CC-BY 3.0 Unported license.
Immunodeficiency and bone marrow failure with mosaic and germline TLR8 gain of function
Aluri et al report the discovery of a novel cause of immune dysregulation: inborn errors causing gain of function in Toll-like receptor 8 (TLR8). They provide the first description of pathogenic defects in TLR8 that are associated with development of chronic neutropenia, bone marrow failure, and associated immune deficiency with recurrent infections. Notably, 5 of 6 cases display mosaicism, indicating that the presence of a pathogenic variant in only 5% to 30% of cells is sufficent to cause disease.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
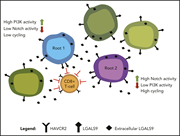
Single-cell RNA-seq reveals developmental plasticity with coexisting oncogenic states and immune evasion programs in ETP-ALL
Early T-cell progenitor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ETP-ALL) is a high-risk subtype of T-cell ALL. Using single-cell RNA-sequencing, Anand and colleagues characterized a subset of NOTCH1-mutated ETP-ALL and its immune microenvironment and revealed distinct stem cell states, one that is fast cycling and Notch activation dependent and another that is slow cycling and Notch independent. They also show that leukemic cells modulate a dysfunctional CD8+ T-cell immune response, apparently through expression of galectin-9. Collectively, these data provide some insights to this leukemia’s propensity to resist induction therapy or to relapse.
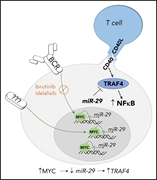
miR-29 modulates CD40 signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia by targeting TRAF4: an axis affected by BCR inhibitors
Deregulation of B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling and CD40-mediated T-cell interactions within the lymph node microenvironment are pivotal to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) pathogenesis. Sharma et al performed expression profiling of CLL cells recently emigrated from nodes to identify a BCR signaling–repressible microRNA, miR-29, that acts as a negative regulator of CD40 responsiveness. These data indicate that microRNAs can act to coordinate CLL responsiveness to T-cell signals and facilitate the co-occurrence of BCR and CD40 signaling activation.
Halting the FGF/FGFR axis leads to antitumor activity in Waldenström macroglobulinemia by silencing MYD88
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
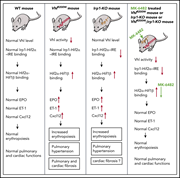
Therapeutic inhibition of HIF-2α reverses polycythemia and pulmonary hypertension in murine models of human diseases
Ghosh et al convincingly demonstrate the crucial role of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor HIF-2 in murine models of 2 congenital polycythemias, Chuvash erythrocytosis and erythrocytosis due to mutation of iron-regulatory protein 1 (IRP1). Oral administration of a specific HIF-2α inhibitor normalizes the expression of HIF-2–regulated genes and corrects erythrocytosis and pulmonary hypertension in both models, suggesting potential therapeutic efficacy of such inhibitors in patients.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
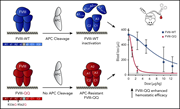
Activated protein C has a regulatory role in factor VIII function
Activated factor VIII (FVIIIa) is rate limiting for factor X activity in hemostasis. Wilhelm and colleagues provide novel insights into the physiological role of activated protein C (APC) in FVIIIa regulation in vivo by generating FVIII mutants resistant to APC-mediated proteolysis. FVIII-QQ demonstrates superior hemostatic efficacy relative to wild-type FVIII in murine models. This raises the possibility of development of APC-resistant factor VIII for hemophilia replacement therapy or gene replacement therapy.
TRANSPLANTATION

Working model for the role of soluble BAFF in promotion of and BCR-activation of pathogenic B cells in chronic GVHD. In our paper, we now demonstrate a mechanistic role for BAFF in chronic GVHD (cGVHD) using a mouse model. Our data afford the working model depicted here. BAFF levels and BAFF production are significantly increased in cGVHD mice. Recipient Fibroblastic Reticular Cells (FRCs) and Donor T Follicular Helper (TFH) Cells are likely cellular sources of this pathologic BAFF. Excess BAFF in cGVHD promotes survival of subsets of activated B cells. In turn, BAFF and alloantigen work together to augment B Cell Receptor (BCR) activation, in part, by increasing co-stimulatory NOTCH2 on B cells in mice that go on to develop cGVHD manifestations. At the molecular level, these B cells exposed to a high BAFF, NOTCH ligand and alloantigen environment are able to maintain SYK protein even after BCR re-engagement, perpetuating a BCR-responsive B cell compartment in cGVHD.
BAFF promotes heightened BCR responsiveness and manifestations of chronic GVHD after allogeneic stem cell transplantation
LETTER TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
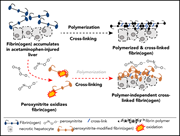
Immunofluorescent labeling of fibrin(ogen) deposits associated with areas of hepatocellular necrosis in an acetaminophen-injured mouse liver. See the article by Poole et al on page 2520.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals


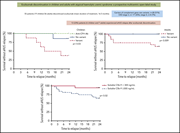

Eculizumab and aHUS: to stop or not
Clinical Trials & Observations