Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a review series on platelets and cancer
Platelets are critical for hemostasis and thrombosis, but recent research highlights their role in many other processes, including inflammation, wound healing, and lymphangiogenesis. Edited by José López, this series focuses on the emerging role of platelets in cancer, influencing tumor growth and metastasis, immune evasion, and tumor angiogenesis. The reviews present the current understanding of mutual cross talk between platelets and tumors, communication mediated by RNA transfer and extracellular vesicles, and the potential of antiplatelet agents for cancer treatment.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
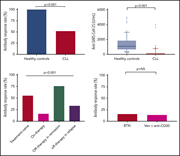
Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) have been previously shown to have poor responses to antibacterial and antiviral vaccines. In a Plenary Paper that is also this month’s CME article, Herishanu and colleagues discuss the outcome of vaccination against COVID-19 in 167 patients with CLL, again demonstrating a significantly impaired vaccine response. The lowest response rates were seen in patients undergoing active treatment, while the highest responses were seen in patients who were in complete remission after therapy; however, even treatment-naïve patients had lower responses than healthy controls. In this series, no responses were achieved in patients treated with anti-CD20 antibodies within 12 months of vaccination.
REVIEW SERIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
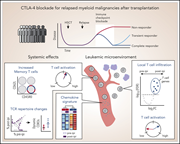
Molecular and cellular features of CTLA-4 blockade for relapsed myeloid malignancies after transplantation
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Relapsed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has a very poor prognosis. Previous studies have demonstrated that immune checkpoint blockade can increase the graft-versus-leukemia response. Using parallel transcriptomic analysis of bone marrow and immunophenotyping of peripheral blood, Penter et al show that clinical response to ipilimumab is associated with increased CD8+ T-cell infiltration and activation associated with increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
Mouse multipotent progenitor 5 cells are located at the interphase between hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
Brief Report
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
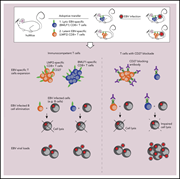
CD27 is required for protective lytic EBV antigen–specific CD8+ T-cell expansion
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Linking the KIR phenotype with STAT3 and TET2 mutations to identify chronic lymphoproliferative disorders of NK cells
Clinical Trials & Observations
Large granular lymphocyte (LGL) leukemia arises in either T cells or natural killer (NK) cells. Distinguishing chronic lymphoproliferative disease of NK cells (CLPD-NK) from reactive NK cell expansion is hampered by the absence of a readily identified clonal marker. Pastoret et al used NK receptor phenotyping and next-generation sequencing to divide CLPD-NK from reactive NK expansion, demonstrating that STAT3 and TET2 mutations represent clonal markers in 2 subsets of CLPD-NK. Furthermore, TET2 mutations were found in both NK and myeloid cells, linking CLPD-NK and other myeloid malignancies.
LRPAP1 autoantibodies in mantle cell lymphoma are associated with superior outcome
Clinical Trials & Observations
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein–associated protein 1 (LRPAP1) was previously identified by B-cell receptor expression cloning as a frequent autoantigen of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Thurner and colleagues analyzed 312 patients from 2 European MCL Network trials. They found that 13% of patients had LRPAP1 autoantibodies and that the presence of these autoantibodies is associated with superior failure-free and overall survival.
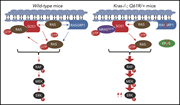
NrasQ61R/+ and Kras−/− cooperate to downregulate Rasgrp1 and promote lympho-myeloid leukemia in early T-cell precursors
Prognostic impact of corticosteroids on efficacy of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in large B-cell lymphoma
Brief Report
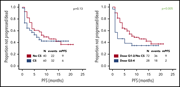
Corticosteroids are used to treat the acute complications of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. Strati et al examine the impact of corticosteroids on patient outcomes following CAR T-cell therapy for large B-cell lymphoma. Use of higher doses of steroids is associated with shorter progression-free survival at 10 months and decreased overall survival.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
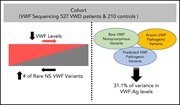
von Willebrand factor antigen levels are associated with burden of rare nonsynonymous variants in the VWF gene
Clinical Trials & Observations
von Willebrand disease (VWD) is phenotypically heterogeneous, and 35% of patients with type 1 VWD have no known pathogenic von Willebrand factor (VWF) gene variant. Sadler et al sequenced the entire genomic VWF locus of 737 patients with type 1 VWD or low VWF levels. They report that an accumulation of rare nonsynonymous variants, both pathogenic and nonpathogenic, contributes to the level of VWF and accounts for 31% of the variance in VWF antigen levels.
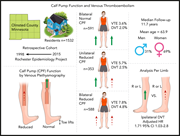
Reduced calf muscle pump function is a risk factor for venous thromboembolism: a population-based cohort study
Clinical Trials & Observations
The calf muscle pump contributes to venous return from the legs, and reduced calf pump function (rCPF) is linked to chronic venous insufficiency, poor wound healing, and all-cause mortality. Since venous stasis is an established risk factor for venous thromboembolism (VTE), Houghton et al examined the impact of rCPF on thrombotic risk. In a cohort study of 1532 patients, rCPF appears to be a risk factor for VTE and is associated with higher mortality.
TRANSPLANTATION
Posttransplant cyclophosphamide is associated with increased cytomegalovirus infection: a CIBMTR analysis
Clinical Trials & Observations
Posttransplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) has supported engraftment and control of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) in haploidentical transplantation, making haplo-transplantation a viable therapeutic option with an increased donor pool. In an analysis of the CIBMTR database, Goldsmith and colleagues report that PTCy is associated with increased CMV infection that in turn is associated with increased non-relapse mortality.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Utility of a safety switch to abrogate CD19.CAR T-cell–associated neurotoxicity
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
CD69 and CD8 immunofluorescence of a spleen section from an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)–infected and anti-CD27 antibody–treated mouse with reconstituted human immune system compartments by 28-parameter Chip Cytometry. Blocking the costimulatory molecule CD27 compromises a subset of protective CD8+ T-cell responses that preferentially target lytic EBV antigens. See the article by Deng et al on page 3225.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals