Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
T-cell–redirecting bispecific antibodies in multiple myeloma: a revolution?
So called T-cell–redirecting bispecific antibodies have the potential to transform therapy for patients with relapsed multiple myeloma. In this Blood Spotlight, Moreau and Touzeau describe the efficacy, safety, and directions in development of the range of agents in clinical trials, including products selectively targeting myeloma cells via the surface antigens BCMA, GPRC5D, or FcRH5.
REVIEW ARTICLE
There and back again: the once and current developments in donor-derived platelet products for hemostatic therapy
Kogler and Stolla provide a concise “state of the art” review on platelet transfusion therapy. They focus on current knowledge about the optimal use and storage options for donor-derived products and explore the potential of stem cell–derived alternatives.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
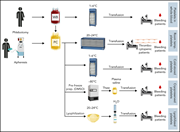
First study of extended half-life rFVIIIFc in previously untreated patients with hemophilia A: PUPs A-LONG final results
Clinical Trials & Observations
Severe hemophilia A is routinely managed with prophylactic replacement of factor VIII (F8), but a significant minority of patients develop anti-F8 antibodies. Extended half-life (EHL) products were developed to reduce the frequency of infusions required. In the first prospective trial of a recombinant F8-EHL product in previously untransfused patients, Königs et al report a low 15.6% incidence of development of high-titer inhibitors.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
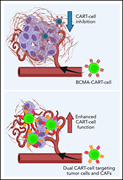
Targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts in the bone marrow prevents resistance to CART-cell therapy in multiple myeloma
Chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR T) cell therapy shows great promise as a treatment for relapsed multiple myeloma, but T-cell exhaustion is limiting. Sakemura et al document that cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the bone marrow niche inhibit standard CAR T-cell antimyeloma activity. They describe a new approach that eliminates CAFs. The authors demonstrate promising in vitro and preclinical in vivo efficacy of CAR T cells that dually target BCMA on myeloma cells and either SLAMF7 or fibroblast-activating protein on CAFs.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
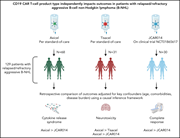
Impact of CD19 CAR T-cell product type on outcomes in relapsed or refractory aggressive B-NHL
Clinical Trials & Observations
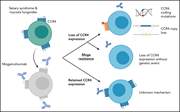
Resistance to mogamulizumab is associated with loss of CCR4 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Expression of the chemokine receptor CCR4 is upregulated in all stages of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCLs). Mogamulizumab, a humanized anti-CCR4 monoclonal antibody that induces antibody-dependent, cell-mediated cytotoxicity, is FDA approved for treatment of relapsed CTCL, yet primary resistance and early relapse are common. Beygi and colleagues reveal that in samples from 17 patients with CTCL failing mogamulizumab therapy, the majority lost CCR4 expression, variously due to gene disruption, loss-of-function mutations, or epigenetic mechanisms.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
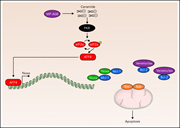
Ceramide-induced integrated stress response overcomes Bcl-2 inhibitor resistance in acute myeloid leukemia
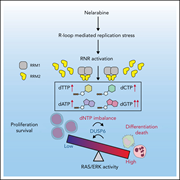
Disruption of dNTP homeostasis by ribonucleotide reductase hyperactivation overcomes AML differentiation blockade
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
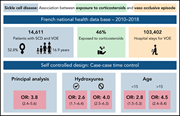
Risk of vaso-occlusive episode after exposure to corticosteroids in patients with sickle cell disease
Clinical Trials & Observations
Walter et al interrogated a large population-based dataset to evaluate the association between corticosteroid exposure and hospitalization for vaso-occlusive episodes (VOEs) in sickle cell disease (SCD). Using rigorous methods and adjusting for several confounders, they identified a moderately strong association between outpatient corticosteroid exposure and hospitalization for VOEs. While the study was not designed to assess cause and effect, their findings suggest caution when considering the prescription of corticosteroids to people with SCD.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A skin section from a patient with Sézary syndrome was stained for CCR4, highlighting expression of CCR4 by malignant skin-infiltrating lymphocytes. On rebiopsy at progression during treatment of the patient with mogamulizumab, CCR4 expression was no longer detectable. See the article by Beygi et al on page 3732.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




Highjacking myeloma’s niche with beefed-up CAR-Ts