Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
BLOOD SPOTLIGHT
Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Cines and Greinacher provide a succinct Blood Spotlight review of current knowledge about COVID-19 and vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia. This problem remains highly relevant in low- and middle-income countries that can only afford adenoviral vector-based vaccines for ongoing vaccination campaigns. It is also important to understand which vaccine constituent(s) triggers the immune response to the implicated platelet antigen, platelet factor 4, to design safer delivery systems for vaccinations against this and future emergent infectious diseases.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
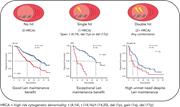
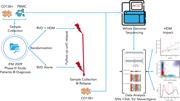
Optimizing the value of lenalidomide maintenance by extended genetic profiling: an analysis of 556 patients in the Myeloma XI trial
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this era of precision medicine, Panopoulou and investigators provide clarity on the efficacy of lenalidomide maintenance in high-risk patients based on extended genetic profiling in the randomized Myeloma XI trial. The authors proved that patients whose myeloma bears isolated del(1p), del(17p), t(4;14) derived exceptional benefit from lenalidomide posttransplantation. Whereas myeloma bears multiple poor prognosis genetic markers, lenalidomide also provides benefit; however, overall survival remains poor, and novel therapies are urgently required.
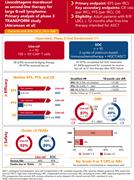
Lisocabtagene maraleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: primary analysis of the phase 3 TRANSFORM study
Clinical Trials & Observations
Abramson and colleagues report on the primary analysis of the TRANSFORM study, a randomized trial of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) following a cycle of bridging therapy (if needed) vs standard-of-care salvage chemotherapy and autologous transplantation in second-line therapy of patients with primary refractory or early relapse large B-cell lymphoma. Liso-cel significantly improves event-free survival as well as complete response rate and progression-free survival but not overall survival after a median of 18 months follow-up. These data establish liso-cel as a standard of care for these patients with a previous poor prognosis.
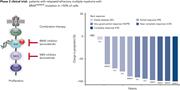
A phase 2 clinical trial of combined BRAF/MEK inhibition for BRAFV600E-mutated multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
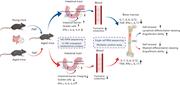
Fecal microbiota transplantation from young mice rejuvenates aged hematopoietic stem cells by suppressing inflammation
Current models view “inflamm-aging” as a driver of hematopoietic dysfunction in older individuals, and methods to rejuvenate hematopoiesis are highly sought. Zeng and colleagues investigated the effect of replacement of the aged intestinal microbiome with juvenile microbiota in murine models, remarkably demonstrating that fecal microbiota transplants reduce inflammation, restoring lymphoid differentiation and engraftment capacity of aged hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Further, the authors showed that metabolites of specific microbiota species improved the reconstitution capacity of HSCs in aged mice, challenging the field to explore ways to translate these insights into a clinically feasible therapy.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
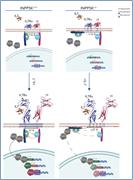
INPP5K controls the dynamic structure and signaling of wild-type and mutated, leukemia-associated IL-7 receptors
Interleukin-7 receptor (IL7R) signaling is critical for the maintenance of specific lymphoid leukemias and some autoimmune conditions. Moës and colleagues present a novel and original mechanism by which the lipid 5-phosphatase inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase K (INPP5K) regulates IL7R signaling and oncogenic IL7R mutants. The authors’ data may have relevance for other IL7R-like receptors including IL21R.
Flotetuzumab and other T-cell immunotherapies upregulate MHC class II expression on acute myeloid leukemia cells
Brief Report
Rimando et al explore T-cell–engaging immunotherapeutic approaches to salvage relapse of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Using cell lines and primary AML cells in vitro and in xenogeneic transplant models, the authors defined how both the dual-affinity retargeting compound flotetuzumab and chimeric antigen receptor T cells against AML-associated surface antigens induced upregulation of major histocompatibility (MHC) class II molecules via interferon-gamma signaling. These data advance prospects for improved post-HCT therapy for currently incurable AML.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
High-dose melphalan treatment significantly increases mutational burden at relapse in multiple myeloma
MYELOID NEOPLASIA

Supplementary figure 17: Schematic Model summarising our findings. HOXA9 nucleates a repressive complex with SAFB, which is required for the maintenance of the leukaemia state predominantly through the active repression of myeloid differentiation.
HOXA9 forms a repressive complex with nuclear matrix–associated protein SAFB to maintain acute myeloid leukemia
Transcription factors play pivotal roles in hematopoietic development and are commonly deregulated in acute myeloid leukemia. Agrawal-Singh et al reveal the protein interactome of the homeodomain-containing transcription factor HOXA9. The authors demonstrate that as well as having an oncogene-promoting role, HOXA9 also plays a distinct and critical repressive action on gene regulation that explains why leukemia cells remain in an undifferentiated state.
TRANSPLANTATION
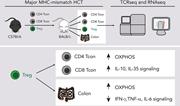
Analysis of the T-cell repertoire and transcriptome identifies mechanisms of regulatory T-cell suppression of GVHD
Infusion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) is emerging as a clinically attractive, but still poorly understood, approach to mitigate graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Lohmeyer and colleagues used murine models to reveal how Tregs affect the transcriptomic, metabolic, and functional state of pathogenic effector T cells, thereby blunting GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Tregs undergo activation and clonal expansion during GVHD suppression and do not interfere with the induction of genes associated with tumor control, features that can be further exploited therapeutically.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Indirect fluorescence resonance energy transfer demonstration of IL7Rα/γc ectodomains proximity after IL-7 addition (2 ng/ml, 2 minutes at 37°C) in sorted B220+CD43+ bone marrow B lymphocytes from mice. See the article by Moës et al on page 1708.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





Lenalidomide maintenance based on a genetic profile
Clinical Trials & Observations