Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PERSPECTIVE
Hitting the therapeutic bull’s-eye with targeted therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia
The ultimate therapeutic goal in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is complete disease eradication alongside restoration of immune function. In this Perspective, Wierda and colleagues review the transformative impact of targeted therapies (such as Bruton tyrosine kinase and BCL2 inhibitors, as well as CD20 monoclonal antibodies, particularly when used in combination) on improving outcomes in CLL. They further outline ongoing research and collaborative strategies aimed at refining the use of these agents not only to eliminate residual disease but also to reconstitute functional immunity in all patients with CLL.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Outcomes of PLAT-02 and PLAT-03: evaluating CD19 CAR T-cell therapy and CD19-expressing T-APC support in pediatric B-ALL
Clinical Trials & Observations
CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells have transformed the treatment of relapsed pediatric B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia; however, approximately 50% of patients still experience relapse, highlighting the need to enhance CAR T-cell persistence. Annesley et al demonstrate durable leukemia-free remissions following autologous CD19.4-1BB CAR T cells in a multicenter phase 2 trial. They also evaluate a novel strategy to provide exogenous CD19 antigen stimulation through serial infusions of T cells expressing a truncated form of CD19 (termed T-cell antigen-presenting cells) with the goal of prolonging CAR T-cell persistence and remission duration. Their findings demonstrate that the approach is safe and may extend CAR T-cell persistence, supporting further clinical investigation of this strategy.
Eliminating the need for sequential confirmation of response in multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Clinical trials ideally specify objective measures for key end points, and convention has it that in multiple myeloma, 2 time-separated measures of monoclonal protein levels are required to define progression. Claveau et al challenge this requirement and provide compelling evidence that 2 sequential measurements should not be required for all patients for definition of progression. Simultaneous measurement of 2 parameters has a positive predictive value of 98% with a sensitivity of 70% for progression, and the authors propose that allowing use of this definition in future clinical trials will avoid loss of data from patients who leave studies without completion of time-separated assessments.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
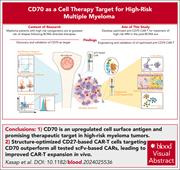
Targeting high-risk multiple myeloma genotypes with optimized anti-CD70 CAR T cells
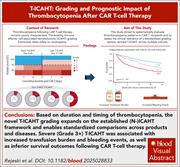
T-ICAHT: grading and prognostic impact of thrombocytopenia after CAR T-cell therapy
Immune effector cell–associated hematotoxicity (ICAHT) is increasingly recognized as a toxicity of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, but grading efforts have primarily focused on neutropenia using the neutropenia (N)-ICAHT system. In a multicenter observational study, Rejeski et al examined patterns of thrombocytopenia after treatment with commercial CD19 CAR-T products for B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. They propose a thrombocytopenia grading system, T-ICAHT, which incorporates depth, duration, and timing of platelet nadirs and uses thresholds that closely align with N-ICAHT criteria. On validation with 3 external cohorts, T-ICAHT demonstrated both clinical and prognostic utility, supporting the integration of T-ICAHT into the broader ICAHT framework to standardize thrombocytopenia grading for CAR T-cell recipients.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
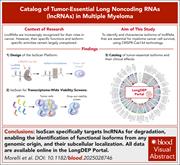
CRISPR-Cas13d functional transcriptomics reveals widespread isoform-selective cancer dependencies on lncRNAs
The isoform-specific functions of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) remain poorly understood. Morelli et al used RNA-targeting CRISPR-Cas13d to identify and characterize lncRNA isoforms that are essential for multiple myeloma cell survival. This work provides a comprehensive catalog of tumor-essential lncRNAs in multiple myeloma, laying the groundwork for future research to elucidate the distinct functional roles of individual lncRNA isoforms in tumor cell viability.
Transcriptional remodeling shapes therapeutic vulnerability to necroptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia
While the majority of children and adolescents with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) can be cured with chemoimmunotherapy regimens, drug resistance remains a significant cause of treatment failure, highlighting the need for new therapeutic strategies. Saorin et al used functional genomic approaches along with a large cohort of primary B-ALL and T-ALL specimens and patient-derived xenograft models to uncover regulatory mechanisms of necroptosis. They show that interference with transcriptional regulation enhances RIPK1-dependent necroptosis and leukemic cell death. These findings suggest that combining necroptosis induction with histone deacetylase inhibition may offer a promising strategy to overcome treatment resistance in ALL.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
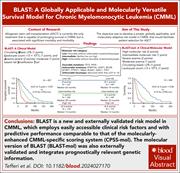
BLAST: a globally applicable and molecularly versatile survival model for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
Allogeneic transplant is the only curative therapy for chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), but the disease’s biological heterogeneity makes patient selection challenging. Tefferi et al describe a mutation-agnostic survival prediction model for patients with CMML based on circulating blasts ≥2%, leukocytosis ≥13 × 109/L, and severity of anemia to formulate a clinical stratification tool called BLAST. While this model requires further validation in larger patient cohorts, it offers a potentially useful framework to guide treatment decisions and assess therapeutic response in this complex disease.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
Sequential combinations of rapid immunoassays for prompt recognition of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Early recognition and treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) are crucial to prevent severe complications. However, although current immunoassays provide rapid diagnosis, their sensitivity and specificity are suboptimal. Steinauer et al prospectively validated and compared an approach combining pretest probability with tandem rapid immunoassays to improve the accuracy and speed of HIT diagnosis and show high sensitivity and specificity. Although these findings require external prospective validation, this combined approach could offer both rapid and reliable diagnostic results, potentially improving outcomes for patients with suspected HIT.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Super-resolution microscopy of myeloma cells with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) compartment analysis. A tumor-essential isoform of the lncRNA small nucleolar RNA host gene (red) localizes specifically to the ER, marked by lysine-aspartic acid-glutamic acid-leucine antibody staining (green). Identified through CRISPR-Cas13d screening, this isoform is one of hundreds of tumor-essential lncRNA isoforms uncovered in myeloma and other cancers, and it plays a key role in maintaining ER homeostasis. See the article by Morelli et al on page 847.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals







Rest, then rejuvenate: CD19 boost to improve CAR persistence
Clinical Trials & Observations