Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Up-front carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone with transplant for patients with multiple myeloma: the IFM KRd final results
Clinical Trials & Observations
The aim of initial therapy for newly diagnosed transplant-eligible patients with multiple myeloma (NDMM) is to maximize the depth and duration of the first response. The depth of response, now best measured by minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, serves as a surrogate marker for survival. Roussel et al report a phase 2 trial of frontline carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) with autologous stem cell transplant in NDMM, finding that >60% of patients can achieve stringent complete responses and MRD negativity.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
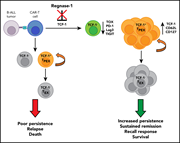
Regnase-1 suppresses TCF-1+ precursor exhausted T-cell formation to limit CAR–T-cell responses against ALL
Durable chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell-mediated leukemia eradication is associated with persistence of CAR T cells. Zheng and colleagues used immunocompetent murine models and human xenografts to demonstrate that deficiency of the ribonuclease regnase-1 enhances CAR T-cell persistence and immunity against acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) by reducing degradation of the transcription factor TCF-1 and thereby augmenting formation of immunity-promoting “precursor exhausted” T cells.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Characterization of DLBCL with a PMBL gene expression signature
Duns et al provide a comprehensive characterization of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) that display a typical primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBL) gene expression signature yet are nonmediastinal. These findings add to our understanding of the pathobiology of DLBCL by illustrating that evolutionary convergence on specific tumorigenic pathways can result in mimicry of gene expression despite disparate mutational patterns and anatomical presentations.
The CLL International Prognostic Index predicts outcomes in monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis and Rai 0 CLL
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
In this month’s CME article, Parikh and colleagues describe a minor adjustment to the CLL-International Prognostic Index (IPI), adding the lymphocyte count to test its utility in patients with either monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis or very early–stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) (Rai stage 0). They reveal that it predicts time to treatment and survival in these patients. As most new presentations fit into these categories, this information will be of value to hematologists and patients alike.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
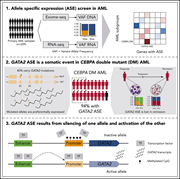
Allele-specific expression of GATA2 due to epigenetic dysregulation in CEBPA double-mutant AML
Despite an ever more granular elucidation of genetic mutations in subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), the precise events linking gene changes to distinct phenotypes remain elusive. Mulet-Lazaro et al report that epigenetic dysregulation in a particular AML subtype (good prognosis CEBPA double mutant) leads to allele-specific expression of the key stem cell-regulating transcription factor GATA2. This could have implications for our understanding of leukemogenesis.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
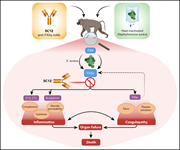
Factor XII plays a pathogenic role in organ failure and death in baboons challenged with Staphylococcus aureus
Silasi et al report new data on the role of factor XII in systemic inflammation and pathological coagulation induced by systemic inactivated Staphylococcus aureus in baboons. They show remarkable efficacy of factor XII–neutralizing antibodies in this primate sepsis model.
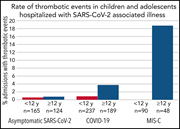
Rate of thrombosis in children and adolescents hospitalized with COVID-19 or MIS-C
Clinical Trials & Observations
Thrombotic events are a frequent complication in hospitalized adults with severe COVID-19. Children and adolescents are less likely to be hospitalized with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection than adults, but they are uniquely affected by a postinfectious hyperinflammatory syndrome termed multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C). Whitworth and colleagues provide much-needed data on the thrombosis rates and risk factors for this syndrome in pediatric patients with COVID-19, informing decisions about thromboprophylaxis and suggesting a higher probability of thrombosis in patients with MIS-C.
LETTER TO BLOOD
Increased prevalence of CRLF2 rearrangements in obesity-associated acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Immunostaining for C5b-9 terminal complement complex (red; nuclear staining in blue) in proximal tubules of a kidney from a baboon challenged with heat-inactivated Staphylococcus aureus. See the article by Silasi et al on page 178.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals





KRd: the new KiD in the French myeloma induction class
Clinical Trials & Observations