Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
HOW I TREAT
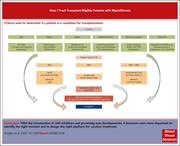
How I treat transplant-eligible patients with myelofibrosis
Allogeneic transplantation is curative for patients with both primary myelofibrosis (MF) and MF transformed from polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia, but patient selection is critical. Kröger and colleagues explore key concepts through 3 clinical vignettes that illustrate how current evidence can be used to guide decision-making. The authors emphasize the utility of several prognostic scores and predictors of outcomes posttransplant, provide practical advice about how to use ruxolitinib in the peritransplant period, and discuss common posttransplant complications, such as poor graft function and persistent disease.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Fractionated vs single-dose gemtuzumab ozogamicin with determinants of benefit in older patients with AML: the UK NCRI AML18 trial
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
The conjugated anti-CD33 monoclonal antibody, gemtuzumab ozogamicin (GO), is highly active against acute myeloid leukemia (AML), but dosing and scheduling issues have bedeviled its stable integration into routine clinical care regimens. In this month’s CME article, Freeman and colleagues present the mature results of a large trial showing for the first time in a randomized comparison that the addition of 2 fractionated doses of GO to intensive induction chemotherapy is better than 1 in patients with intermediate- and good-risk AML, including in those patients undergoing allogeneic transplantation.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
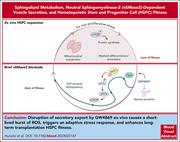
Neutral sphingomyelinase blockade enhances hematopoietic stem cell fitness through an integrated stress response
Sphingolipids are emerging as important regulators of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) fitness. Hurwitz et al report that genetic disruption of the gene encoding the sphingolipid enzyme neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2) activates the integrated stress response in HSCs. Transient inhibition with the nSMase2 inhibitor GW4869 during ex vivo HSC culture recapitulates this activation and durably improves long-term repopulating capacity in competitive transplantation assays. This approach may improve the regenerative capacity of graft products during ex vivo expansion.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
Alternative splicing of its 5′-UTR limits CD20 mRNA translation and enables resistance to CD20-directed immunotherapies
While CD20 is a long-established therapeutic target, the regulation of its expression has not been well understood, nor has the basis for the significant interindividual variation observed. Ang and colleagues advance our knowledge by revealing that CD20 mRNA undergoes alternative splicing to generate distinct 5′-UTR variants which are variably translated and collectively determine the cell-surface CD20 levels in malignant B cells. Alternative splicing explains some therapeutic resistance and can be manipulated to enhance CD20-directed immunotherapy.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
Loss of function of ENT3 drives histiocytosis and inflammation through TLR-MAPK signaling
While most histiocytic disorders are driven by somatic activating mutations in mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway genes, H syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive multisystem histiocytic disorder characterized by germ line loss-of-function mutations in SLC29A3, the gene encoding equilibrative nucleoside transporter 3 (ENT3). Shiloh et al elucidate the role of the resultant defective lysosomal nucleoside transport, demonstrating that it increases toll-like receptor signaling and drives pathological MAPK pathway activation in the absence of somatic mutations. The authors also provide anecdotal evidence of response to MAPK inhibition in 1 patient, suggesting a potential therapy for other patients with H syndrome.
LETTER TO BLOOD
A human genome editing–based MLL::AF4 ALL model recapitulates key cellular and molecular leukemogenic features
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
S100 staining of a Rosai-Dorfman disease–like histiocytic lesion with emperipolesis from a patient with H syndrome, a genetic disorder predisposing to histiocytosis. The germ line SLC29A3 mutation induces pathological activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling by a noncanonical pathway. See the article by Shiloh et al on page 1740.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Back MatterBack Matter
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals






Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in AML: the next chapter
Clinical Trials & Observations