Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
SPECIAL REPORTS
Diagnosis, prognostic factors, and assessment of ALL in adults: 2024 ELN recommendations from a European expert panel
In a pair of Special Reports, Gökbuget and colleagues present updated European Leukemia Net (ELN) consensus reports on (1) the diagnosis, prognostic factors, and assessment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and (2) the management of adult ALL. These updated reports summarize the current state of the art for diagnosis, characterization, and management of ALL, providing guidance for physicians caring for these adult patients.
Management of ALL in adults: 2024 ELN recommendations from a European expert panel
In a pair of Special Reports, Gökbuget and colleagues present updated European Leukemia Net (ELN) consensus reports on (1) the diagnosis, prognostic factors, and assessment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), and (2) the management of adult ALL. These updated reports summarize the current state of the art for diagnosis, characterization, and management of ALL, providing guidance for physicians caring for these adult patients.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Postinduction molecular MRD identifies patients with NPM1 AML who benefit from allogeneic transplant in first remission
Clinical Trials & Observations
Brief Report
Othman et al used prospective data from the United Kingdom National Cancer Research Institute AML17 and AML19 studies to determine the implications of molecular measurable residual disease (MRD) status for improving survival with allogeneic transplantation in first complete remission (CR1-allo) of NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The authors demonstrate that CR1-allo improves overall survival in patients who are MRD+ but not in those who are MRD-, independent of FLT3 status. These results suggest that MRD determination should be standard of care for determining the need for CR1-allo in NPM1-mutant AML.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
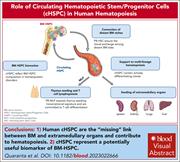
Circulating hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell subsets contribute to human hematopoietic homeostasis
Quaranta and colleagues investigated the phenotype and role of circulating hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells (cHSPCs) in humans. Using immunophenotyping, transcriptome sequencing, functional assays, and clonal tracking, the authors demonstrated that cHSPCs decline with age, are enriched for early committed progenitors, and have a transcriptional profile that differs from their marrow counterparts. cHSPCs are poised for differentiation and seed hematopoiesis at extramedullary sites.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
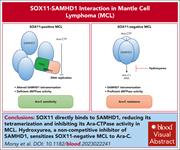
SOX11 is a novel binding partner and endogenous inhibitor of SAMHD1 ara-CTPase activity in mantle cell lymphoma
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
PI3Kγ maintains the self-renewal of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells by regulating the pentose phosphate pathway
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway is often abnormally activated in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), but the specific function of individual isoforms is not clear. Gu et al dissected the function of different PI3K isoforms in promoting the survival of leukemia stem cells (LSCs) in AML. The authors report that PI3Kγ-AKT signaling is enriched in LSCs and critical for self-renewal, while it is dispensable for normal hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). This suggests that targeting PI3Kγ may eliminate LSCs without damaging normal HSCs, providing a target for eliminating the source of leukemic relapse.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
let-7 miRNAs repress HIC2 to regulate BCL11A transcription and hemoglobin switching
BCL11A is the major repressor of fetal hemoglobin (HgbF) synthesis, but the process by which it is repressed during fetal development and derepressed in adult hematopoiesis is not known. Huang and colleagues characterized a microRNA (miRNA) inhibitory pathway responsible for HgbF suppression in adult erythroid cells. The authors previously identified HIC2 as a transcriptional repressor of BCL11A that regulated hemoglobin switching. Here, they report that HIC2 transcriptional downregulation is mediated by let-7 and that BCL11A upregulation with subsequent repression of HgbF depends on the activity of let-7 miRNA.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
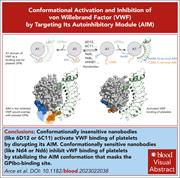
Conformational activation and inhibition of von Willebrand factor by targeting its autoinhibitory module
Activation of von Willebrand factor (VWF) is modulated by the A1 domain with surrounding elements that constitute an autoinhibitory module (AIM), but the details of the AIM structure and function are not clear. Arce et al performed a targeted screen to identify nanobodies binding to the N-terminal (NAIM) and the C-terminal (CAIM) domains. Nanobodies binding the NAIM sequence activate VWF and induce platelet activation, while those binding the CAIM inhibit ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation and reduce VWF-mediated platelet adhesion. Crystal structure suggests a direct interaction between NAIM and CAIM to modulate its conformation, and nanobodies can either stabilize or disrupt its inhibitory conformation.
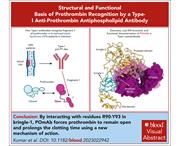
Cryo-EM structure and functional basis of prothrombin recognition by a type I antiprothrombin antiphospholipid antibody
Brief Report
Antiprothrombin antibodies are often found in patients with other antiphospholipid antibodies, but their functional interaction with prothrombin is not clear. Prothrombin adopts closed and open conformations, and Kumar and coauthors recently reported type I and type II antibodies, of which type I antibodies recognize only the open form. The authors isolated a type I antibody from human plasma that only binds the open form, prolongs clotting times, and functions as a true anticoagulant.
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A cryogenic electron microscopy structure of prothrombin open monoclonal antibody (POmAb), a type I antiphospholipid antibody, reveals the mechanism resulting in stabilization of the open form and anticoagulant effect in plasma. See the article by Kumar et al on page 2005.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals