Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
PLENARY PAPER
Investigation of product-derived lymphoma following infusion of piggyBac-modified CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T cells
Clinical Trials & Observations
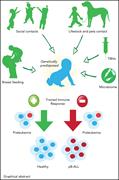
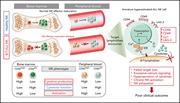
Transposons present potential advantages over current retroviral transduction systems for the generation of gene-modified cellular therapy, including chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, but this technology is only just entering clinical trials. In a Plenary Paper, Micklethwaite and colleagues report the first clinical trial of piggyBac transposon–modified CAR T cells generated from HLA-matched sibling allogeneic donors. They report a high rate of complete remission in patients with refractory B-cell lymphomas postallograft, but also the first known cases of CAR T-cell lymphoma in 2 of 10 patients. These data have implications for the development of piggyBac transposon clinical gene transfer tools.
PERSPECTIVE
Requirements for operational cure in multiple myeloma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Thirty years after Barlogie first began academic discussions about how to cure multiple myeloma, Mohty et al provide their perspective on how we could define "cure" it operationally in 2021. After reviewing earlier operational definitions and maturing clinical trial data on outcomes for patients achieving sustained minimal residual disease negativity at the 10−6 level of sensitivity with ongoing intensive combination therapy, the authors outline their views on how we may be able to reliably predict very- long-term disease-free survival and probable cure.
REVIEW ARTICLE
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Omidubicel vs standard myeloablative umbilical cord blood transplantation: results of a phase 3 randomized study
Clinical Trials & Observations
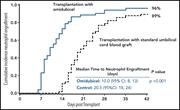
Delayed engraftment and risk of graft failure have restricted the use of cord blood (CB) in allotransplantation. Horwitz et al report results of a phase 3 trial comparing use of a single CB unit expanded ex vivo for 21 days with nicotinamide in combination with stem cell factor, Flt3 ligand, interleukin-6, and thrombopoietin (omidubicel) with a standard unmanipulated single or double CB transplant. Omidubicel resulted in faster neutrophil engraftment (12 vs 22 days), platelet recovery, and B-cell and natural killer cell reconstitution than unmanipulated CB products, with lower incidence of viral and fungal infections and more time out of hospital.
HEMATOPOIESIS AND STEM CELLS
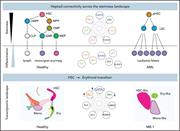
Disruption of a GATA2-TAL1-ERG regulatory circuit promotes erythroid transition in healthy and leukemic stem cells
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
Multimodal single-cell analysis of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma reveals distinct subclonal tissue-dependent signatures
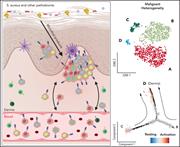
Herrera et al used cutting-edge single-cell analyses to dissect the relationship between cutaneous and circulating cells in a small number of patients with Sézary syndrome. Their data on inferred copy number variation and transcriptomic signatures of malignant T cells suggest that Sézary syndrome cells emerge from the skin and colonize blood at different time points, generating intratumoral heterogeneity.
Activated natural killer cells predict poor clinical prognosis in high-risk B- and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Duault and colleagues investigated samples from 20 patients with B- or T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and identified defective maturation of natural killer (NK) effector cells and accumulation of less cytotoxic hyperactivated cytokine-producing NK cells. Increased frequency of activated cytokine-producing NK cells is an independent predictor of poor clinical outcome in ALL. These findings suggest that NK cell profiling may have prognostic potential in this setting.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
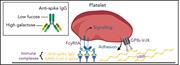
Aberrant glycosylation of anti-SARS-CoV-2 spike IgG is a prothrombotic stimulus for platelets
COVID-19 illness highlights the complex interplay of inflammation, immunity, hemostasis, and thrombosis. Bye et al show that immune complexes of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein and anti-spike immunoglobulin G (IgG) increase the formation of platelet-mediated thrombosis on von Willebrand factor in vitro, but only when the glycosylation of the Fc domain of the IgG is altered in a fashion recently identified in patients with severe COVID-19. These data may help explain the thromboinflammation in patients and point to new approaches to its prevention.
RED CELLS, IRON, AND ERYTHROPOIESIS
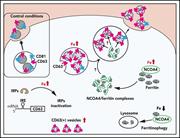
CD63 is regulated by iron via the IRE-IRP system and is important for ferritin secretion by extracellular vesicles
The interplay between intracellular and extracellular ferritin is not well understood despite the recognition 3 years ago that cellular ferritin can be exported into plasma by the exosome pathway. Yanatori et al report new insights into the triggers for ferritin secretion and how this is coordinated with iron metabolism. They demonstrate that CD63, a tetraspanin protein and constituent of extracellular vesicles, is induced by iron and in turn that this increases the secretion by various cells of CD63- positive extracellular vesicles containing iron-loaded ferritin.
LETTERS TO BLOOD
Development of CAR T-cell lymphoma in 2 of 10 patients effectively treated with piggyBac-modified CD19 CAR T cells
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Confocal microscopy image showing iron repletion leads to colocalization of NCOA4 (green) and CD63 (red) into the same vesicles (yellow). These data are vital for understanding iron regulated ferritin secretion via CD63+ extracellular vesicles. See the article by Yanatori et al on page 1490.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals




Expect the unexpected: piggyBac and lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations