Issue Archive
Table of Contents
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Isatuximab for relapsed and/or refractory AL amyloidosis: results of a prospective phase 2 trial (SWOG S1702)
CME
Clinical Trials & Observations
The primary therapeutic goal in AL amyloidosis is to eliminate the plasma clone responsible for the production of amyloidogenic light chains. In this month’s CME article, Parker and colleagues report the results of a 43-patient phase 2 study that evaluates the single agent isatuximab, a CD38 monoclonal antibody, in patients with relapsed/refractory AL amyloidosis. With a hematological response rate of 77%, organ response rates between 50 and 57%, and an excellent safety profile, the current study lays the foundation for future use of isatuximab across treatment settings and combination strategies.
IMMUNOBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOTHERAPY
A T-cell–based metric of immune age predicts outcomes in older patients with myeloma receiving daratumumab-based therapy
It has been proposed that the effectiveness of immunotherapy for multiple myeloma (MM) depends on the patient’s immune status. Bruins and colleagues present new evidence suggesting that immune age, determined by high-dimensional profiling of T and natural killer cells from patients with MM, better reflects the immune status of the patients and outperforms their calendar age in predicting clinical outcomes after daratumumab-based therapy. Studies like this one for other immunotherapies may guide clinical decision-making to reduce the risks of infection, treatment discontinuation, and inferior survival.
Pooled CAR-T screening in pig-tailed macaques identifies designs with enhanced proliferation, trafficking, and persistence
The use of pooled in vivo screens has improved our ability to identify candidate chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) constructs with enhanced antitumor potential, but the approach relies on immunocompromised mice. Maynard and colleagues addressed this limitation by leveraging immunocompetent nonhuman primate models to systematically compare CAR T-cell designs, identifying the MyD88-CD40 costimulatory domain as superior to conventional domains in enhanced activation and resistance to exhaustion. This approach highlights the importance of pooled screenings in relevant models to identify optimal CAR T-cell designs.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
TCA cycle mode switch determines the fate of pirtobrutinib-tolerant persister cells in mantle cell lymphoma
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor resistance represents a significant clinical challenge in the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Wang and colleagues provide experimental data supporting tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle addiction as the main mechanism involved in MCL adaptation to BTK inhibition therapy, a process that involves lymphoma cells transitioning to a nonproliferating state, which is reversible when the BTK inhibitor is stopped. This metabolic switch may offer an opportunity for future targeted therapies.
A phase 2 study of zanubrutinib in combination with rituximab and lenalidomide in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Clinical Trials & Observations
Due to the toxicity of chemotherapy-based regimens in older, frail adults with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, new regimens free of DNA-damaging chemotherapy are being evaluated. In this 40-patient phase 2 study, Xu and colleagues show that the combination of zanubrutinib, rituximab, and lenalidomide (ZR2) in newly diagnosed older (≥75 years) patients unfit for anthracycline-based immunochemotherapy is highly effective, with 65% complete remission, 67.1% 2-year progression-free survival, and 84.4% overall survival rates, comparing favorably with historical data. Importantly, ZR2 responses correlate with immunological features of an activated tumor microenvironment.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
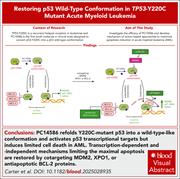
Restoring p53 wild-type conformation in TP53-Y220C–mutant acute myeloid leukemia
TP53-Y220C, a recurrent mutation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), is associated with poor outcomes. Carter and colleagues present findings that PC14586 (rezatapopt), a small molecule designed to target mutant p53, restores p53 wild-type conformation in TP53-Y220C mutant AML, inhibiting growth in AML cell lines that contain the Y220C mutant protein but not restoring the proapoptotic activities of p53. An ongoing clinical trial with PC14586 should illuminate whether this novel approach has therapeutic efficacy.
Plasma lipid levels predict chemotherapy response and survival in acute myeloid leukemia
Brief Report
It is known that patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) have plasma lipid profiles distinct from those of healthy individuals, with specific lipid species correlating with cytogenetic and prognostic subtypes. O’Brien and colleagues show that specific gene mutations in AML result in unique plasma metabolite and lipid signatures. While metabolites were associated with the AML mutational landscape, lipids were highly associated with refractory status. Interestingly, among all lipids, sphingomyelin (d44:1) was predictive of AML survival in the original cohort and an independent validation cohort, underscoring the importance of lipids as potential biomarkers of AML progression.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
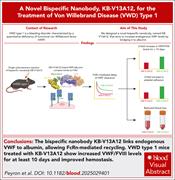
A bispecific nanobody for the treatment of von Willebrand disease type 1
Von Willebrand disease type 1 is characterized by quantitative deficiency of von Willebrand factor (VWF), which often causes bleeding. Peyron and colleagues introduce a new therapeutic approach to the disease with the development of a novel bispecific antibody (KB-V13A12) that links endogenous mouse VWF to albumin, extending VWF half-life twofold with cessation of provoked bleeding. Clinical trials in patients with type 1 von Willebrand disease will be necessary to test the therapeutic efficacy of this approach.
LETTER TO BLOOD
FLAG-IDA plus venetoclax for children, adolescents, and young adults with newly diagnosed AML
BLOOD WORK
ERRATA
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION (CME) QUESTIONS
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
Ribosome biogenesis is a key regulator of cell size and stemness. Fibrillarin, an rRNA methyltransferase and a marker of ribosome biogenesis, was upregulated in pirtobrutinib-tolerant persister cells in the giant cell state compared with parental mantle cell lymphoma cells with regular cell dimensions. Blue: DAPI; green: fibrillarin. See the article by Wang et al on page 2544.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals










Isatuximab: surface strike, deep response in AL amyloidosis
Clinical Trials & Observations