Issue Archive
Table of Contents
EDITORIAL
Introduction to a review series on oncogenic signaling and immune evasion in hematologic malignancies
Introduced by Associate Editor Robert Zeiser, this Review Series focuses on the problem of immune escape by acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The series opens with a review of how AML escapes T-cell–driven elimination and then focuses on how p53 function impinges on AML recognition by immune cells. The series finishes with a summary of new approaches to tackling this major problem.
BLOOD COMMENTARIES
REVIEW SERIES
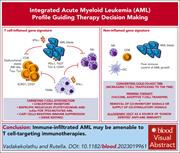
Escape from T-cell–targeting immunotherapies in acute myeloid leukemia
Introduced by Associate Editor Robert Zeiser, this Review Series focuses on the problem of immune escape by acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The series opens with a review of how AML escapes T-cell–driven elimination and then focuses on how p53 function impinges on AML recognition by immune cells. The series finishes with a summary of new approaches to tackling this major problem.
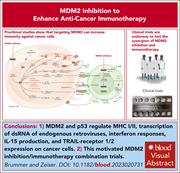
The role of the MDM2/p53 axis in antitumor immune responses
Introduced by Associate Editor Robert Zeiser, this Review Series focuses on the problem of immune escape by acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The series opens with a review of how AML escapes T-cell–driven elimination and then focuses on how p53 function impinges on AML recognition by immune cells. The series finishes with a summary of new approaches to tackling this major problem.
Tricking the trickster: precision medicine approaches to counteract leukemia immune escape after transplant
Introduced by Associate Editor Robert Zeiser, this Review Series focuses on the problem of immune escape by acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The series opens with a review of how AML escapes T-cell–driven elimination and then focuses on how p53 function impinges on AML recognition by immune cells. The series finishes with a summary of new approaches to tackling this major problem.
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS
Real-world and clinical trial outcomes in large B-cell lymphoma with axicabtagene ciloleucel across race and ethnicity
Clinical Trials & Observations
Locke and colleagues describe the safety and efficacy outcomes of axicabtagene ciloleucel for large B-cell lymphoma across racial and ethnic groups for 1290 standard-of-care patients in the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research registry and 275 patients treated in clinical trials. While consistency in survival and most safety outcomes were evident across groups, non-Hispanic Black patients had significantly lower response rates and progression-free survival in routine practice, potentially reflecting barriers to access.
LYMPHOID NEOPLASIA
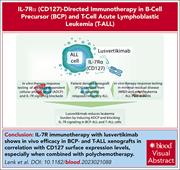
The IL-7R antagonist lusvertikimab reduces leukemic burden in xenograft ALL via antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis
Lenk and colleagues identified that 85% of cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) express interleukin-7 receptor (IL-7R). The authors reveal that blocking IL-7R signaling with lusvertikimab induces antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis in patient-derived xenografts and shows in vivo efficacy, especially when combined with chemotherapy regimens. These preclinical data form the basis for future clinical trials of this approach.
MYELOID NEOPLASIA
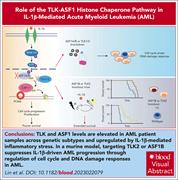
The TLK-ASF1 histone chaperone pathway plays a critical role in IL-1β–mediated AML progression
Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) is secreted by the microenvironment in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and can promote AML growth. Lin et al show that IL-1β upregulates Tousled-like kinases (TLKs) and antisilencing function-1B (ASF1B) in AML cells. Targeting TLK2 or ASF1B suppresses IL-1β–driven AML progression and may provide a future route to developing new therapies.
PHAGOCYTES, GRANULOCYTES, AND MYELOPOIESIS
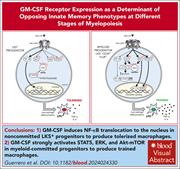
GM-CSF receptor expression determines opposing innate memory phenotypes at different stages of myelopoiesis
The innate immune system has memory capability with the adaption of functional responses by macrophages and neutrophils following an initial challenge. Guerrero and colleagues reveal a key role for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) during the establishment of innate immune memory. Depending on the degree of differentiation in the myeloid series, GM-CSF induces 2 opposing memory programs, with macrophages derived from committed progenitors having a trained proinflammatory phenotype and macrophages derived from primitive progenitors showing a tolerized phenotype. The authors postulate that the twin effects provide a mechanism for temporal harmonization of immune memory.
PLATELETS AND THROMBOPOIESIS
Notch1 regulates hepatic thrombopoietin production
Steady-state regulation of hepatic thrombopoietin (TPO) production is principally dictated by sensing of aged platelets by Ashwell-Morell receptors (AMRs) on hepatocytes. Using murine models, Sun et al identified hepatic Notch1 and platelet Delta-like 4 as key regulators of TPO production downstream of the AMRs, furthering our understanding of how we might therapeutically modulate TPO levels in patients with disorders of platelet number.
THROMBOSIS AND HEMOSTASIS
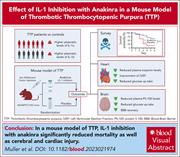
Reduction of mortality, cardiac damage, and cerebral damage by IL-1 inhibition in a murine model of TTP
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is an uncommon but potentially fatal disorder with limited treatment options, particularly in the acute relapse setting. Muller et al demonstrate the pathological role of interleukin-1 (IL-1) in tissue damage during relapsed disease in patients and report the therapeutic potential of IL-1 receptor antagonist therapy in a murine model of TTP. This work suggests anakinra therapy should be evaluated in clinical studies.
LETTER TO BLOOD
High efficacy of CD19 CAR T cells in patients with transformed Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Clinical Trials & Observations
BLOOD WORK
ERRATUM
-
Cover Image
Cover Image
![issue cover]()
A scanning electron microscopy image of the structural analysis of desialylated platelets shows extended protrusions on the platelet surfaces. See the article by Sun et al on page 2778.
- PDF Icon Front MatterFront Matter
- PDF Icon Table of ContentsTable of Contents
- PDF Icon Editorial BoardEditorial Board
Advertisement intended for health care professionals
Email alerts
Advertisement intended for health care professionals